Conservation scientist Joli Rumi Borah found that a traditional indigenous farming method from India that feeds millions of people in the Global South has carbon and biodiversity and cultural benefits as well.
Borah, currently a postdoctoral research fellow at University of British Columbia, Vancouver, Canada, says carbon stocks and biodiversity recovered where shifting cultivation, called jhum by the indigenous Naga people, was found in Nagaland, Northeast India.
"My research showed that farmers in Northeast India have adopted various innovative ways to improve crop yield and enhance forest regeneration," she says, adding that this was evident in the high levels of carbon stocks and bird diversity in the jhum cultivation landscapes in Nagaland.
Borah, who studied jhum as part of her PhD research at University of Sheffield, UK, suggested there was significant conservation value in jhum cultivation, which is an important traditional farming method that covers an area of 280 million hectares and provides subsistence to 200-300 million people in the Global South.
"Effectively managing jhum cultivation is crucial for reducing carbon emission and biodiversity loss while ensuring food security for the local communities," she says adding that the biggest challenge in the project was the extreme remoteness of the region and the lack of previous studies.
"Living and working with the Indigenous Naga communities in Nagaland helped me realize the importance of community-based conservation for positive societal and environmental outcomes," she says, "I learnt that unlike the widely held perceptions of jhum cultivation as a primitive and environmentally unsustainable practice, it is a dynamic and complex system that is well adapted to heavy rainfall and the environmental conditions in mountainous regions and less harmful for the environment and biodiversity compared to permanent agriculture (e.g., oil palm or rubber plantation)."
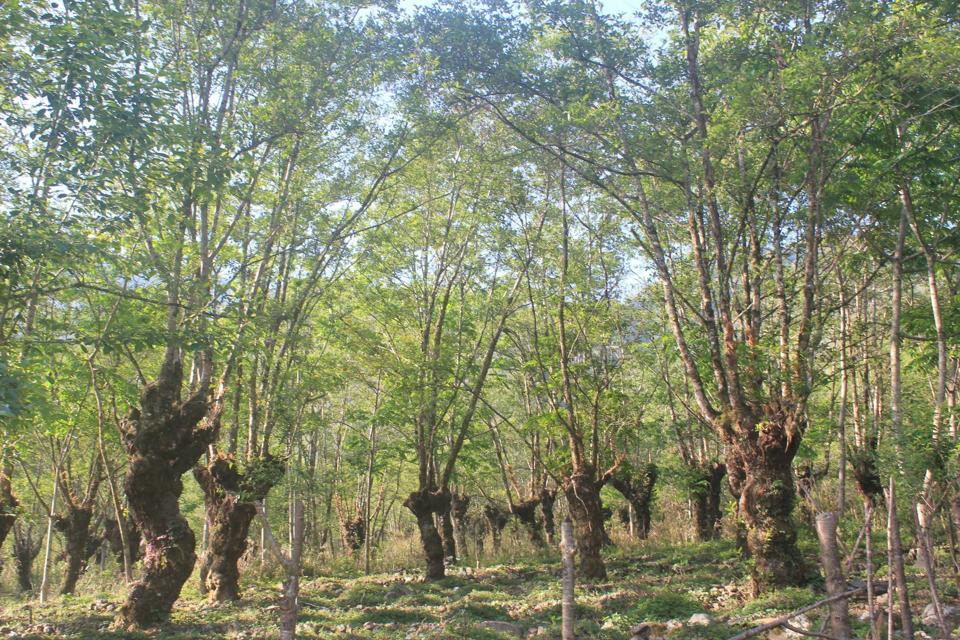

Communities Close to Nature
Borah was born and raised in the Brahmaputra valley of Assam, Northeast India.
"Growing up in this biodiverse region, I developed a fascination for nature from a very young age," she says, adding that local concerns drove her from the start of her journey in STEM.
"During undergrad, I wrote a term paper on human-elephant conflict, a major concern in and around my hometown, North Lakhimpur and co-founded a conservation NGO to help create public awareness for biodiversity conservation," she says.
Borah would go on to receive a full scholarship to do a master’s degree in wildlife sciences at the Wildlife Institute of India, in Dehradun, India.
"Being from the Global South, I witnessed first-hand how some of the global challenges such as deforestation, food insecurity and climate change impacted the local communities and so, finding nature-based solutions to these challenges is very personal for me," she says, "Breaking the linguistic and economic barriers and building just and meaningful partnerships with local communities and scientists from the Global South will also help make science more inclusive and equitable."
Over the course of two years, as a project assistant at the National Centre for Biological Sciences in India, studying the impacts of logging on bird communities in the Eastern Himalayas of Northeast India, she closely experienced how the Indigenous Bugun tribe worked in collaboration with the government and scientists to conserve this biodiversity hotspot.
"This instilled my interest in pursuing a PhD in conservation science to find such ways to reconcile biodiversity conservation and human well-being," she says.
Borah has also been working actively in breaking the language barrier by communicating science in my mother tongue Assamese on various platforms such as blogs, podcasts, magazines, and Assamese Wikipedia over the last decade.
"This can be a crucial step in decolonizing science by incorporating multiple ways of knowing and doing," she says.

Another Indian scientist looking at the relationship with crops and communities is Rajeev Varshney.
He spent decades getting to know everything about the chickpea, plumbing the depths of its genome to unlock secrets of yield, nutrition, drought tolerance and pest and disease resistance.