The pandemic saw a boom in legal recreational cannabis sales across Canada. From March 2020 to February 2021, sales totaled $2.5 billion, double the $1.25 billion of the previous 12 months. Surveys likewise reported more cannabis users and more frequent usage in 2020 than the year before.
The increases were often blamed, despite a lack of evidence, on the COVID-19 pandemic and related societal disruptions. Many people were stuck alone at home and feeling stressed. Some commentators later walked back their claims after it became clear there was no data to support them, but the narrative still persists.
Although it’s a compelling anecdote, our new research found that the growth in cannabis sales was more likely from industry expansion, rather than the pandemic.
A rapidly expanding industry
The number of licensed stores grew rapidly after Canada legalized recreational cannabis in October 2018. There were barely more than 100 stores open that first month, but by March 2019, that number had doubled, and by February 2021 the total had reached 1,500.
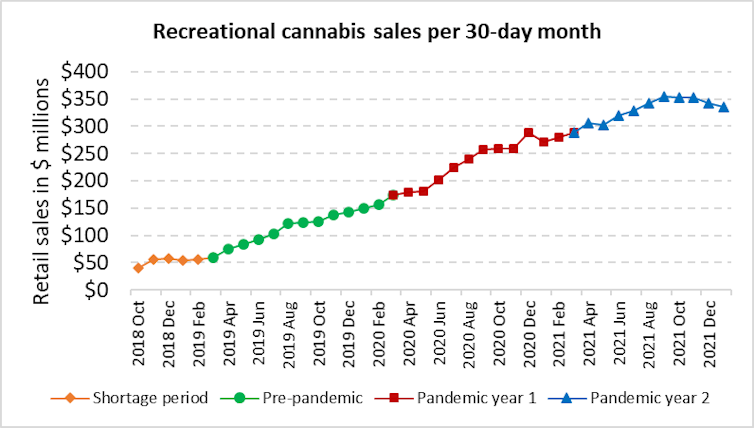
Nationwide monthly sales began at $42 million in October 2018 and still totalled only $59 million in March 2019. But by February 2021 they exceeded $262 million. National sales now exceed $347 million monthly, thanks partly to having at least 3,100 licensed stores.
Read more: Cannabis store openings in Canada only slightly affected the number of users
We know sales growth was partly related to store growth, but product selection also widened as more producers and product formats entered the market. Most notably, cannabis-infused foods, drinks and vape oils began hitting store shelves in January 2020. Cannabis vapes quickly became the second-best selling product format after smokeable cannabis.
No sales jump in March 2020
Our multidisciplinary research team analyzed monthly per capita recreational cannabis sales, both nationally and provincially, using Statistics Canada data from March 2019 to February 2021. This covered the first 12 months of the pandemic and the 12 months that preceded it.
Surprisingly, we found no sign of a sustained sales jump after the pandemic hit in March 2020. Many stores were frantically busy for a few days as people stocked up before lockdowns began, but those brief surges apparently were counterbalanced by quieter days afterwards. Instead, we detected a small sales drop in January 2020 that presumably came from consumers trimming their post-holiday spending.

Our calculations revealed a modest acceleration in month-over-month sales growth in 2020. However, this boost coincided more with the arrival of vapes and other new products in January, rather than the pandemic’s onset in March.
Overall, we didn’t see any pandemic-related cannabis sales gains big enough to worry regulators or to interest economists. Instead, the growth seemed largely due to continued increases in stores and products.
Growth’s implications
It’s important to understand why cannabis sales grew, because Canadian regulators need to understand the increase was an industry feature, not a pandemic side effect. The federal and provincial governments should take this into account as they work on adjusting cannabis regulations.
The lack of sustained pandemic effects on sales also matters to cannabis businesses. The pandemic surely increased producers’ operating complexity and costs, but we can’t blame it for lacklustre revenues.

Our results are also relevant to public health. Between 2018 and 2020, the percentage of Canadians who self-reported using cannabis rose to 20 per cent from 14 per cent. The proportion reporting daily, or near daily, use similarly climbed to 7.9 per cent from 5.4 per cent. It’s estimated that one-third of such users could eventually develop a cannabis use disorder.
Our research strongly implies the economic impacts are not a temporary pandemic blip. It also suggests that the pandemic may not be a good explanation for increased cannabis use.
Cannabis-related health issues
Early indicators suggest the increase in regular use might be resulting in other health harms. For example, cannabis-related visits to emergency rooms across Canada increased substantially in 2020 and 2021.
Our findings might also interest policy-makers outside of Canada. Many other countries, ranging from Malta to Mexico, are in the process of legalizing cannabis.
Meanwhile, U.S. Congress continues to struggle with cannabis legislation. America badly needs to revise its messy patchwork of cannabis laws, but its politicians haven’t been able to agree on how to proceed.
Gaining a better understanding Canada’s legalization experience can not only inform Canadian regulators, businesses and healthcare providers, but also offer lessons for many other countries too.
Daniel Myran receives funding from CIHR and the University of Ottawa Department of Family Medicine.
Michael J. Armstrong does not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organisation that would benefit from this article, and has disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.
This article was originally published on The Conversation. Read the original article.







