In this lesson, I’d like to discuss playing over what’s known as a I - VI - II - V (“one-six-two-five”) chord progression, which is common in a variety of musical styles, from country to rock to folk to jazz and blues.
You’ll find it in many old blues tunes, such as some by Sonny Terry and Brownie McGhee, through the later recordings of Eric Clapton and many others. The examples I offer here are played in the key of F and with a swing-eighths feel. And all of the chords have a dominant 7 quality or implied tonality. So the basic underlying progression is F7 - D7 - G7 - C7.
Figure 1 shows a rhythm part based on this progression: I begin with a boogie pattern on F5 (a low F note with C, the 5th, above it) to F6 (with C moving up to D, the 6th), played through bar 1 and beat 1 of bar 2.
This is followed by the chords Eb7/Bb to D7/A, both with the 5th in the bass, which creates a warm sound. D7/A is the VI (six) chord, and I approached it from a half step, or one fret, above.
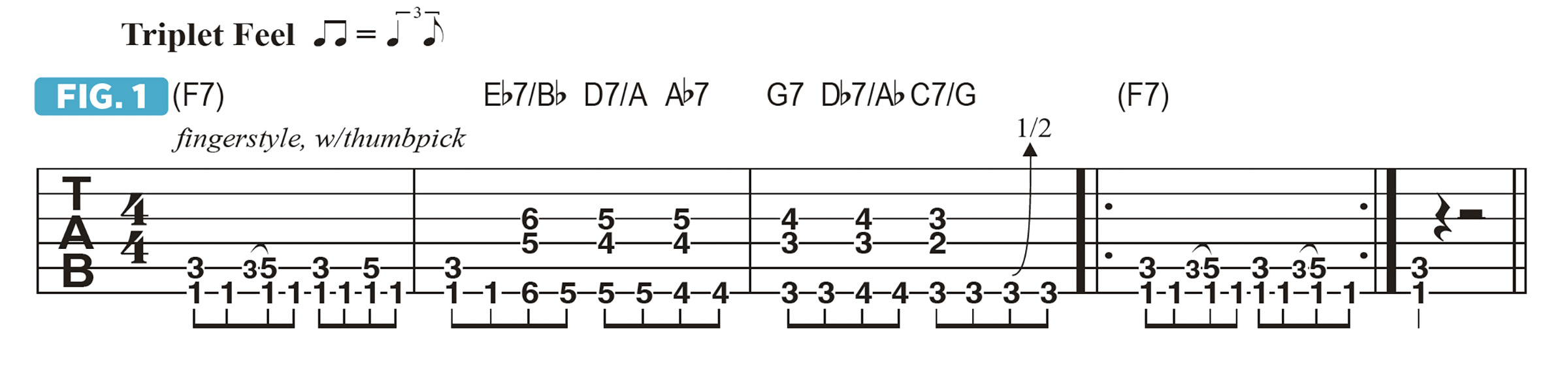
The bar ends with Ab7 to G7 at the start of bar 3, again utilizing “half step above” approach, which I then also apply to Db7/Ab to C7/G. The figure ends with a return to the I, F5 to F6, which can be looked at as implied F7 chord.
Now, one could easily play licks based on the F blues scale (F, Ab, Bb, B, C, Eb) over the entire progression, and it would work well. But in this lesson, I’d like to demonstrate “making the changes,” which means acknowledging each chord melodically.
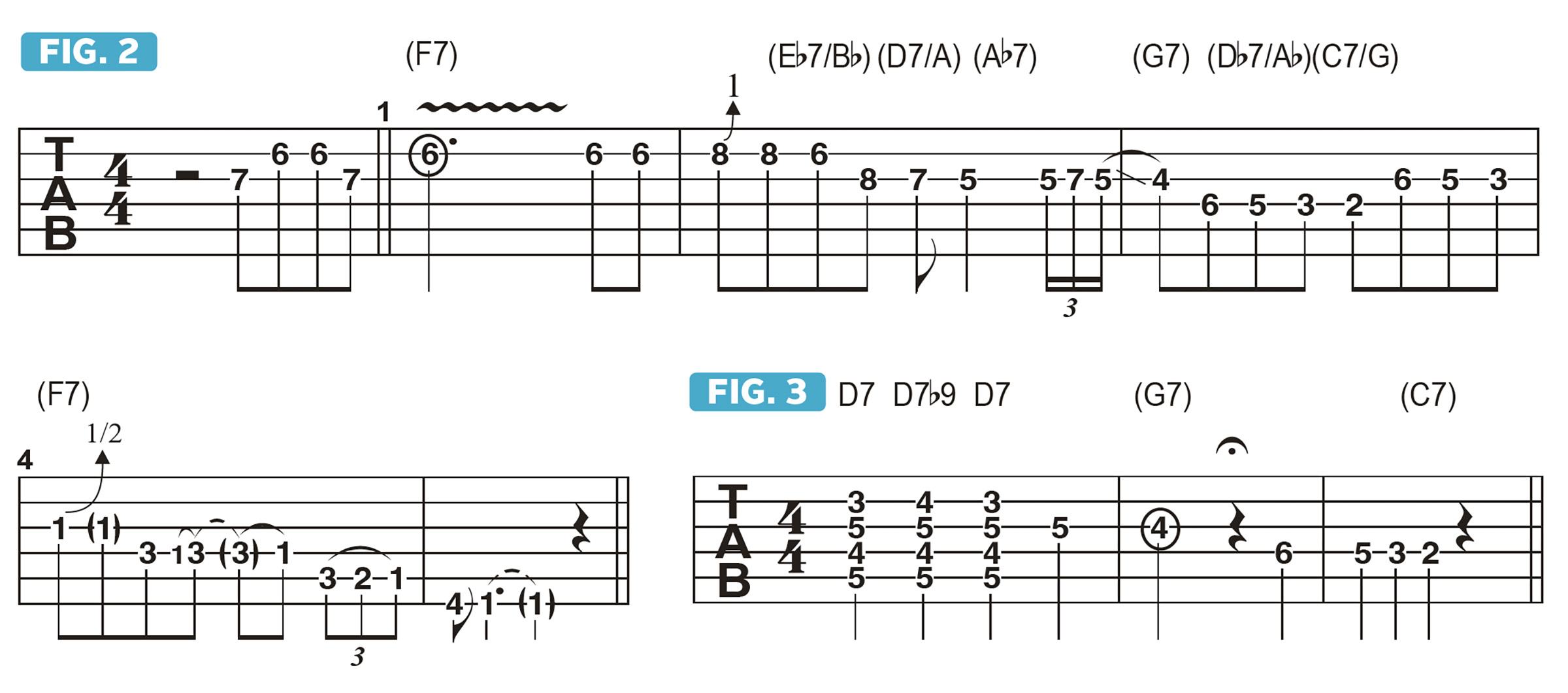
Figure 2 presents a solo that does this. I begin over F7 with a simple melody based on F major pentatonic (F, G, A, C, D). In bar 2, I set up the arrival of D7/A by playing Eb, a half step above the D root, which is known as the flatted 9th, or b9. This is mirrored in the chord progression via Eb7/Ab to D7/A.
I take the same approach in bar 3 for the next chord, G7, as I play Ab to G (b9 to root), and the subsequent chord, C7/G, by playing Db to C (again, b9 to root), setting up the return to F7 and a lick based on the F blues scale. Taking this same approach with each of these changes like this sounds pleasing while making things easier to think about.
In terms of setting up the change from F7 to D7, Figure 3 illustrates D7 and D7b9, which includes the Eb note. I then play B, the 3rd of G7, then E, the 3rd of C7.
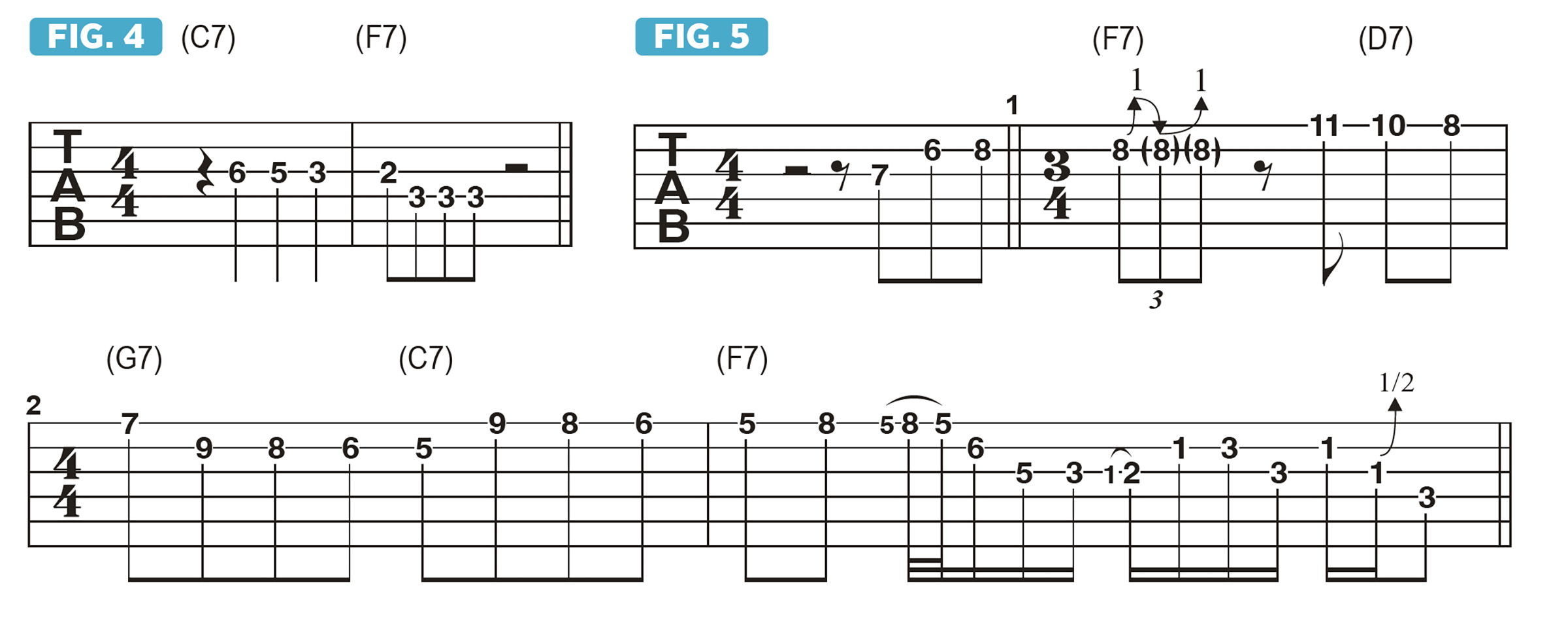
Figure 4 shows how the descending line Db , C, Bb sets up a nice resolution to A, the 3rd of F7. Figure 5 demonstrates the same concept applied in a higher register.
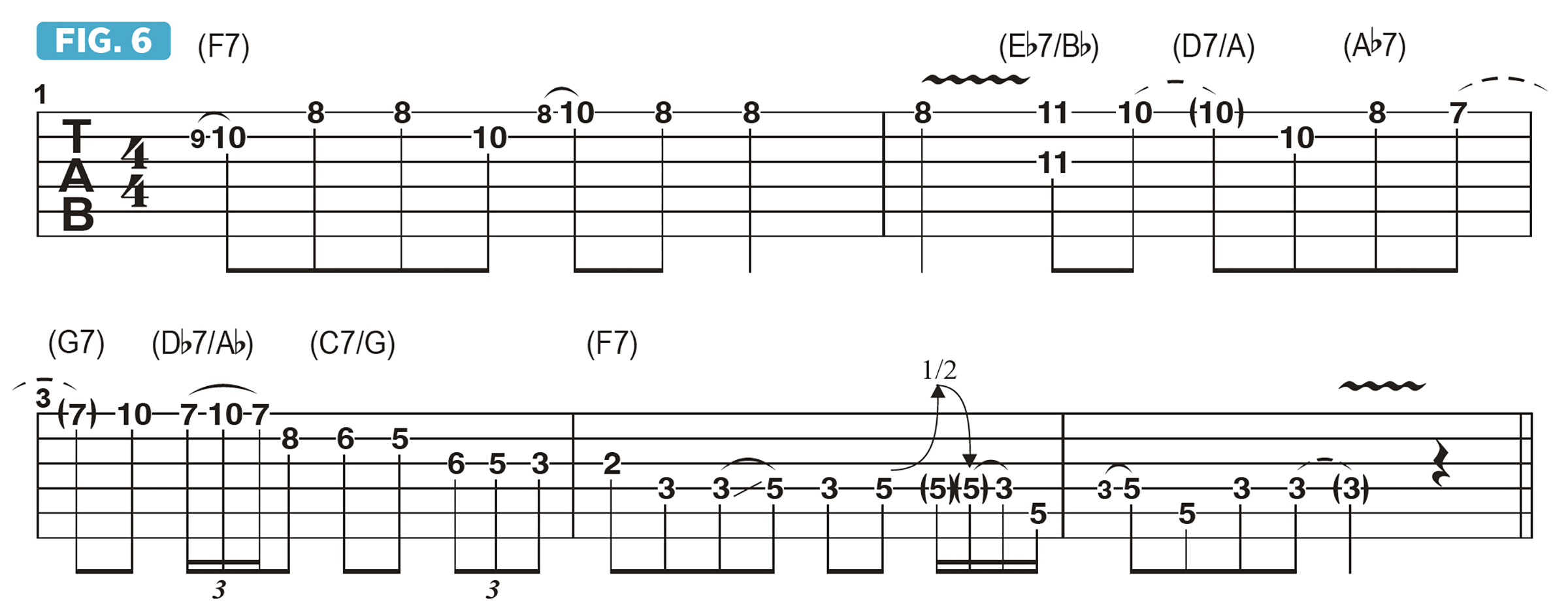
Finally, Figure 6 offers another melodic example. After playing F major pentatonic over F7, I play Eb to D to set up D7. Bar 3 ends with Db to C, played over C7, setting up the return to the I chord, F7.







