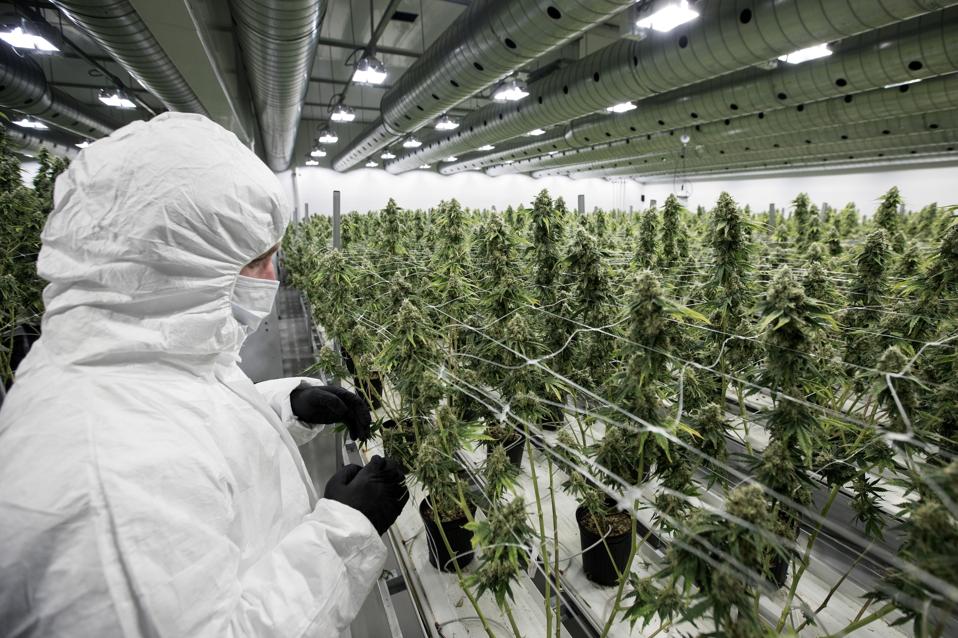
Before he sells it, Suehiko Ono, the founder and CEO of EOS Farms, a legal cannabis cultivation brand in Massachusetts, bombards his cannabis with radiation.
That may sound weird, but it’s not. If you purchased legal cannabis in the United States, there’s a good chance you bought what some scandalized critics dismissed as “nuclear weed” they would never (knowingly) touch, too. If you’re in Canada, there’s a near-100 percent chance your weed is irradiated.
And that’s not a bad thing—at least scientifically. Marketing is another issue.

Though cannabis dispensaries and product manufacturers don’t advertise it, treating cannabis with radiation to remove enough bacteria and mold for the finished product to pass state testing requirements—a common and EPA-approved technique in food production; that supermarket apple you’re eating was quite likely zapped with radiation—is de rigeuer in Canada, supported by research, and increasingly common in the United States.
Broadly defined, in the context of cannabis and food production, irradiation is the use of ionizing radiation to eliminate contaminants like bacteria and mold.
According to George Terry, the executive vice president of sales at Rad Source Technologies, one of the top suppliers of irradiating devices for the U.S. cannabis industry and the maker of the irradiation devices at EOS Farms, he has clients like Ono in 23 states: California, Colorado, Oregon, Michigan, Illinois, and Washington among them.
For an immunocompromised patient like a cancer survivor, irradiating cannabis could be the difference between a safe smoke and a life-threatening fungal infection, Terry said. When shopping for weed, Terry and some of his acquaintances actually request irradiated cannabis, he claimed.
That might be a hard ask to fulfill, as neither dispensaries nor product manufacturers are required to disclose their remediation methods, just that their product passed lab tests. (When asked whether he sold irradiated cannabis, one of Ono’s retail clients declined to answer.) And that’s what encourages the use of radiation in cannabis remediation.
EOS Farms and many of Ono’s competitors irradiate their cannabis because Massachusetts has testing regulations even stricter than other states. Massachusetts limits the total amount of bacteria and other life forms in cannabis—even beneficial bacteria.
That’s in contrast to other states like California, that restrict or outlaw specified harmful bacteria and molds like e. coli and aspergillus. Other common “remediation” methods in Massachusetts include using ozone and hydrogen peroxide.
Ono went with irradiation, “because it was the only one with no residual effect,” he said during a recent interview, noting that Rad Source’s method of using photons to kill off powdery mildew and other contaminants—techniques also used in medical and pharmaceutical settings to ensure that blood can be safely infused and medical devices are sterilized—was the only one that reliably didn’t affect the cannabis itself, leaving terpenes and cannabinoids intact, he said.
“There are literally no residual effects,” he said. “Out of all the remediation techniques used in the industry, this is the only one that doesn’t leave any residual effects.”
“Anyone who can afford it is going with radiation,” he added, noting that he believes at least 80 percent of other Massachusetts cannabis companies are using some post-cultivation remediation method.
So Ono’s cannabis is clean. Super clean. Usually that’s a boasting point. But since radiation—another way of saying “energy,” in the broadest sense—is poorly understood among members of the public and often conflated with the nastiest and scariest examples, from Hiroshima to Chernobyl to Fukushima rather than clean food and sterile pharmaceutical drugs, Ono recognizes that being open about irradiating cannabis is a liability.
“There’s definitely a fear when you say specific words,” he said. “People react without really digging into it.”
That’s absolutely true with irradiated weed.

In an informal review of cannabis cultivators, distributors, and consumers in several states, none had heard of irradiated cannabis. And all of them said—sometimes in the most colorful of language—that if given the choice or presented with the knowledge, they would pitch irradiated cannabis directly into the bin.
That’s also how this story began, after an employee of Ono’s, tasked with running the radiation machine, shared an anonymous message, lamenting the fact that they were, in their view, nuking pot—and they had never heard of such an ungodly act that, upon further review, is both commonplace and accepted.
This is partially by fiat. As Ono wrote in a Medium post last year, Massachusetts’s strict safety standards—almost as strict as Canada—mean that some remediation method is necessary to pass. It also means that classic “regenerative farming” methods that rely heavily on beneficial bacteria—the same bacteria that Massachusetts testing regulations toss in the same bucket as the E. coli that triggers food poisoning—can’t work without remediation, he said.
Going forward, Massaschusetts should relax its rules to allow for “beneficial microbes,” he said, or at least draw a distinction between benign and harmful microbes.
“This is crucial for good farming practices in general,” he said.
Meanwhile, irradiated weed has a lead in the markets. It’s at best uncertain whether cannabis consumers will ever prefer sun-grown, regeneratively-farmed cannabis over dense, dank, and energy and nutrient-dense hydroponic indoor—and the more intensive the production method, the more use there is for irradiation and other remediation methods.
If Massachusetts won’t accommodate beneficial microbes in this way, the state could at least help with transparency. Perhaps cannabis cultivators that remediate their final product with radiation or another method should be honest brokers, and report both the that the cannabis was remediated and the method used—or be made to do so by law, he said.
“I’m very much in favor of consumer education and transparency,” he said. “I think it should be clear that it’s remediated and what methodology is being used.”
Until then, Ono is aware what a liability being honest about irradiation could be, irrational as it is.
“It’s like saying, ‘I’m afraid of energy, and as a result, I don’t like energy,’” he said.
But with the small profit margins and stiff competition along with the strict rules, cannabis “is fairly cutthroat,” he added. It’s probably a matter of time before a competitor tries to undercut EOS Farms by sharing this very story—even if they do something very similar, something of which most of their customers weren’t even aware before Ono said something.