
Curious Kids is a series for children of all ages. If you have a question you’d like an expert to answer, send it to curiouskidsus@theconversation.com.
What is most likely going on in Area 51? – Griffin, age 10, South Lyon, Michigan
One of the reasons people can never be entirely sure about what is going on at Area 51 is that it is a highly classified secret military facility. It was not until 2013 that the U.S. government even acknowledged the existence and name “Area 51.”
This information came out as part of a broader set of documents released through a Freedom of Information Act request, which is something regular citizens and groups can do to ask the U.S. government to provide details about government activities. In this case, the request made public formerly classified CIA information regarding the historical development and testing of the U-2 spy plane. The information also revealed where it was tested: Area 51!
As a national security historian, I know there’s a long history of secrets at Area 51. I also know that none of those secrets have anything to do with space aliens.
The place
The base commonly referred to as Area 51 is located in a remote area of southern Nevada, roughly 100 miles (161 kilometers) from Las Vegas. It is in the middle of a federally protected area of the U.S. Air Force’s Nevada Test and Training Range, now known as the Nevada National Security Site, which is inside the larger Nellis Air Force Range.
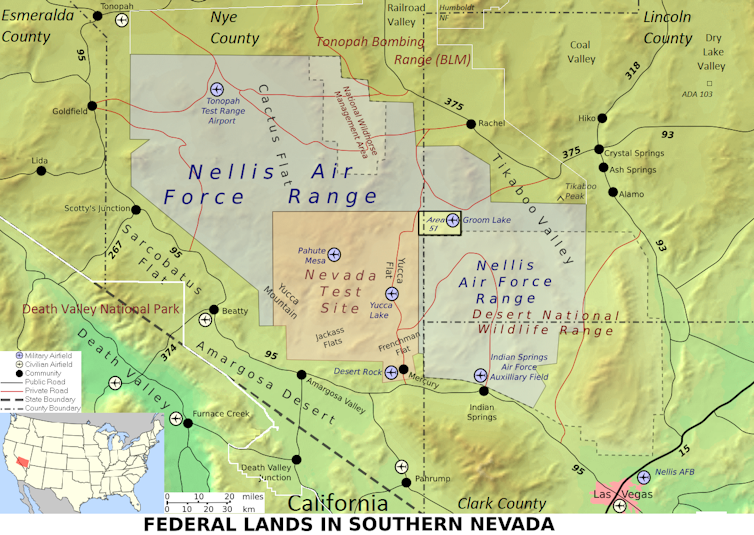
Area 51 is the secret code name for the site. The airfield at Area 51 is called Homey Airport, and the overall facility is often referred to as Groom Lake. Groom Lake is a salt flat, or dried-out lake, adjacent to the airport.
The history
In the early years of the Cold War between the United States and the Soviet Union, both nations sought new technological developments that might give one country more power than the other. A great amount of information about scientific achievements, such as on rockets or weapons – but also even on ways to grow more food or make fuel more efficient – was kept secret as an issue of national security.
A key part of not fighting another world war was, and still is, developing technologies to see what the other side is doing – that is, surveillance technologies that can spy on the enemy. The information gathered by new and improved surveillance technologies about new innovations with planes and weapons was very important to governments.
This meant that both the surveillance information and the technology to get it were closely held national security secrets. Very few people in the governments of the U.S. and Soviet Union knew about the secrets from the 1940s all the way up until the end of the Cold War in 1991.
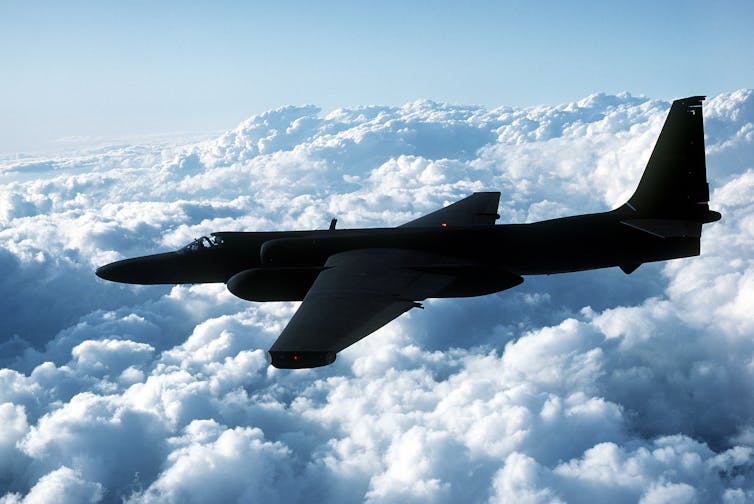

Central to all this was the U.S.’s U-2 spy plane. It could fly higher and faster than other airplanes and was made to travel over targets all around the world to take high-resolution photographs and measurements. Area 51 was selected in 1955 to test the U-2 in part because its remote location could help keep the plane secret.
Area 51 became the test site for other secret new aircraft. This included the A-12, which, like the U-2, was a fast-flying reconnaissance plane. The A-12 was first test flown at Homey Airport in 1962. It had a bulging disc-like center to carry additional fuel. Its shape and shiny titanium body could well have been responsible for some people’s reports about seeing spherical ships, also known as flying saucers.
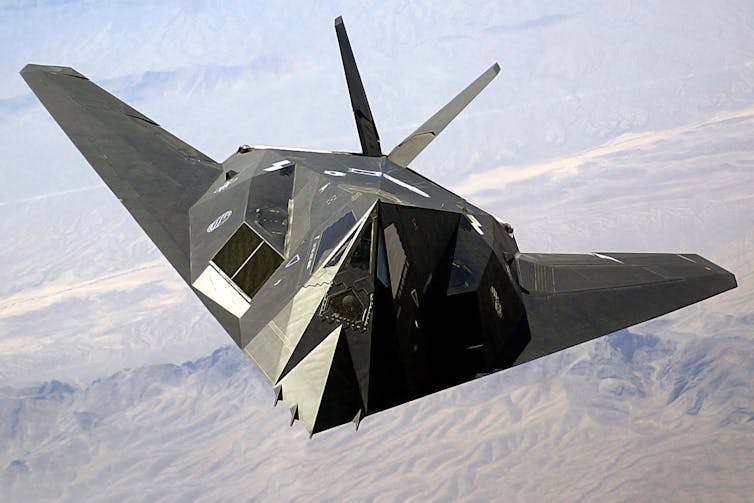
Another important – and odd-shaped – aircraft first tested at Area 51 was the stealth fighter known as the F-117. It first flew at Homey Airport in 1981.

Secrets and speculation
“More Flying Objects Seen in Clark Sky,” read the June 17, 1959, headline in the Reno Evening Gazette newspaper. Reports like this of unidentified flying objects in the 1950s and 1960s fueled controversy and attention for Area 51. This was for three main reasons:
- Area 51 was highly secret and not publicly accessible.
- The area was home to test flights of secret new airplanes that moved fast and in different ways than expected.
- The Cold War was an era of political tension, and there were many movies and TV shows about space aliens at the time.
When the government does not tell the public the full truth, no matter the reasons, secrets can lead to wild speculation. Secrecy can leave room for conspiracy theories to develop.
Area 51 remains off-limits to civilian and regular military air traffic, a decade after the government acknowledged its existence. The 68 years of government secrecy has helped to amplify suspicions, speculation and conspiracy theories. These conspiracy theories include crashed alien spaceships, space aliens being experimented on, and even space aliens working at Area 51.

There are much simpler explanations for what witnesses have seen near Area 51. After all, the public now knows about what was being tested at Area 51, and when. For example, as U-2 and A-12 flights increased in the 1950s and 1960s, so did local sightings of UFOs. As balloons and planes crashed, and secret testing of new technologies as well as captured Soviet equipment continued, so did reports of UFO crashes and landings.
In fact, many UFO sightings match almost exactly with dates and times of flights of then-classified experimental aircraft. We also know that prototype drones and more recent versions have been tested at the site.
In the end, there is no reason to think that anything other than earthly technologies have been behind the strange sights and sounds at Area 51.
Hello, curious kids! Do you have a question you’d like an expert to answer? Ask an adult to send your question to CuriousKidsUS@theconversation.com. Please tell us your name, age and the city where you live.
And since curiosity has no age limit – adults, let us know what you’re wondering, too. We won’t be able to answer every question, but we will do our best.
Christopher Nichols does not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organization that would benefit from this article, and has disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.
This article was originally published on The Conversation. Read the original article.







