Gross profit margin helps to evaluate executive management's ability to maintain profits.
Canva
What Is Gross Profit Margin?
Gross profit margin is a type of profit margin that is used to measure a company’s profitability relative to sales and is expressed as a percentage. It is a ratio of gross margin, or gross profit, to revenue, and the metric is a way to evaluate a company’s ability to generate income from its sales after deducting production costs.
What Does Gross Profit Margin Indicate?
Investors use gross profit margin to evaluate how a company’s executive management is effectively and efficiently generating profit from sales. Generally, the higher the margin, the more profitable the company is. The two main components are revenue and the costs associated in the production of goods and services (also known as cost of sales or cost of goods sold). High costs are likely to cut into profitability, while low costs would help to boost it. At the same time, if costs remain the same from one quarter to the next, an increase in sales will help lift income, while a decrease in sales could lower it.
How to Calculate Gross Profit Margin
Gross profit is calculated by dividing gross margin (revenue minus cost of sales) by revenue. Both gross margin and revenue appear at the top of a company’s income statement. For publicly traded companies, their quarterly and annual financial statements are filed on a regular basis with the Securities and Exchange Commission.
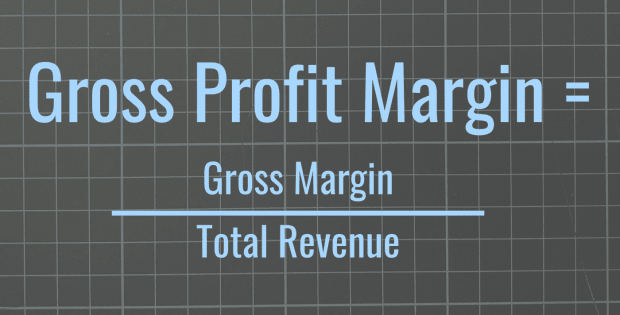
Gross Profit Margin = Gross Margin (or Revenue – Cost of Sales) / Revenue
How to Interpret Gross Profit Margin
Below is an example of Apple’s sales and cost of sales from fiscal years 2017 to 2021. (Note: Apple’s fiscal years end toward the end of September, compared to the January–December period that is typical for many companies.) Gross profit margin held steady from 2017 to 2020 but picked up in 2021 as Apple’s net sales rose faster than its cost of sales. The data suggest that even as sales wavered from 2017 to 2020, executive management kept production costs in check, and maintaining those expenses into 2021 helped to boost the company’s gross profit margin.
What Are the Limitations of Gross Profit Margin?
Gross profit margin measures only the top line items and doesn't show exposure to other costs such as operating expenses, tax payments, and interest charges. Focusing on sales and cost of sales is narrow in scope, but using it in conjunction with other profitability ratios could provide a broader picture of a company’s ability to produce earnings.
The two other profit margins related to gross profit margin are operating profit margin and net profit margin. Together, these three types of profit margin focus on items in the income statement and how sales and associated costs lead to earnings.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
The following are answers to some of the most common questions investors ask about gross profit margin.
How Does Gross Profit Margin Differ from Gross Margin?
Gross profit margin takes gross margin, which is cost of sales minus revenue, and divides that by revenue. It expresses gross margin relative to revenue as a ratio.
What Is a Good Profit Margin?
A recent study showed that for companies with market capitalization exceeding $1 billion, the median average gross profit margin was 42 percent. Being at or above this average would be considered good.







