What Are Industrial Production and Capacity Utilization?
Industrial production and capacity utilization measure the output of manufacturing in the U.S. and are used to gauge consumer spending, inflation, and economic growth. Industrial production is a measure of the change in the production output of factories, mines, and utilities, while capacity utilization is a measure of their industrial capacity and how much of it is being used.
What Are the Origins of Industrial Production and Capacity Utilization?
Industrial production is one of the oldest economic indicators covering the U.S., with more than 100 years of historical data. When the Federal Reserve was established in 1917, one of its prerogatives was to monitor business activity via output.
In 1922, the central bank started covering manufacturing, mining, and agriculture, and it established indexes. In 1956, the focus was on manufacturing, mining, and electric and gas utilities—and these three industries continue to make up the current index of industrial production. The Federal Reserve expanded monitoring output via capacity, and the index of capacity utilization was created in 1967.
Why Are Industrial Production and Capacity Utilization Important?
The latest data on industrial production and capacity utilization reflect output from the previous month. Both measures are often used to gauge the direction of inflation and where the economy might be headed, and are considered leading indicators. Manufacturing makes up about a fifth of gross domestic product, and indexes of industrial production and capacity utilization are used to track that output.
How Are Industrial Production and Capacity Utilization Compiled?
Industrial production and capacity utilization are compiled as indexes by the Federal Reserve and are set to a reference period, which are typically updated every five years. The current series of data are set against a base year of 2017, and the base year for the next series of data is likely to be set at 2022. The Fed says the data are typically obtained from private trade associations and from government agencies, and the collected data are used to estimate monthly industrial production.
According to the central bank, the industrial production index is constructed from two main types of source data: output measured in physical units and data on inputs to the production process, from which output is inferred. These data can include anything from the number of planks of lumber produced to the amount of hours worked on a production line.
As of 2022, the index was based on 296 types of industries according to the definition set by the North American Industry Classification System, or NAICS. Manufacturing accounted for the overwhelming majority (77 percent) of the proportion of component industries in industrial production, followed by mining (12 percent), and utilities (11 percent). Manufacturing covers production of durable goods such as cars, computers, and fabricated metal products, and of nondurable goods including food, beverages, textiles, clothes, gasoline and plastics.
Below are graphs of industrial production and capacity utilization from 2013 to 2022.
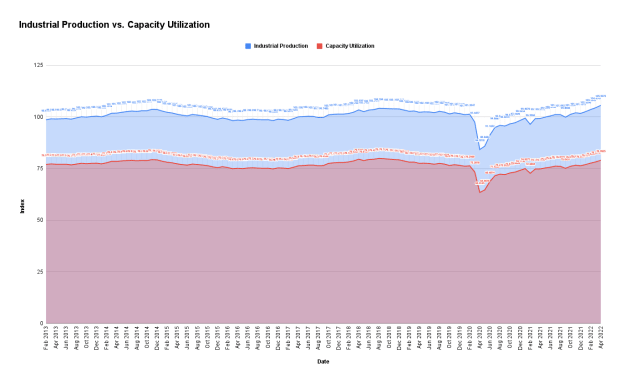
Industrial Production
Industrial production is expressed as an index, but investors and analysts look at the month-on-month change. From 2013 to 2022, the index ranged from a low of 84.2 in April 2020, when manufacturing decelerated due to lockdown measures in the early days of the COVID-19 pandemic, to a high of 105.6 in April 2022, as companies sought to keep up with demand due to supply-chain disruptions.
Capacity Utilization
Capacity utilization is expressed as a percentage of total capacity in manufacturing, mining, and utilities, with 100 indicating full capacity. Capacity from 2013 to 2022 ranged from a high of 79.9 in August 2018 to a low of 63.4 in April 2022, when many manufacturers curbed production due to COVID-19 restrictions. In 2022, capacity returned to pre-pandemic levels.
When Are Industrial Production and Capacity Utilization Data Released?
The Federal Reserve typically releases reports on industrial production and capacity utilization at the middle of the month, usually between the 15th and the 18th of the month, at 9:15 a.m. ET.
Upcoming Release Dates for Remaining Months of 2022
How Are Industrial Production and Capacity Utilization Interpreted?
Industrial production and capacity utilization have a near-perfect relationship. The correlation coefficient between the two from May 2013 to April 2022 was 0.999, according to TheStreet.com’s analysis. That is just below 1, which would indicate 100 percent correlation. Industrial production’s changes are in lockstep with those of capacity utilization on a month-on-month change basis over the 10-year period.
High readings on industrial production and capacity utilization would indicate that the economy is growing at a quick pace and consumer demand is strong. But there are risks to prices increasing due to wage pressures and rising costs for raw materials, and such factors could cause inflation at the consumer and producer levels to accelerate. Conversely, low readings on both indicators would suggest weak consumer demand, translating into slowing economic growth and declining prices.
Still, the correlation between industrial production and the consumer price index was low to moderate from 2013 to 2022, with a coefficient of 0.34.
How Do the Stock and Bond Markets React to the Release of Industrial Production and Capacity Utilization?
The stock and bond markets often react to the pace of growth in industrial production. Moderate growth would indicate that the economy was expanding at a decent pace, potentially sending stock and bond prices higher. Growth that was unexpectedly quick over a period of a few months or so could portend a sudden pick-up in inflation, which would raise concerns that the Federal Reserve would tighten monetary policy, and fears of rising interest rates could cause stock and bond prices to fall.
From January to April 2022, industrial production rose an average 0.9 percent, which was above the average 0.7 percent increase from 2013 to 2022. Inflation accelerated during the first four months, causing the central bank to send signals of a possibly tighter monetary policy stance. That sent stock and bond prices lower, with major stock indexes entering bear market territory, and yields rising to their highest in years.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
The following are answers to some of the most common questions investors ask about industrial production and capacity utilization.
Are Industrial Production and Capacity Utilization Leading or Lagging Indicators?
Industrial production and capacity utilization are lagging indicators because they are based on manufacturing data from the previous reporting month.
What’s the Relationship Between Industrial Production and GDP?
Growth in industrial production would indicate expansion in the economy in general. Manufacturing as a whole accounts for about a fifth of GDP, so it has a less significant impact on the economy than services do.
What Industries Are Included in Industrial Production?
Manufacturing, mining, and gas and electric utilities are the main components included in industrial production. The Federal Reserve continues to make changes when necessary to reflect worker production in existing industries as well as emerging ones. Over the past century, the index initially focused on agriculture but eventually removed that, and in the past few decades has added computer equipment and semiconductors to the mix.







