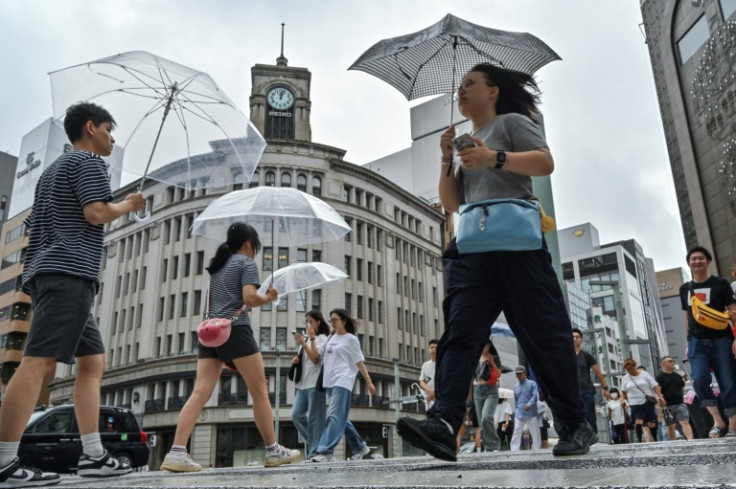
A "very strong" typhoon buffeted Japan's Pacific coast with fierce winds and heavy rain on Friday, forcing the cancellation of hundreds of flights and trains in the Tokyo area and leaving over 4,000 homes without power.
Located about 300 kilometres (190 miles) south of Tokyo, Typhoon Ampil was packing gusts of up to 216 kph as it headed north, the Japan Meteorological Agency said.
The eye of the typhoon was not expected to make landfall, instead barrelling north-eastward up the Honshu coast and skirting the Tokyo region, home to around 40 million people, before heading back into the Pacific from Saturday.
The JMA rated the weather system as "very strong", one notch below its highest category of "violent typhoon", with maximum wind speeds of 105 knots (120 mph, 195 kmh).
The agency warned people they "should be on high alert for storms, high waves, landslides and flooding" in a social media post.
The US military's Joint Typhoon Warning Center forecast maximum sustained wind speeds of 110 knots and gusts of 135 knots by 3:00 pm off the coastal Chiba region east of the capital.
Over 4,000 households in Tokyo's neighbouring prefectures, mainly Chiba, were without power as of Friday morning due to the typhoon, according to the utility operator.
All Nippon Air cancelled 335 domestic and international flights on Friday, with more planned for Saturday, affecting about 72,000 passengers.
Japan Airlines has so far scrapped 361 flights, hitting 57,000 customers.
Major parts of Japan's network of bullet train services were also to be closed Friday -- including the busy section between Tokyo and Nagoya -- while Tokyo Disneyland's operator said the park would close from 3:00 pm.
The typhoon comes as Japan marks the "obon" holiday week when millions return to their hometowns, and days after Tropical Storm Maria dumped record rains in parts of the north.
"We will check our phones for any information on the internet and if the typhoon seems OK, then we'll go outside," said Isamu Teruya, 47, a visitor from Saga Prefecture who arrived in Tokyo on Thursday.
"If the rain is really bad, then we will stay inside our hotel and relax," Teruya told AFP.
Typhoons in the region have been forming closer to coastlines, intensifying more rapidly and lasting longer over land due to climate change, according to a study released last month.
Researchers from universities in Singapore and the United States analysed more than 64,000 modelled historic and future storms from the 19th century through the end of the 21st century to come up with the findings.