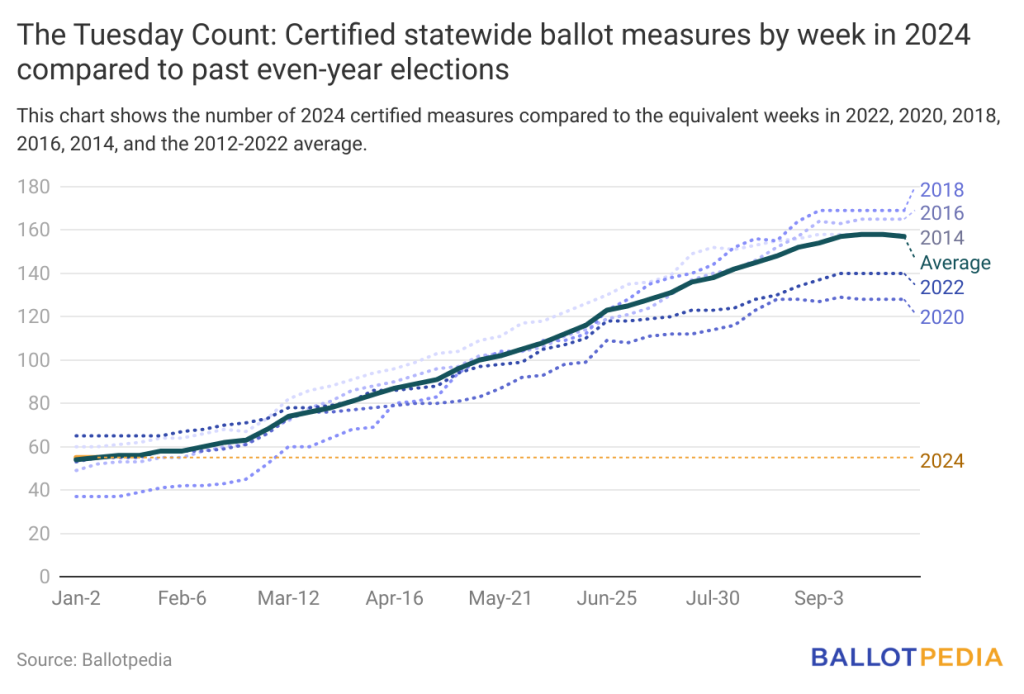
For 2024, 55 statewide ballot measures have been certified for the ballot in 25 states, which is equivalent to the average for this point in the election cycle from 2012 to 2022. The average number of statewide ballot measures certified for an even-numbered year during this period was 157.
- Here’s an update on the latest ballot measure activity:
- While zero new measures were certified for the ballot during the previous two weeks, one was withdrawn from the ballot—the California Fast Food Restaurant Minimum Wage and Labor Regulations Referendum. This was the first veto referendum withdrawn in California under a new law passed in Sept. 2023.
- Signatures have been submitted and are pending verification or another pre-certification action for four initiatives in Alaska, Michigan, and Florida:
- In Massachusetts and Washington, enough signatures were verified for 12 indirect ballot initiatives for them to appear before their respective state legislatures:
- Massachusetts App-Based Drivers as Contractors and Labor Policies Initiative
- Massachusetts Authorization of State Auditor to Audit General Court Initiative
- Massachusetts Minimum Wage for Tipped Employees Initiative
- Massachusetts Regulated Access to Psychedelic Substances Initiative
- Massachusetts Repeal Competency Assessment Requirement for High School Graduation Initiative
- Massachusetts Unionization and Collective Bargaining for Transportation Network Drivers Initiative
- Washington Initiative 2081, Parental Right to Review Education Materials, Receive Notifications, and Opt Out of Sexual-Health Education Initiative
- Washington Initiative 2109, Repeal Capital Gains Tax Initiative
- Washington Initiative 2111, Prohibit Income Taxes Initiative
- Washington Initiative 2113, Police Vehicular Pursuits Initiative (2024)
- Washington Initiative 2117, Repeal Carbon Cap and Invest Program Measure (2024)
- Washington Initiative 2124, Opt-Out of Long-Term Services Insurance Program Initiative (2024)
In Alaska, Massachusetts, Michigan, and Washington, initiated state statutes are indirect. This means the initiative is first presented to the state legislature. Legislators have a certain number of days, depending on the state, to adopt the initiative into law. In Michigan and Washington, when legislators take no action or reject the initiative, the initiative is put on the ballot for voters to decide. In Massachusetts, petitioners collect a second round of signatures to place the initiative on the ballot.
In Florida, the process is direct—the initiative goes to the ballot after signature verification.
The next signature deadline for citizen-initiated ballot measures is January 16, 2024, in Alaska, where signatures could be filed for an initiative to repeal the state’s system of top-four primaries and ranked-choice voting, in addition to the minimum wage initiative.
The following chart shows the number of ballot measures certified across each week of an even-numbered year.
Additional: