You've surely heard about it, but what is Unreal Engine 5, exactly? In this Unreal Engine explainer, we'll answer exactly that and bring you up to speed with everything you need to know about the software and why it's coming to dominate in game design, VFX, virtual production, archviz and more.
In a nutshell, Unreal Engine is a real-time digital creation platform for making games, visualisations, VFX and more. The software is becoming increasingly popular for making video games, competing with Unity, but it's become a staple of many other types of digital art workflows too – and is still free for most people.
Below, I'll explain what Unreal Engine is, what it can do and how to use it. I'll cover the main features and tools as well as the digital industries where Unreal Engine is dominant. To learn more, see our roundup of Unreal Engine tutorials. Also see our guide to the best 3D modelling software. Many 3D formats are compatible with Unreal.
What is Unreal Engine 5?
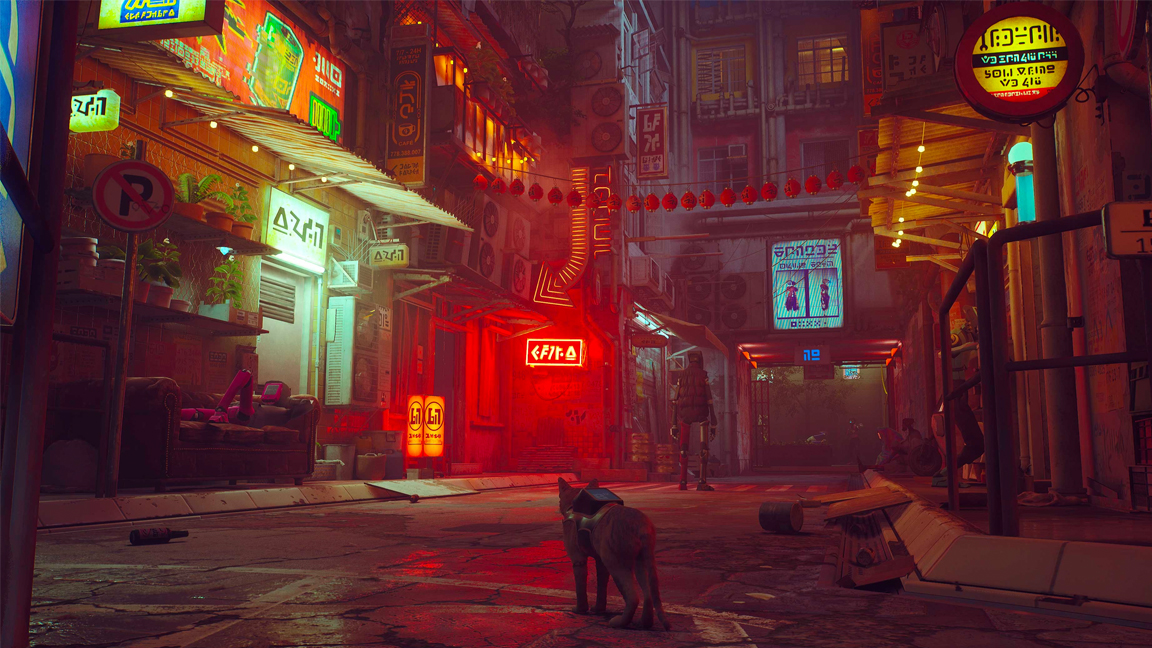

What is Unreal Engine? Put simply, it's a real-time 3D creation platform developed by Epic Games for a range of creative fields, including video game development, visualisation and VFX.
By real-time, we mean that changes are seen immediately in the software as opposed to traditional VFX pipelines that rely on offline rendering. This enables rapid iteration and experimentation, accelerating the creative process, and it makes Unreal ideal for game development, virtual production and interactive experiences.
The platform includes a powerful set of tools that enable creatives to design virtual worlds and scenes. Compared to other game engines (see our guide to the best game development software) UE5 stands out for the ability to achieve high-fidelity photorealistic graphics, which makes it ideal for complex games that demand high performance visuals, including highly realistic environments.
Its powerful visual scripting system, Blueprints, makes the engine relatively accessible, reducing the need to be a coding expert. Standout tools include Nanite, a virtualised geometry system that allows for importing and rendering detailed assets, and Lumen, a real-time global illumination and reflections system that dynamically adapts to changes in scene geometry and lighting.
Who is Unreal Engine 5 for?
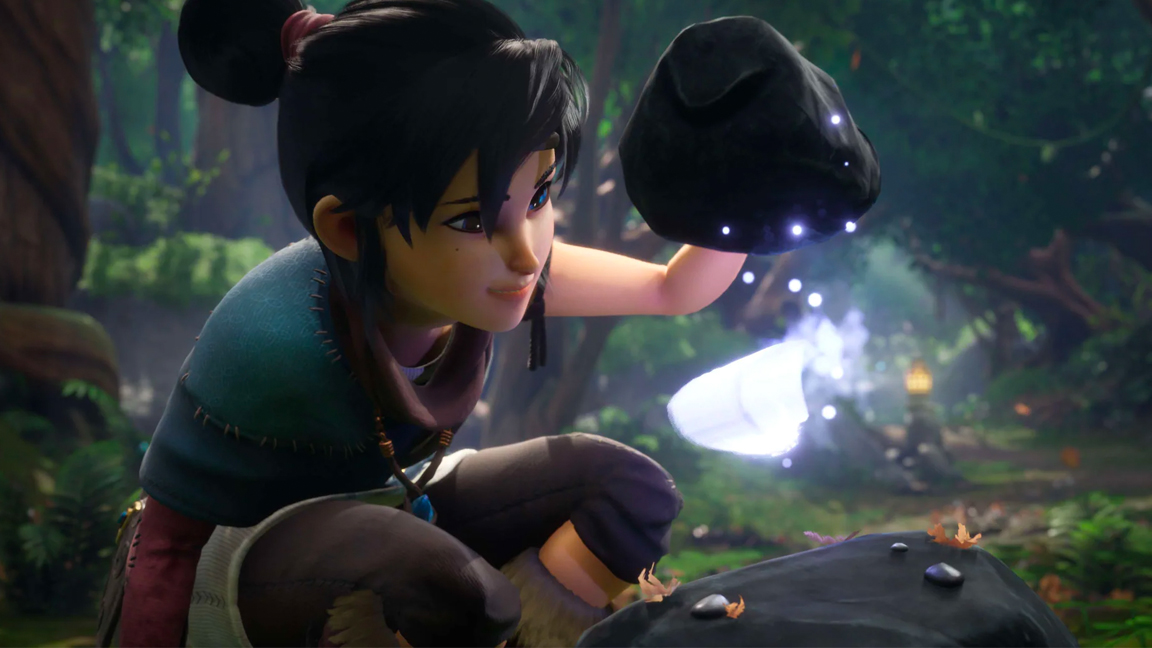

Unreal Engine began life as an engine for creating video games. It was used to create the likes of Fortnite, Final Fantasy VII Remake, PlayerUnknown’s Battlegrounds and more recently Ready or Not.
Its flexibility, performance and accessibility means it's used by major studios to create AAA games but also by indie developers, allowing them to create games with a fidelity that previous would not be possible on a budget. Epic Games claims that 48% of next-gen games are now made using Unreal Engine 5.
We've seen games like Ninja Theory's Senua's Saga: Hellblade II creating realistic humans alongside the four-person team of Quantum Error. And since Unreal Engine 5 is free to use, it's also led to an explosion of non-commercial fan and enthusiast remakes of classic games with modern graphics (see our piece on the best Unreal Engine 5 remakes).
Outside of games, Unreal Engine has also seen a growing interest in the TV and film industries, with Jon Favreau championing its use for the creation of virtual worlds for both The Lion King and The Mandalorian. Some filmmakers are starting to make entire short films in Unreal Engine, and they can sometimes be hard to distinguish from reality at first glance.
One new film technology developed using Unreal Engine is the LED Volume stage, a blend of a virtual and physical movie stage. We visited an LED Volume at SCAD in Atlanta to see how this new form of filmmaking is helping bridge the gap between traditional movie making techniques modern CG visual effects.
The platform is also used for 3D visualisation and animation in archviz and to create digital twins for product design and marketing. It's been used for advertising campaigns for the likes of Aston Martin.
Some core industries that use Unreal Engine are listed below:
- Video games Unreal Engine is for any team size, and suits games design for PC, consoles and even VR and AR.
- Filmmaking Whether its Barbie or House of the Dragon, many studios are making use of Unreal Engine's real-time workflow using LED Volume sets. The Rogue Trooper movie looks set to become the first feature film to be animated entirely using Unreal Engine 5.
- Architecture arch-viz has evolved with real-time rendering using Unreal Engine, which can use files created in many 3D, CAD, and BIM apps.
- Automotive Designers can create in VR and explore how cars perform before they've even been made with rapid virtual prototyping and new collaboration tools.
- Broadcast and live TV Unreal Engine's real-time tools can help ensure live broadcasts look stunning; from motion graphics to video walls, inserts and virtual sets.
What's the latest version of Unreal Engine 5?
The latest version of the software, Unreal Engine 5.6, was released in June 2025, and it can be downloaded from the Unreal Engine website.
The update was launched during Unreal Fest Orlando 2025 and was accompanied by the release of a Witcher 4 tech demo to showcase some of the new features.
Updates in Unreal Engine 5.6 include:
Animation: the Curve Editor has been redesigned for speed and performance and easier manipulation of keyframes. The Sequencer includes a new navigation tool and real-time audio scrubbing for syncing animations and effects, and Tween Tools have been optimized for quick and precise animation fine-tuning. The Physics Control Rig gets new features for controlling physics-based animations, and
MetaHuman Animator: now includes Live Link Face (Beta) for Android devices for real-time animation capture. MetaHuman Creator is now fully integrated, allowing for creation, tweaking, and animation of MetaHumans directly in the editor.
Performance: Lumen gets enhancements to Global Illumination through hardware ray tracing, benefiting large open worlds and there's faster streaming of geometry for smoother loading of large static worlds.
Unreal Engine 5 standout features
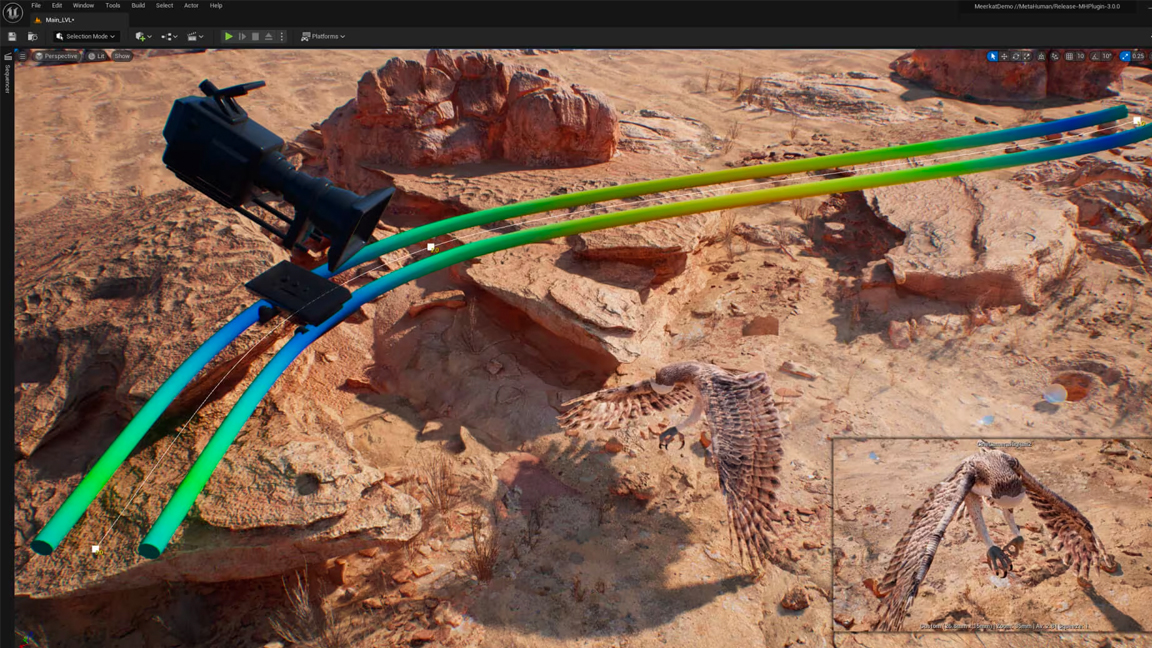
Unreal Engine's strength comes from the powerful features it offers, from simulation effects using Niagara and virtual camera controls to animation rigging. The magic is how easy Unreal Engine makes these advanced features to use; this largely a 'no-programming' platform.
- Photoreal ray tracing in real time Unreal Engine ships with an incredible physically based ray tracing engine. Lighting, reflections and shadows can be independently driven by the ray tracing technology. This does come at a hardware cost though as the calculations are understandably pretty intensive.
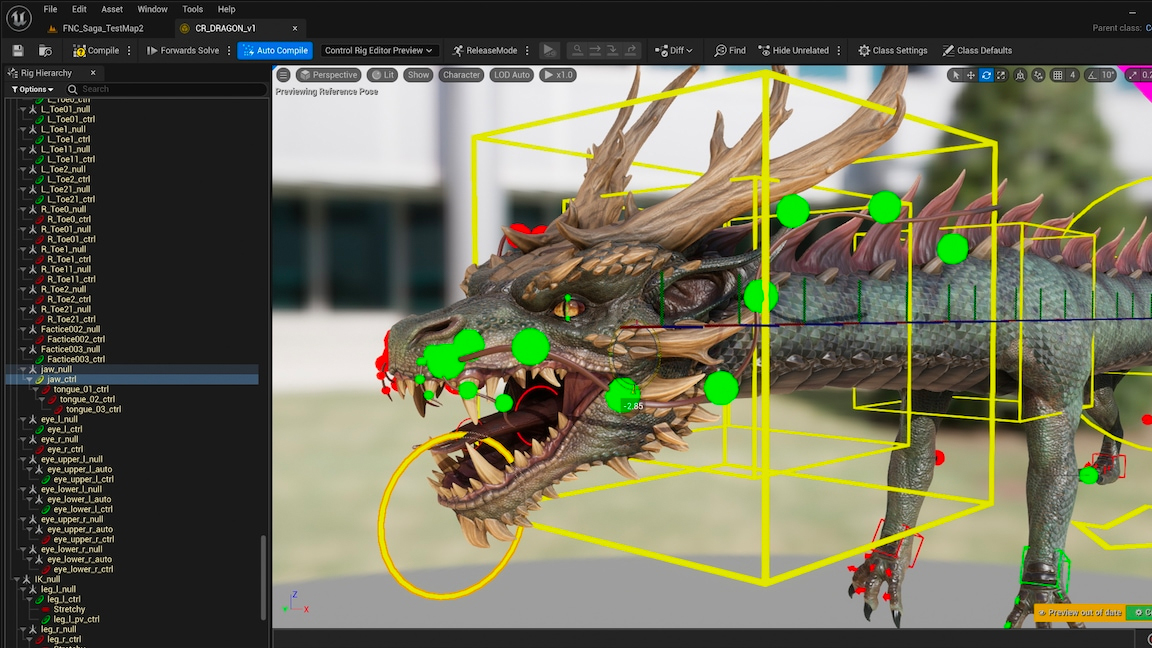
- Character animation authoring Character rigs can be created easily with the Control Rig tool. These can then be posed and animated, all within Unreal Engine.
- Simulation and effects Using Niagara particles you can create stunning water, smoke and other effects in real time; the Chaos disolver enables life-like destruction physics, flowing cloth and hair.
- Virtual Camera system One of the emerging uses of Unreal Engine is for film and TV where it is now possible to control cameras inside the engine using an iPad Pro. This enables the compositing of live action and virtual worlds to be seamlessly brought together.
- Robust multiplayer support Arguably Unreal Engine’s strongest feature is its multiplayer framework. The engine ships with a scalable client/server architecture that enables even the most demanding multiplayer functionality.
Unreal Engine 5 must-know tools
Unreal Engine includes an impressive set of tools and features that enable creatives from a wide range of industries to create according to their imagination. Some of the more general tools include modelling, texturing, lighting, texturing and rendering but alongside these there are a number of more significant and substantial features which are explored below.
Lumen
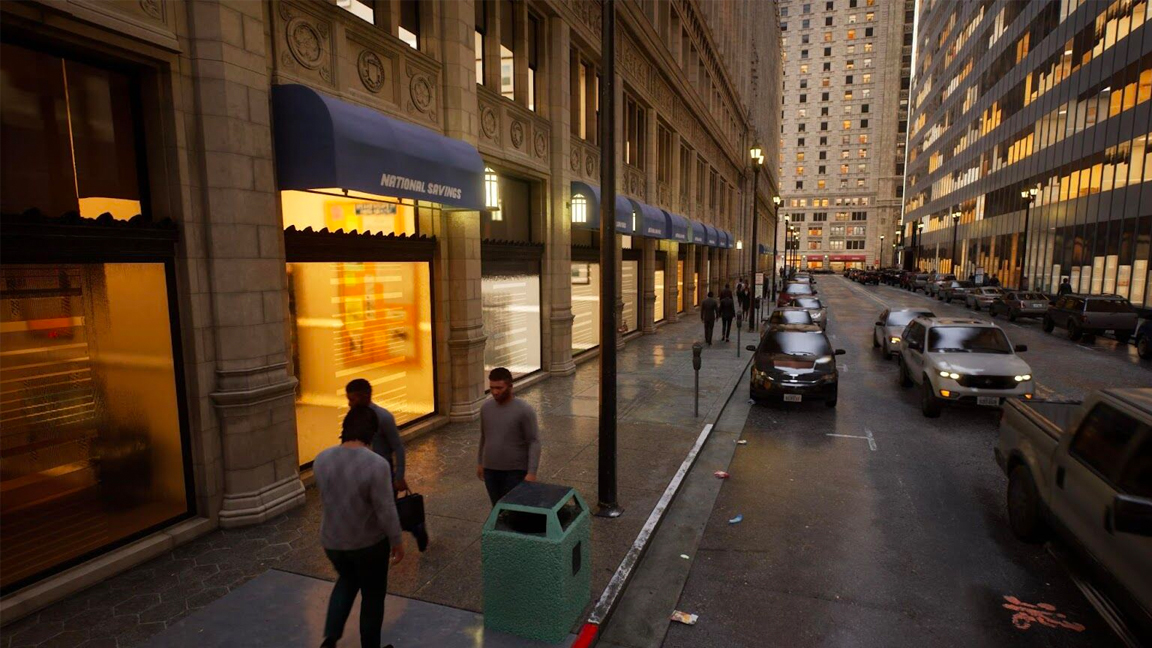

Lumen is Unreal Engine’s global illumination (GI) system which was released in version 5. GI is the name attributed to the process of simulating realistic lighting in a scene. This includes indirect lighting such as light bouncing and light bleeding. This functionality has only recently been added to Unreal Engine with the process of light baking being the only option previously available.
Artists familiar with offline rendering will be familiar with this type of lighting but the number of light bounces required and the subsequent mathematical calculations meant that real-time implementations weren’t possible.
The single biggest advantage of GI, in a games context, is that there is no need for light baking. This was always pretty much the most time-consuming and tedious part of any game designer's workflow and if you wanted to make any change to the lighting setup or arrangement then everything needed rebaking. Lumen changed all that overnight.
Version 5.3 recognises that some designers will still want to benefit from the high-performance nature of baked lighting but could still work with real-time reflections. This is where Lumen reflections have been introduced. Users can now use them even if they’re not using Lumen for global illumination. The fact that they now support multiple reflection bounces is an even bigger win.
Nanite
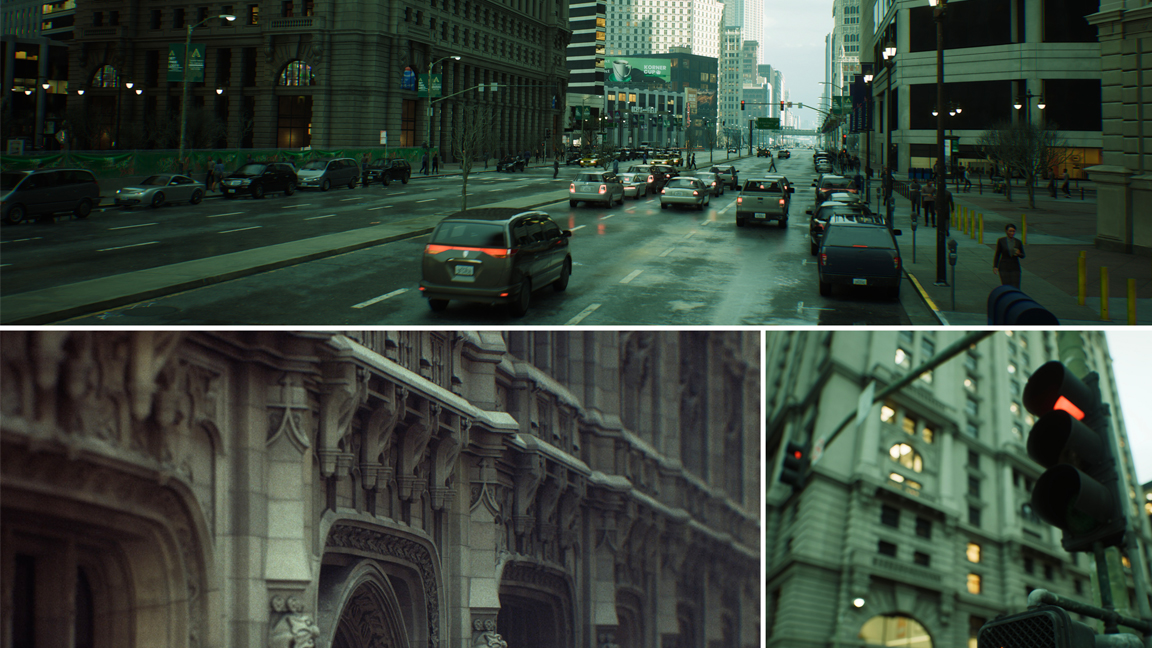

Another game-changing feature of Unreal Engine is Nanite, Unreal Engine’s level of detail (LOD) system. This ensures that detail is only rendered when absolutely necessary. Prior to Nanite, each LOD for a mesh would need to be hard-modelled in. The main downside to this was the sheer amount of time it took and problems would occur if any models were missed. Nanite took all of this off an artist’s plate and implemented it dynamically ‘on the fly’.
Recent versions of Unreal Engine have improved this feature further making it possible to now use Nanite with landscapes as well as the previously supported rocks, houses and similar. This means entire scenes can now be rendered dynamically rather than just specific parts of it. The evolution of Nanite is enabling designers to create high-quality meshes without compromising on the framerate.
MetaHumans
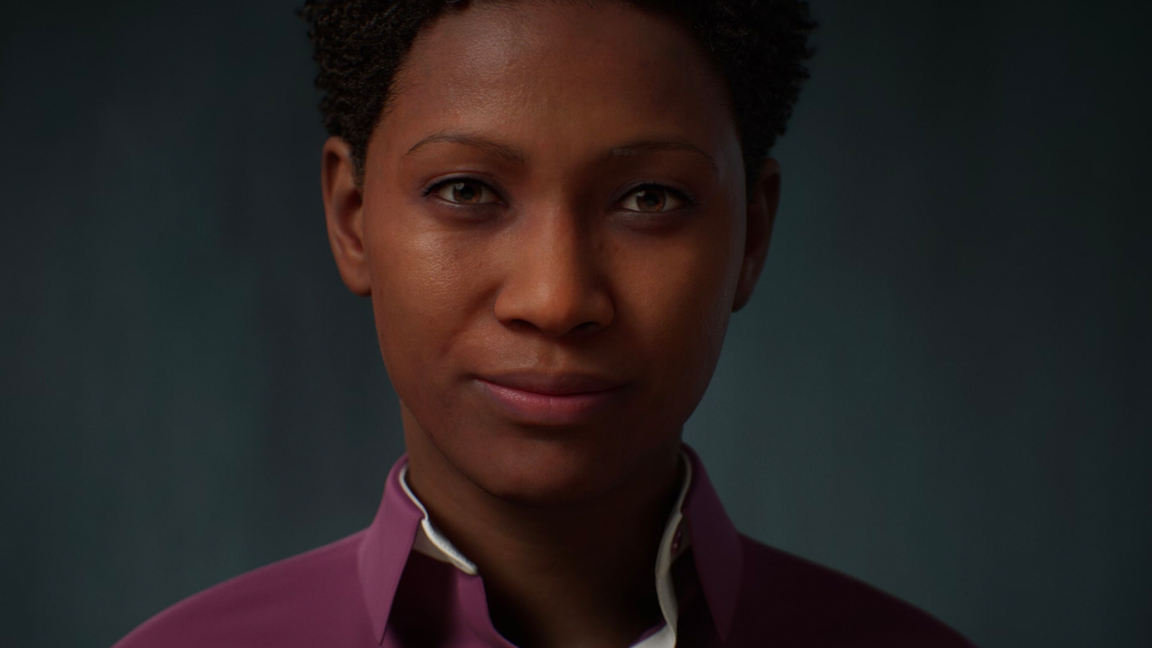

The introduction and increase of the metaverse has led to an explosion of development and possibilities for creating virtual humans. Epic Games’ offering is MetaHumans which enables the creation and animation of realistic digital humans for any Unreal Engine project.
Humans can be created with a minimal amount of character and animation knowledge and placed into games and scenes. When these are partnered with animation data such as mocap data, the characters take on a life of their own.
Temporal Super Resolution

One of the key considerations when experiencing real-time simulations such as games is the frames per second (fps) that it’s viewed at. Ordinarily, the higher the level of detail and quality of textures, the slower the frame rate. This can lead to an unhelpful trade off between the two.
Unreal Engine’s Temporal Super Resolution feature enables the engine to render at much lower resolution but with similar output pixel fidelity to frames rendered at a higher resolution. This makes it possible to achieve much higher levels of detail without compromising on the frame rates.
Niagara
Niagara is Unreal's visual effects system for creating and managing particle effects and other real-time visual effects. The flexible tool allows artists to build complex effects without extensive programming knowledge. It replaces the older Cascade system, providing more advanced features and control.
What is Unreal Editor for Fortnite?
Fortnite is an online video game developed by Epic Games. First released in 2017, Fortnite has captured the imaginations of millions of gamers all around the world. Most games are created by a developer and contributors are picked to work on it.
Epic Games has opted for an alternative approach which lets creators design, develop and publish content into Fortnite. This is achievable through the Unreal Editor for Fortnite (UEFN). With this platform, a truly collaborative approach has been forged for the creation of assets and worlds.
In addition to this, through Fortnite Creative, it is also possible to build islands in Fortnite using their built in tools. Creators can build games and experiences to play with friends, or alternatively publish them to millions of Fortnite players.
How much does Unreal Engine 5 cost?

At the time of writing Unreal Engine is free for most people and most uses. Only if you make a game that earns over $1 million USD do you have to pay Epic Games a 5% royalty. By that point you’re cashing in on a pretty substantial amount of money so the small royalty shouldn't make too much of a dent.
This will continue to be the case for game developers, but Epic has said that it plans to start charging studios who use Unreal Engine for other things, such as 3D visualisation, VFX or animation, using seat-based enterprise software licensing model. This was announced back in 2023, and it's still not clear when it will happen, but it's likely that there will be a minimum revenue requirement like with games.
What do I need to run Unreal Engine 5?
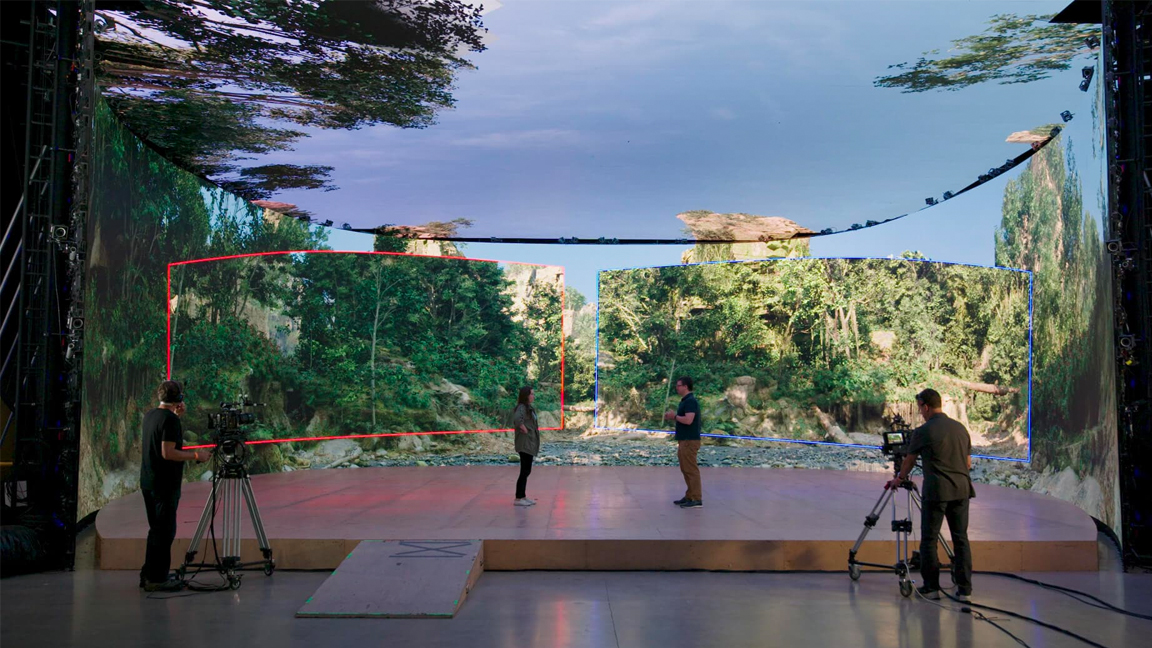

OS: Windows 10 64-bit, macOS Monterey or higher
CPU: Quad-core Intel or AMD, 2.5 GHz or better
RAM: 32GB RAM
GPU: DirectX 11 or 12 or Metal 1.2 compatible, 8GB VRAM
Unreal Engine has a huge range of complex and next-gen features. The required machine spec will largely depend on which of these features you plan on using. Some of the latest features such as ray tracing will require better GPUs compared to simpler scenes with baked lighting.
CPUs are vital for the smooth processing of your scenes. The latest generations of Intel and AMD CPUs will deliver excellent results and the more cores you have the faster the processing will be carried out.
A good GPU will ensure a smooth workflow and minimal lag when viewing scenes in the viewport. Two GPU features to look out for are the number of cores and the size of VRAM. The higher the number of cores and the larger the amount of VRAM, the more able you’ll be to handle graphically complex scenes and large textures. If ray tracing is important to your workflow then make sure you choose a GPU that supports it.
Epic recommends a quad-core Intel or AMD CPU, 2.5 GHz or faster, at least 32GB of RAM and 8GB of VRAM on a DirectX 11 or 12-compatible graphics card with the latest drivers.
See our guide to the best laptops for game development for recommendations.
What's the history of Unreal Engine?

Unreal Engine began life in the mid 1990s as a game engine for the first-person shooter Unreal, which was released for PC in 1998. It was created by Epic Games' founder Tim Sweeney, the designer of the 1991 puzzle game ZZT. Epic MegaGames, as his company was known then, began licensing the engine to other video game developers.
In the early days, Unreal Engine was in direct competition with Quake Engine, developed by id Software. This fierce competition pushed the gaming industry forward in unprecedented ways and resulted in Unreal Engine becoming a powerhouse of code.
Unreal Engine 2 released in 2001 made the move from software rendering to hardware rendering and added support for PlayStation 2, Xbox, and GameCube consoles. From 2004, Unreal Engine 3 became one of the first game engines to support multithreading, and Unreal Engine 4, in 2014, added support for physically based materials and the Blueprints visual scripting system. It was also the first version of Unreal to be free to download with royalty payments based on game revenue. Unreal Engine 5 was released on 5 April, 2022.
Unreal Engine 5: frequent questions
Is Unreal Engine 5 free?
You can download Unreal Engine 5.3 for free to create student and non-commercial projects. It's also free to create video games, with a 5% royalty paid when your game makes more than $1 million.
Why is Unreal Engine 5 so popular?
It's free to get started and experiment with but also incredibly powerful and versatile. But Unreal Engine 5 uses a modular system and Blueprint Visual Scripting setup to create scenes without needing programming knowledge.
Is Unreal Engine 5 good for beginners?
Unreal Engine 5's Blueprint Visual Scripting along with clear and detailed documentation, as well as an easy to understand UI, asset marketplace and regular video training, makes it a great platform for newcomers.
Can I make money using Unreal Engine 5?
Yes, outside of actually making video games, films and more you can earn money by selling assets on the Unreal Engine marketplace. The new Unreal Engine for Fortnite Editor also means you can now make and sell games inside Fortnite, one of the most popular free to play games.
What language does Unreal Engine 5 use?
Unreal Engine uses C++ as its main programming language. It does have a visual scripting system called Blueprints, which means you don't necessarily need to be a programming whizz, but C++ is the foundation for core game logic, performance-critical sections and low-level systems, and you're likely to want to be at least familiar with it.
What are the negatives of Unreal Engine 5?
Unreal Engine 5 might sound too good to be true, but it does have some drawbacks. The engine requires significant computing resources, and it getting started can be a steep learning curve. Unlike with the best no code game engines, you're likely to want to have at least a general familiarity with C++ code.
You might also hear about the notorious 'Unreal Engine 5 stutter'. Games made in the software can suffer from notable temporary breaks in gameplay caused by shader compilation when the game engine needs to compile new shaders (the programs that render graphics) before they're used.
What will be in Unreal Engine 6?
Epic Games hasn't said much about Unreal Engine 6, but Tim Sweeney has suggested that the first preview builds will be available in 2027 or 2028. All we really know is that it will focus on unifying the separate development streams used for the main engine and Unreal Editor for Fortnite.
Tim has mentioned big changes in the pipeline for animation, including Anim Next, a planned unified animation pipeline that will integrate the various tools and should be faster than Animation Blueprints. Elsewhere, the Control Rig system is expected to get improvements in the Deformer Graph and the cinematic editor Sequencer is expected to get a full branching dialogue system with procedural content-generation capabilities.
Epic also intends to simplify the timeline in its in-engine animation tools, to develop new versions of Tween Tools and Motion Trails and to add a physics sim that will run alongside skeletal animation.







