The AI model DenseAV is learning the meaning of words and the location of sounds without human input or text simply by watching videos, researchers said.
In a paper, researchers from MIT, Microsoft, Oxford, and Google explained that DenseAV manages to do so using only self-supervision from video.
To learn these patterns it uses audio-video contrastive learning to associate a particular sound with the observable world. This mode of learning means the visual side of the model can’t gain any insights from the audio side (and vice-versa) forcing the algorithm to recognize objects in a meaningful way.
It learns by comparing pairs of audio and visual signals and determines what data is important. It then evaluates which signals match and which don’t. Since it’s easier to predict what you are seeing from what you are hearing when you understand language and can recognize sounds, this is how DenseAV can learn without labels.
How does it work?
The idea for this process struck MIT PhD student Mark Hamilton while he was watching the movie March of the Penguins. There’s a particular scene where a penguin falls and lets out a groan.
“When you watch it, it’s almost obvious that this groan is standing in for a four-letter word. This was the moment where we thought, maybe we need to use audio and video to learn language,” Hamilton said in an MIT news release.
They found that one side of the brain naturally focused on language while the other focused on sounds like meowing.
His aim was to have his model learn a language by predicting what it’s seeing from what it’s hearing and vice-versa. So if you hear someone saying “grab that violin and start playing it” you’re likely going to see a violin or a musician. This game of matching audio to video was repeated across various videos.
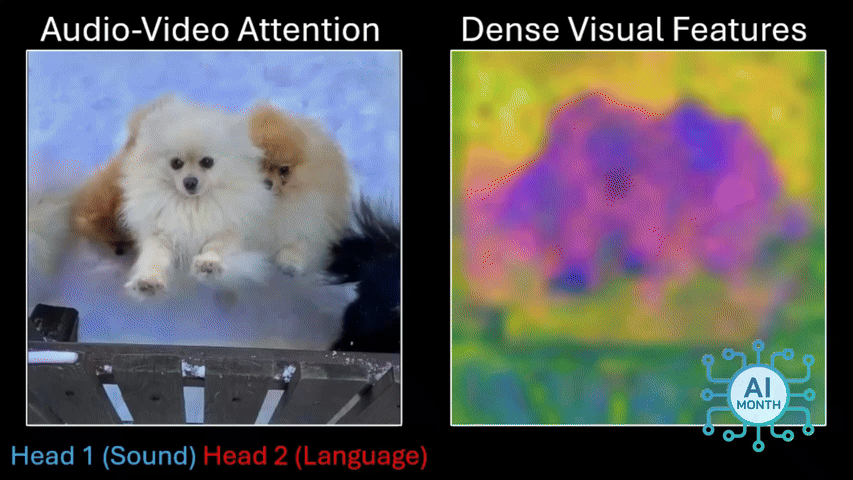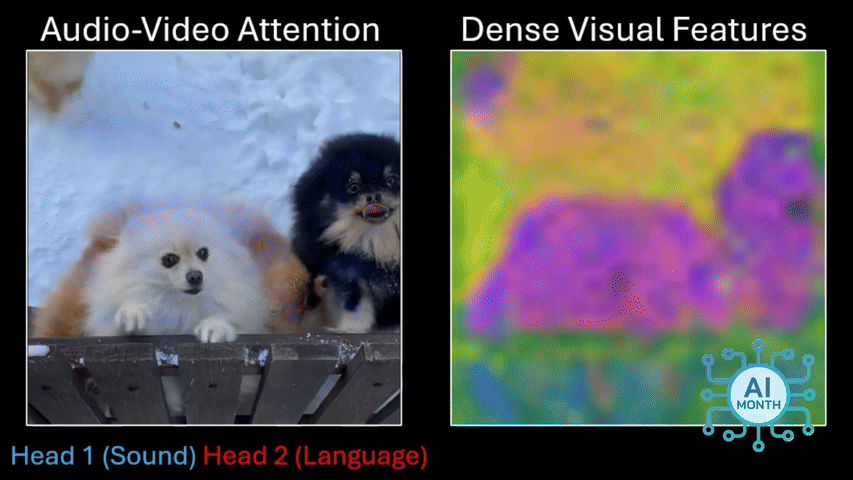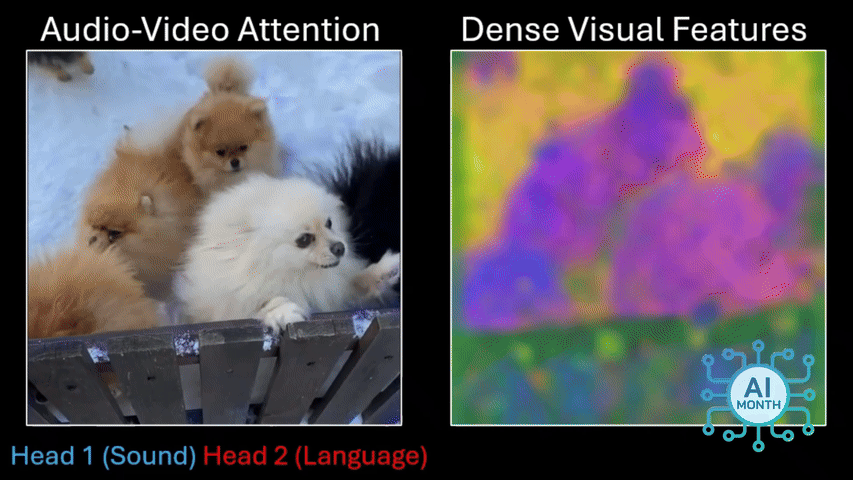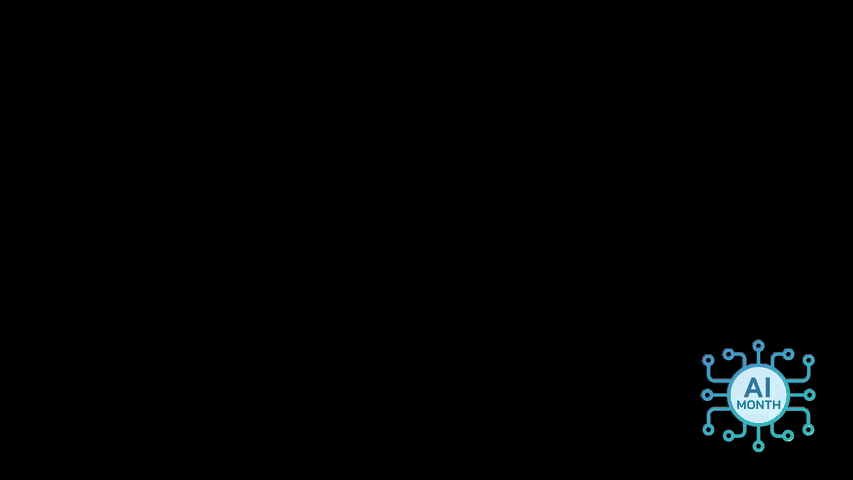
Once this was done, the researchers focused on the pixels a model was looking at when it heard a particular sound — someone saying “cat” would trigger the algorithm to start looking for cats in the video. Seeing which pixels the algorithm selects means you can discover what it thinks a particular word means.
But let’s say DenseAV hears someone saying “cat” and it later hears a cat meowing, the AI might still identify an image of a cat in a shot. However, does it mean the algorithm thinks a cat is the same thing as a cat’s meow?
The researchers explored this by giving DenseAV a “two-sided brain” and they found that one side of the brain naturally focused on language while the other focused on sounds like meowing. So DenseA did actually learn the different meaning of both words without any human intervention.
Why is this useful?
DenseAV is an algorithm capable of discovering the meaning of language and locations of sounds just by watching unlabeled videos. DenseAV is completely unsupervised and never sees text during its training. Learn more: https://t.co/eG755yC9mI pic.twitter.com/3I1jJW8l08June 11, 2024
The massive amount of video content already out there means AI can be trained on things like instructional videos.
“Another exciting application is understanding new languages, like dolphin or whale communication, which don’t have a written form of communication,” Hamilton said.
The next step for the team is to create systems that can learn from video- or audio-only data which is helpful in areas where there’s lots of one type of material but less of the other.







