It may come as a surprise to fellow land-dwellers, but the ocean actually accounts for most of the habitable space on our planet. Yet a big chunk of it has been left largely unmanaged. It’s a vast global common resource, and the focus of a new treaty called the biodiversity beyond national jurisdiction (BBNJ) agreement.
For 15 years, UN member states have been negotiating rules that will apply to the ocean lying more than 200 nautical miles from coastlines, including the seabed and the air space above, referred to as the “high seas”.
Covering nearly half the Earth’s surface, the high seas are shared by all nations under international law, with equal rights to navigate, fish and conduct scientific research. Until now, only a small number of states have taken advantage of these opportunities.
This new agreement is supposed to help more countries get involved by creating rules for more fairly sharing the rewards from new fields of scientific discovery. This includes assisting developing countries with research funding and the transfer of technology.
Countries that join the treaty must also ensure that they properly assess and mitigate any environmental impacts from vessels or aircraft in the high seas under their jurisdiction. This will be especially relevant for novel activities like removing plastic.
Once at least 60 states have ratified the agreement (this may take three years or more), it will be possible to establish marine protected areas (MPAs) in high sea locations of special value.
This could protect unique ecosystems like the Sargasso Sea: a refuge of floating seaweed bounded by ocean currents in the north Atlantic which offers breeding habitat for countless rare species. By restricting what can happen at these sites, MPAs can help marine life persevere against climate change, acidification, pollution and fishing.
There are obstacles to all nations participating in the shared enjoyment and protection of the high seas, even with this new treaty. Nations joining the new agreement will need to work with existing global organisations such as the International Maritime Organization (IMO), which regulates shipping, as well as regional fisheries management organisations.
The new treaty encourages consultation and cooperation with existing bodies, but states will need to balance their commitments with those made under other agreements. Already, some departments within governments work against each other when implementing broad, international treaties. For example, one division may chafe at greenhouse gas pollution regulations imposed at the IMO while a sister agency advocates for more stringent climate change measures elsewhere.
A new research frontier
A key element of the new treaty addresses the disproportionate ability of developed countries to benefit from the scientific knowledge and commercial products derived from genetic samples taken from the high seas. More than 40 years ago, when the law of the sea convention was being negotiated, the same issue arose over seabed minerals in areas beyond national jurisdiction.
Industrialised nations had the technology to explore and intended to eventually mine these minerals, while developing countries did not. At that time, nations agreed that these resources were part of the “common heritage of humankind” and created the International Seabed Authority to manage a shared regime for exploiting them.
The extreme conditions for life in the open ocean have nurtured a rich diversity of survival strategies, from the bacteria that thrive in the extremely hot hydrothermal vents of the deep sea to icefish that breed in the intense cold of the Southern Ocean off Antarctica. These life forms carry potentially valuable information in their genes, known as marine genetic resources.
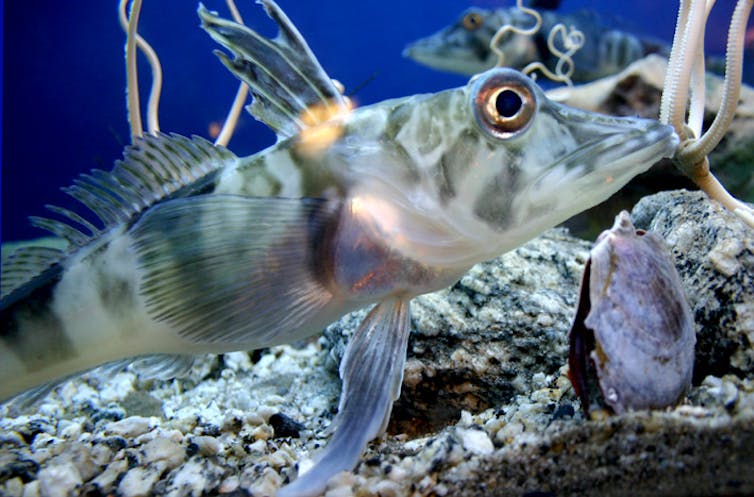

This new agreement provides developing states, whether coastal or landlocked, with rights to the benefits of marine genetic resources. It does not establish an administrative body comparable to that created for seabed mining, however. Instead, non-monetary benefits, such as access to samples and digital sequence information, will be shared and researchers from all countries will be able to study them for free.
Economic inequality between countries will still determine who can access these samples to a large extent, and sharing DNA sequencing data will be further complicated by the convention on biological diversity, another global treaty. The BBNJ agreement will establish a financial mechanism for sharing the monetary benefits of marine genetic resources, though experts involved in the negotiations are still parsing what it will eventually look like.
The best hope for robust marine protected areas and equitable use of marine genetic resources lies in rapid implementation of the BBNJ agreement. But making it effective will depend on how its provisions are interpreted in each country and what rules of procedure are established. In many ways, the hard work is beginning.
Although areas beyond national jurisdiction are remote for most people they generate the air you breathe, the food you eat and moderate the climate. Life exists throughout the ocean, from the surface to the seabed. Ensuring it benefits everyone living today, as well as future generations, will depend on this next phase of implementing the historic treaty.

Don’t have time to read about climate change as much as you’d like?
Get a weekly roundup in your inbox instead. Every Wednesday, The Conversation’s environment editor writes Imagine, a short email that goes a little deeper into just one climate issue. Join the 10,000+ readers who’ve subscribed so far.
Cymie Payne is affiliated with the International Union for the Conservation of Nature (IUCN).
Robert Blasiak is funded in part by the Gordon and Betty Moore Foundation, David and Lucile Packard Foundation and Walton Family Foundation and has contributed in an unpaid capacity to the work of the United Nations Global Compact.
This article was originally published on The Conversation. Read the original article.