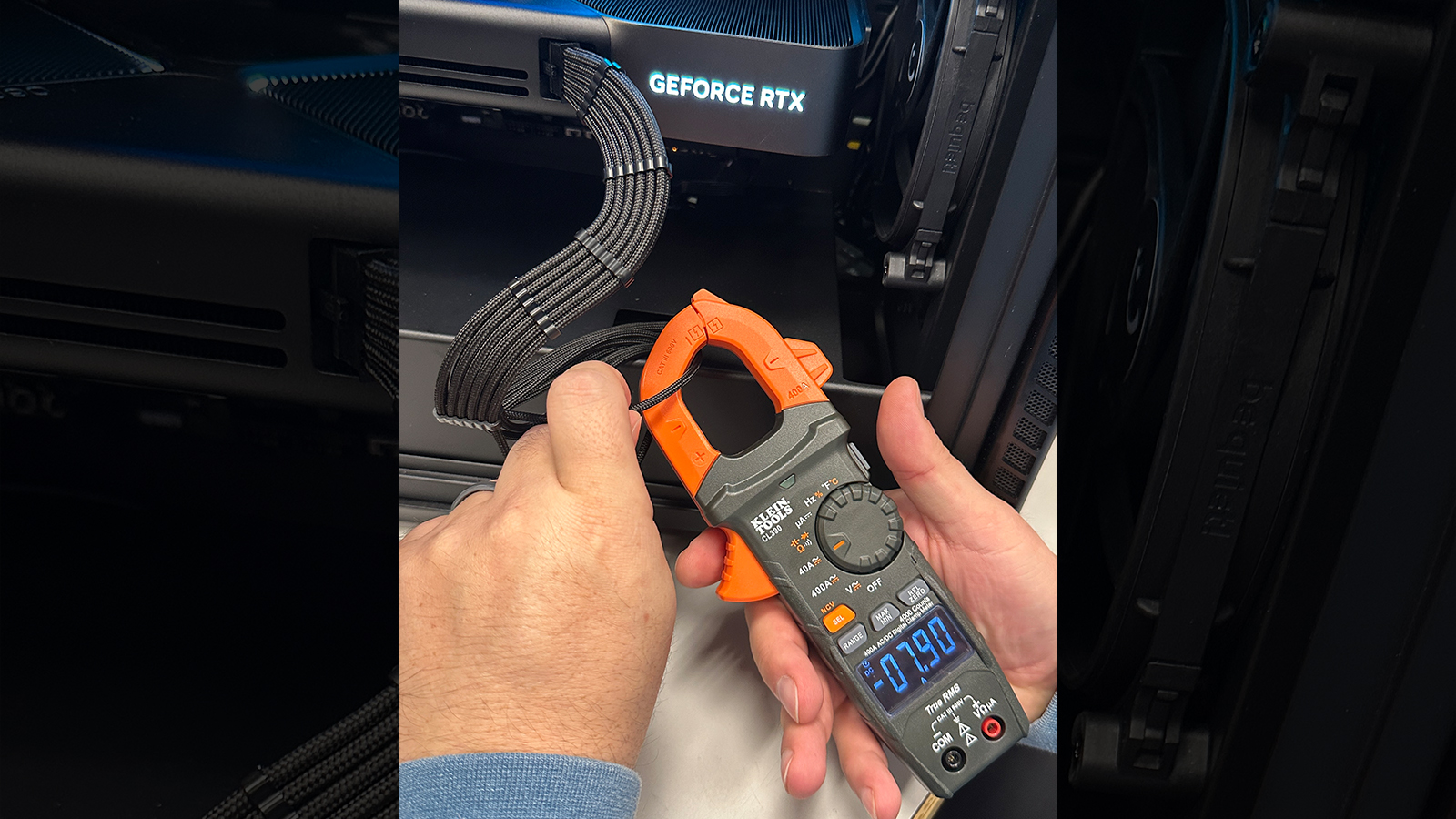
PC integrator Falcon Northwest said on X that it could not replicate the melting RTX 5090 FE power connector issue, even after testing multiple RTX 5090 Founders Edition builds using different power supplies and cable types. It has even run several days of “closed chassis burn-in” and found that all temperatures and amperages stayed within their nominal range.
Popular YouTuber Der8auer had one of the cables of his RTX 5090 GPU overheat to 150 degrees Celsius when it was found to be drawing a current of 22 amps—more than double its 9.5-amp rating. This contradicts what Nvidia assured us, saying that the melting cable incidents with the RTX 4090s are unlikely to happen now.
However, this doesn’t mean that the overheating issue doesn't occur at all. One X user pointed out that Der8auer had connected and disconnected the cable. In contrast, Falcon Northwest would likely not have done that if they had tested customer units before shipment.
HUGE respect for @der8auer 's testing, but we're not seeing anything like his setup's results.We tested many 5090 Founder's builds with multiple PSU & cable types undergoing days of closed chassis burn-in.Temps (images in F) & amperages on all 12 wires are nominal. pic.twitter.com/oDPIUSjOOfFebruary 11, 2025
Another YouTuber, JayzTwoCents, said on X that the 12VHPWR cable on his RTX 5090 GPU was much warmer than the one he used in his RTX 4090. While the temperatures he recorded were still within spec, he wondered whether one cable pulling more power than the others would be a much more widespread issue.
One user theorized the problem could be with the cable or GPU connection, as the RTX 5090 FE’s right-angle connector combines six voltage wires into one single pin. Because of that, there’s no way for the GPU to distribute the voltage load evenly across all the pins. Since electrical current will always take the path of least resistance, imperfections in the connection or cable itself might have caused the overheating and subsequent melting. However, this is still just a theory that must be tested in lab conditions to ensure its validity.
The FE's right angle connector on the PCB combines all 6 voltage wires into one single pin. There's no way for the board itself to distribute the load across the 6 12V wires, current always takes the path of least Resistance. pic.twitter.com/CakKSlKLA6February 11, 2025
Some manufacturers have taken matters into their own hands to avoid a repeat of the melting RTX 5090 connector saga. MSI put yellow tips into its 16-pin power adapter to ensure PC builders knew when the connector was fully inserted into the GPU. Zotac implemented a Safety Light feature that indicates if the power cable is fully seated in the graphics cards and prevents it from turning on if not.
These efforts would likely solve the issue of melting connectors due to loose connections, especially on the GPU side. However, if the problem is the uneven splitting of electrical current causing one or more cables to overheat, we have a deeper issue that might require a rethink of how the RTX 5090 gets power from the power supply.