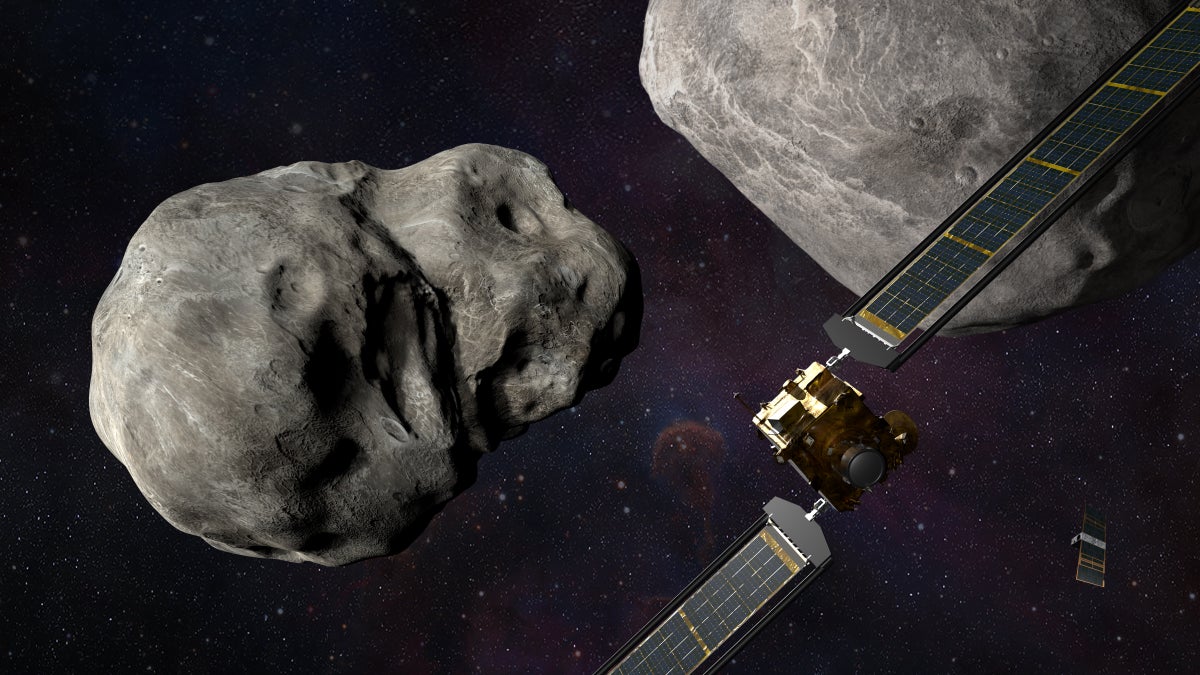
A spacecraft built by Nasa is set to intentionally crash into a small asteroid as part of a planetary protection test mission.
While this asteroid – named Dimorphos – poses no threat to Earth, the aim of the mission is to demonstrate that dangerous incoming rocks can be deflected by deliberately smashing into them.
The spacecraft, known as Double Asteroid Redirection Test (Dart), is expected to collide with the 170-metre wide (560ft) asteroid at 00:14 UK time on September 27.
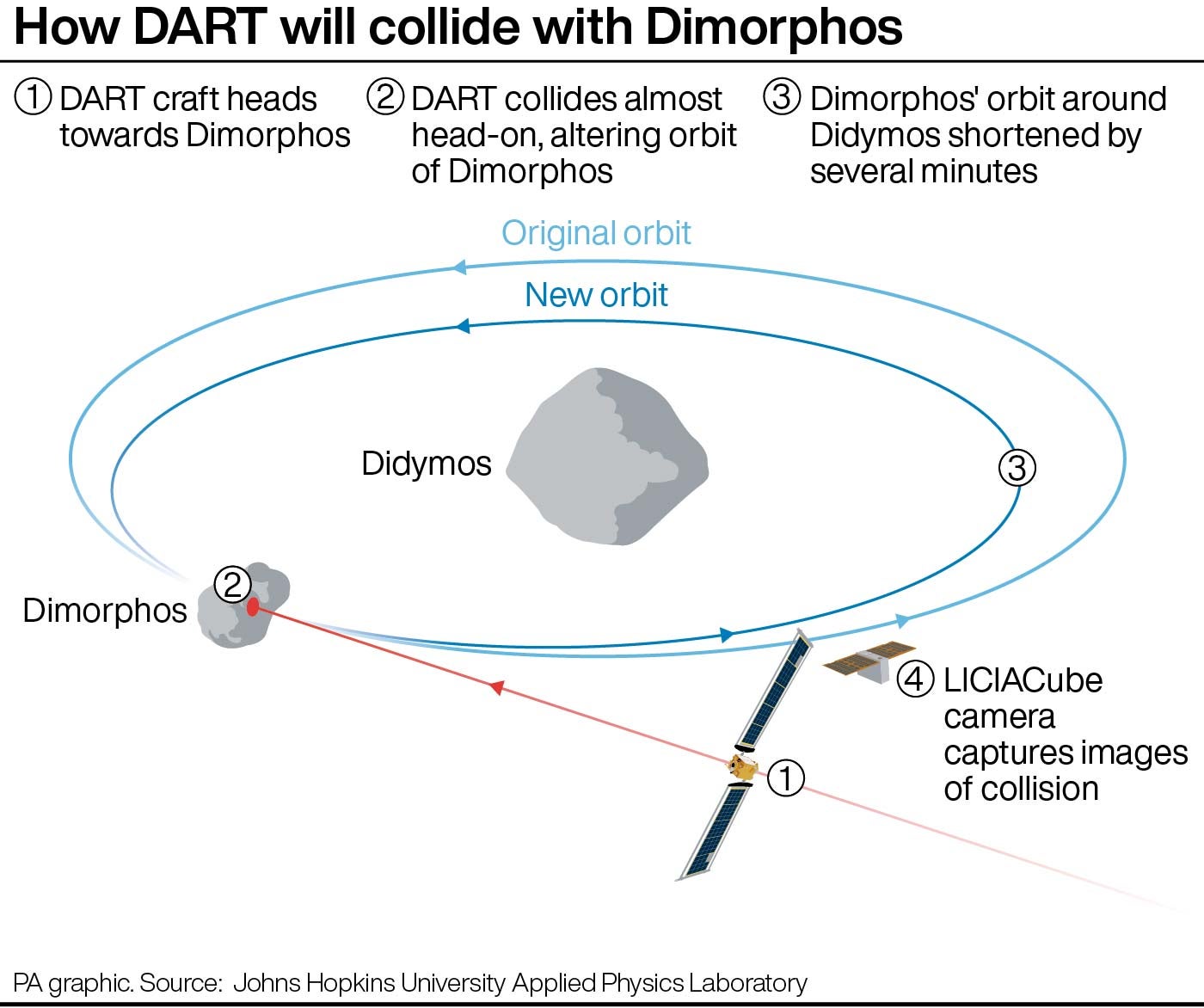
Dimorphos is part of a binary asteroid system and orbits Didymos, which takes around 11 hours and 55 minutes.
But astronomers at Nasa are hoping that Dart, while destroying itself in the process, will shorten this orbital period by about 10 minutes.
Nasa said: “Dart’s target asteroid is not a threat to Earth but is the perfect testing ground to see if this method of asteroid deflection – known as the kinetic impactor technique – would be a viable way to protect our planet if an asteroid on a collision course with Earth were discovered in the future.”
There currently somewhere around 27,000 asteroids in near-Earth orbit.
Rocks that are 140 metres (460ft) and larger in size and come nearer than 4.7 million miles (7.5 million km) during orbit are classed as potentially hazardous asteroids (PHAs).
The Dart mission will be the first ever full-scale demonstration of asteroid deflection technology.
The spacecraft recently captured its first images of Didymos and Dimorphos using an onboard instrument, known as the Didymos Reconnaissance and Asteroid Camera for Optical navigation (Draco).
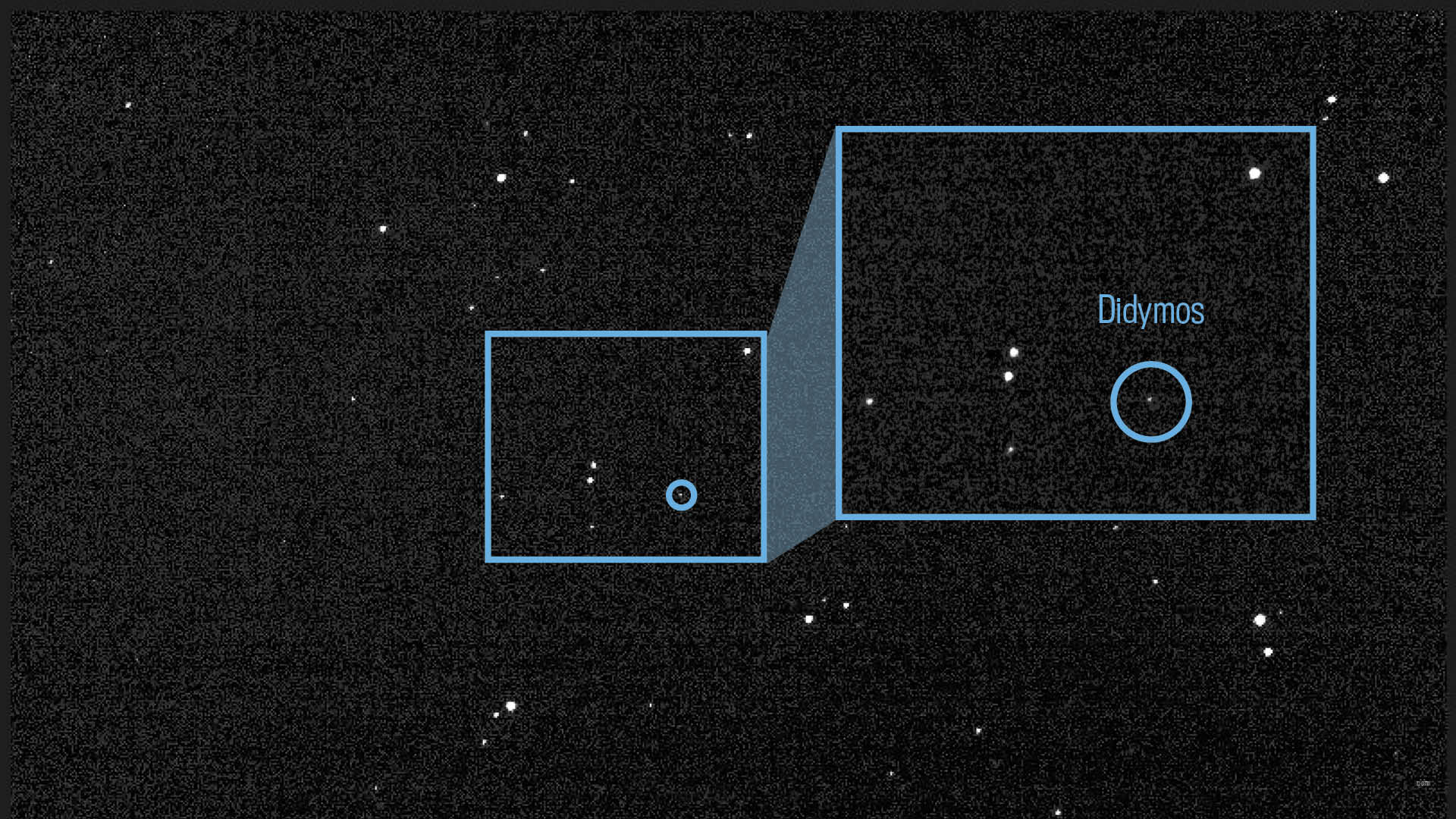
It was about 20 million miles (32 million km) away from the asteroid system when it took the photos in July.
It has taken 10 months for Dart to come close to Dimorphous after launching last November on SpaceX’s Falcon 9 rocket.
The asteroids will be around 6.8 million miles (11 million kilometres) from Earth when the collision happens.
Dart will accelerate at about 15,000 miles per hour (24,140 kilometres per hour) before colliding with Dimorphos.
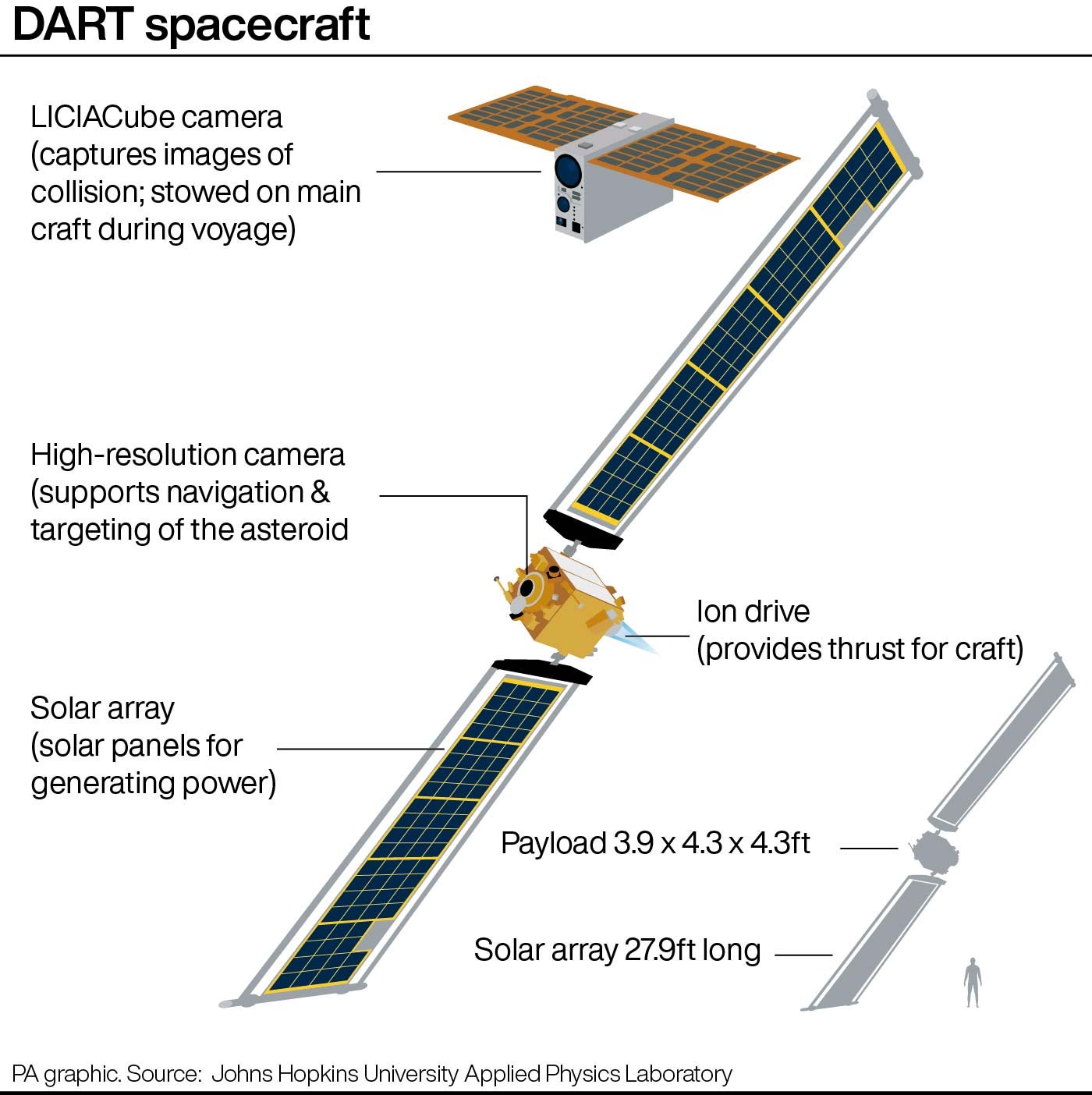
This collision will be recorded by a briefcase-sized satellite known as the Light Italian CubeSat for Imaging of Asteroids (LICIACube), which was provided by the Italian Space Agency.
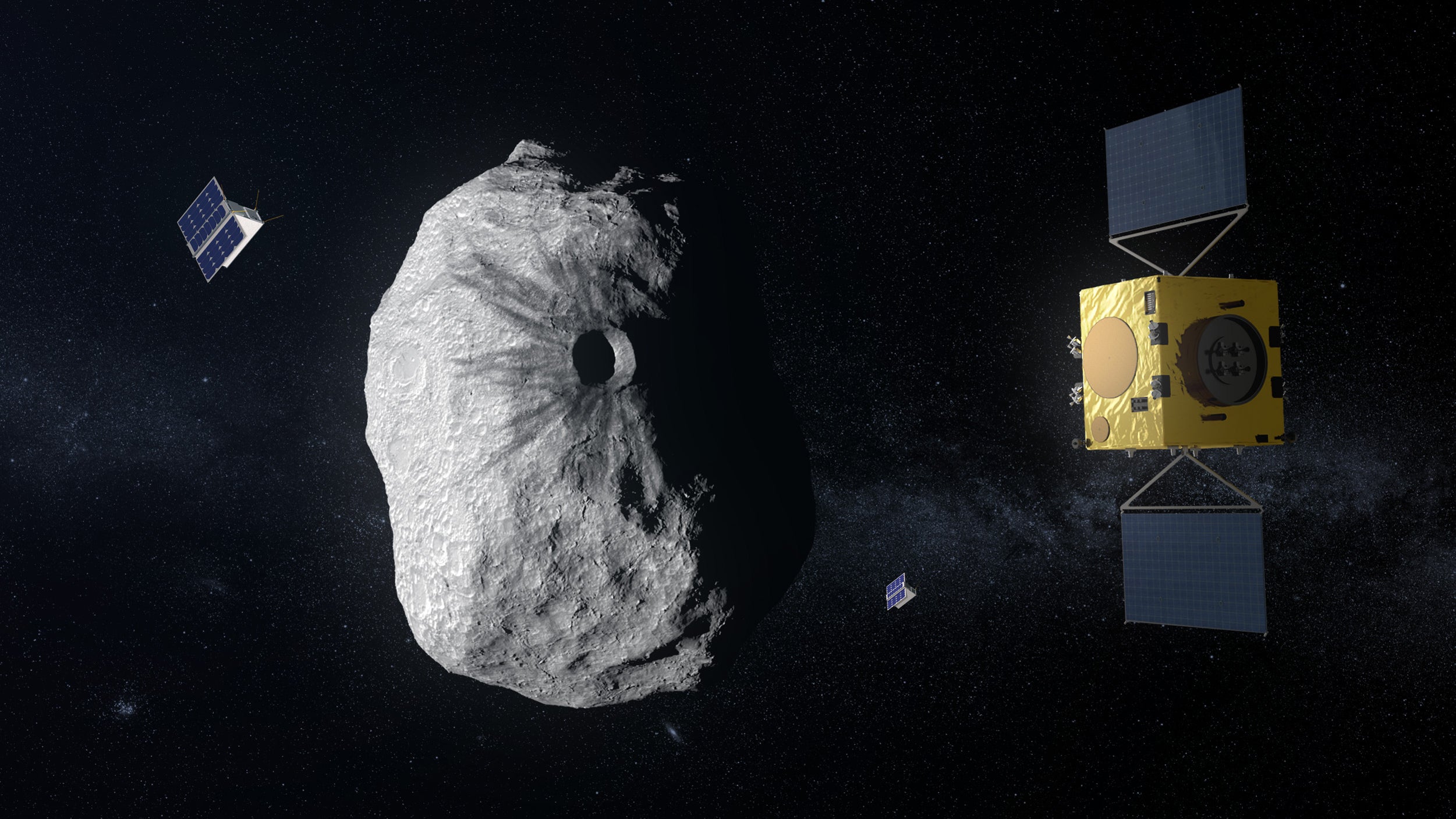

LICIACube, which weighs just 14 kg (31 lbs), hitched a ride with Dart into deep space before recently separating from the spacecraft in a final farewell.
In 2024, the European Space Agency (ESA) will launch its Hera spacecraft, which will go on a two-year journey to the asteroid system to gather information in the aftermath of the crash.
ESA said: “By the time Hera reaches Didymos, in 2026, Dimorphos will have achieved historic significance: the first object in the Solar System to have its orbit shifted by human effort in a measurable way.”







