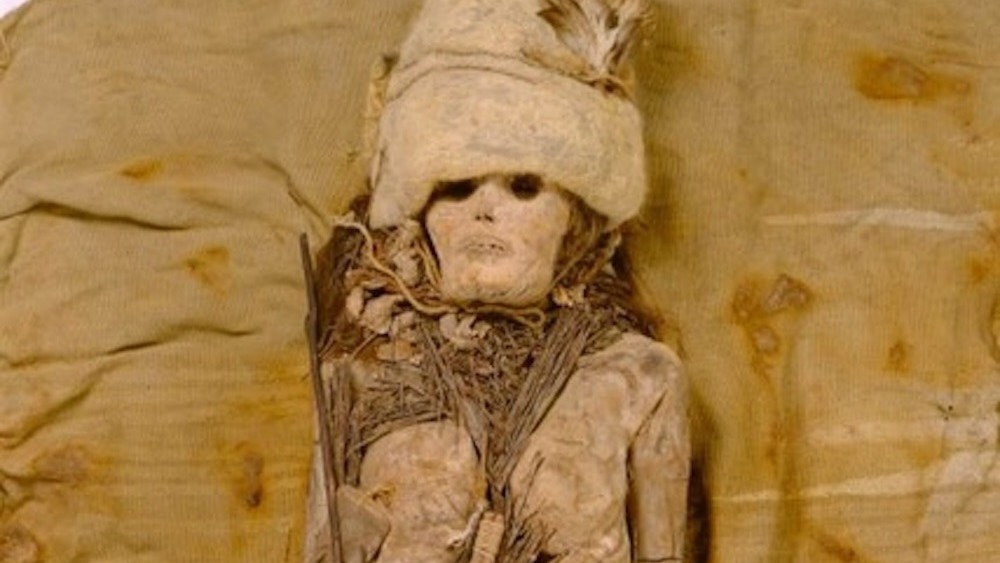
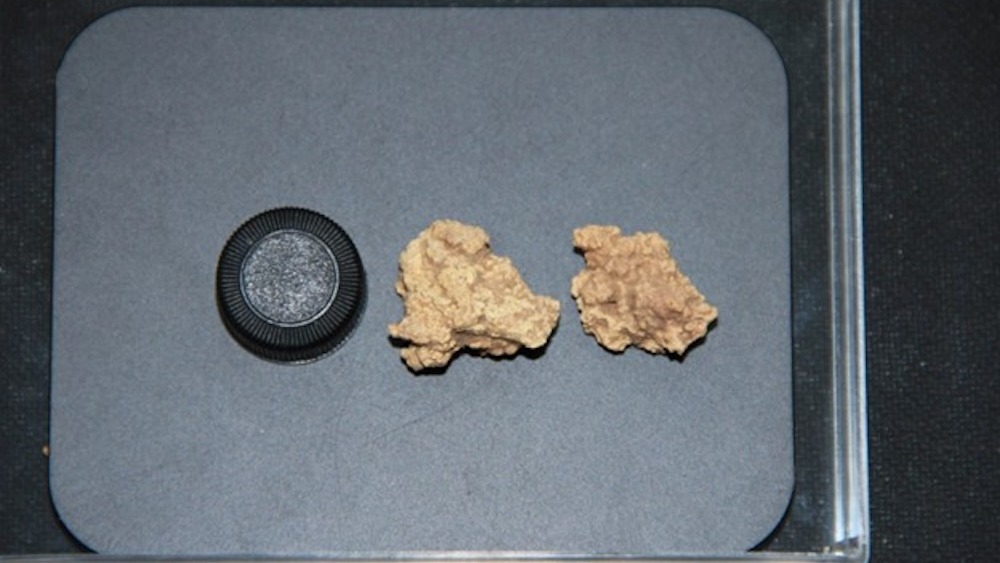
A mysterious white substance smeared on the heads and necks of 3,600-year-old mummies in China is the world's oldest cheese.
Researchers initially discovered the enigmatic material smudged on several of the mummies buried at the Xiaohe Cemetery in northwestern China's Tarim Basin about two decades ago. Now, DNA tests have revealed that the mystery goo was kefir cheese, a probiotic soft cheese, and that it was produced using cow and goat cheeses thousands of years ago, according to a study published Wednesday (Sept. 25) in the journal Cell.
The cheese contained several bacterial and fungal species, including Lactobacillus kefiranofaciens and Pichia kudriavzevii, both of which are found in modern-day kefir grains. These grains are "symbiotic cultures" that consist of a mix of bacteria and yeast, which ferment milk into cheese, similar to a "sourdough starter," according to a statement.
"This is the oldest known cheese sample ever discovered in the world," study senior author Qiaomei Fu, a paleontologist at the Institute of Vertebrate Paleontology and Paleoanthropology at the Chinese Academy of Sciences in Beijing, said in the statement. "Food items like cheese are extremely difficult to preserve over thousands of years, making this a rare and valuable opportunity.
Related: Lavish 2,200-year-old tomb unearthed in China may be that of ancient king
Fu added that "studying the ancient cheese in great detail can help us better understand our ancestors' diet and culture."
The researchers also determined that the L. kefiranofaciens grains were closely related to similar ones originating from Tibet. By sequencing the bacterial genes, researchers could "track how probiotic bacteria evolved over the past 3,600 years," according to the statement.
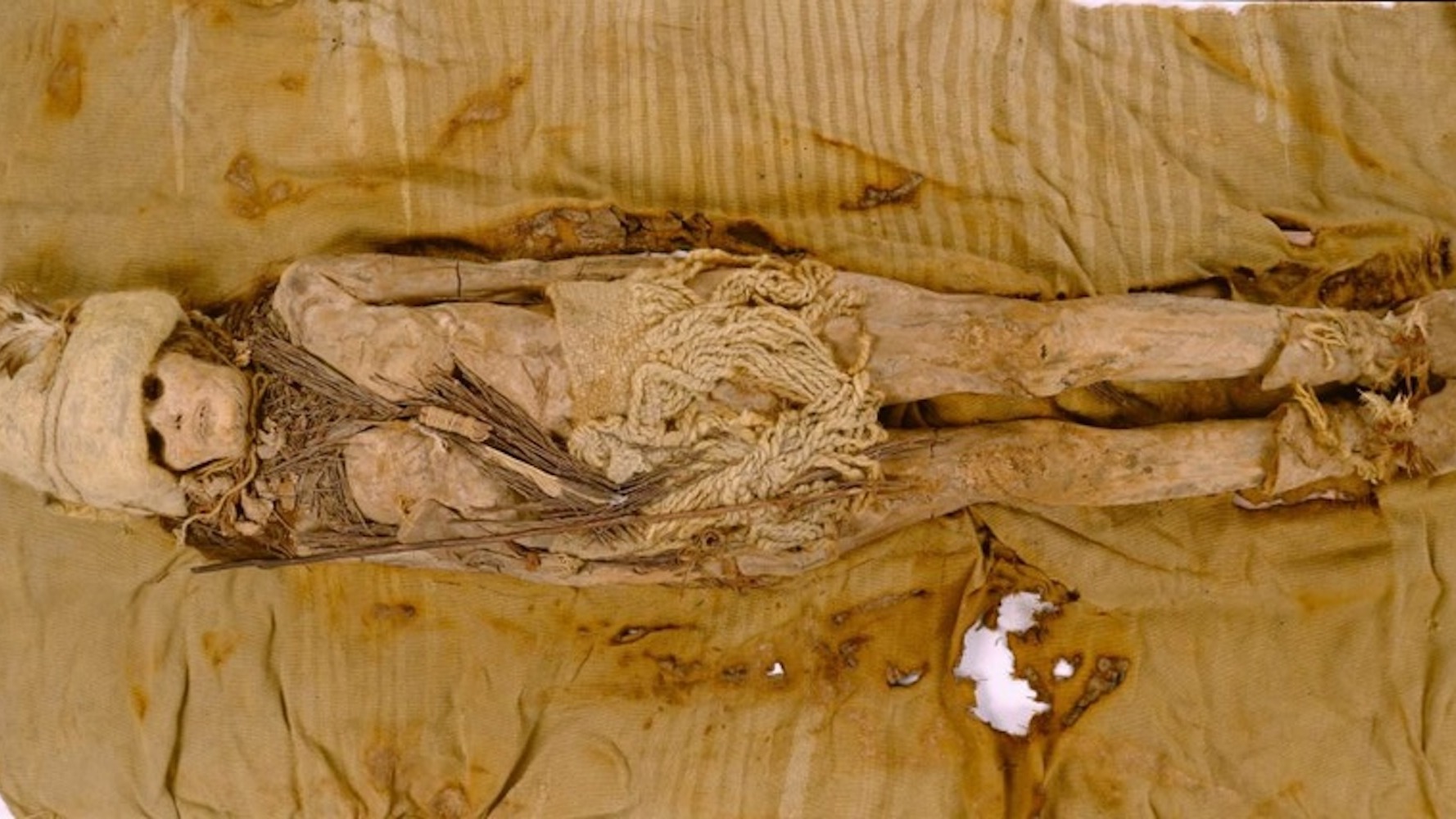

"Our observation suggests kefir culture has been maintained in Northwestern China's Xinjiang region since the Bronze Age," Fu said. "[We can] observe how a bacterium evolved over the past 3,000 years. Moreover, by examining dairy products, we've gained a clearer picture of ancient human life and their interactions with the world."
However, it remains unknown why these individuals were covered with cheese in the first place.