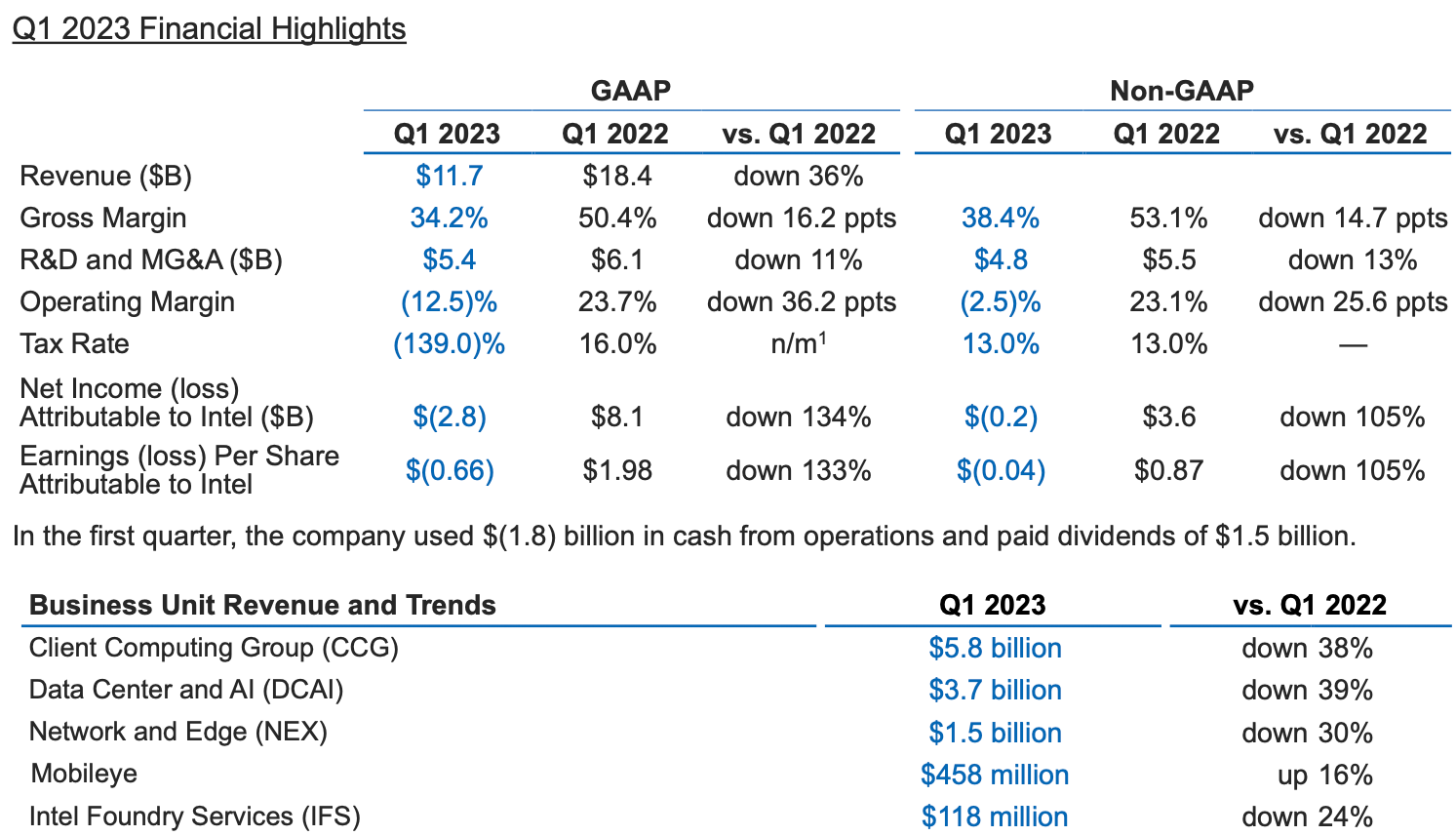
While Intel's sales beat its own expectations in the first quarter, the company on Thursday posted the largest loss in its history as its margins plunged to a new low over the last several years. The company expects its short-term results to continue suffering from weak demand for PCs and servers but remains optimistic about its prospects in the coming years once its next-generation products hit the market.
Biggest Loss Amid Low Margins
Intel's revenue for the first quarter dropped to $11.7 billion, which is $200 million higher than the company predicted back in January, but which is still down 36% year-over-year. The company lost $2.8 billion during the quarter as its gross margin declined to 38.4%. Despite posting the largest loss in its history, Intel paid $1.5 billion in dividends.
"While we remain cautious on the macroeconomic outlook, we are focused on what we can control as we deliver on IDM 2.0: driving consistent execution across process and product roadmaps and advancing our foundry business to best position us to capitalize on the $1 trillion market opportunity ahead," said Pat Gelsinger, Intel's chief executive.
Client PC and Mobile Eye Business Units Make Profits, Others Bleeding
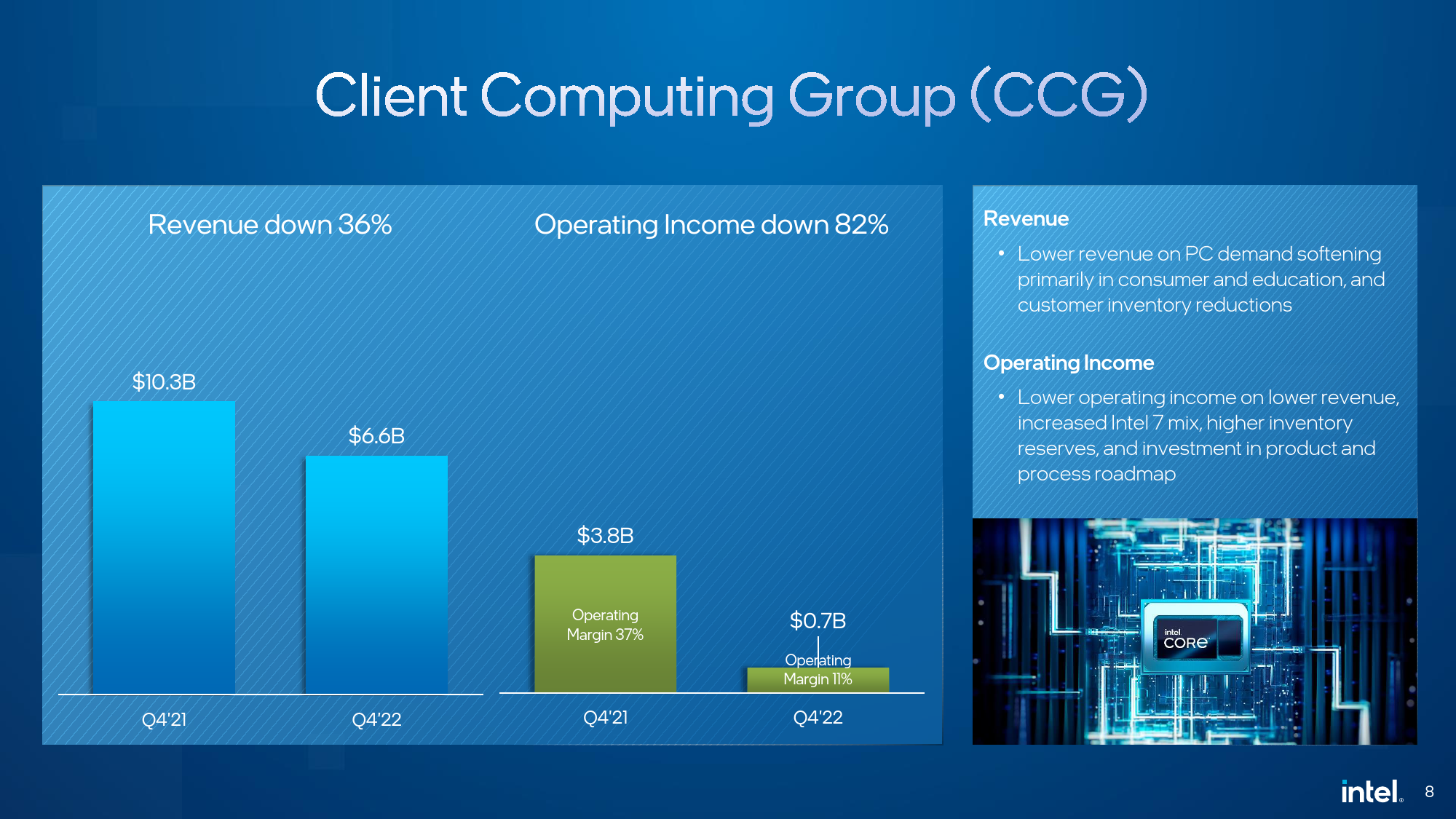
Intel's Client Computing Group (CCG) retained its position as the company's largest source of revenue, but in Q1 FY2023 it only earned $5.8 billion (down 38% YoY), a sharp decline from $9.3 billion in the same period of 2022. The company blames lower revenue on the declining total available market (TAM), continued inventory corrections by PC OEMs, and the increasing popularity of inexpensive CPUs as consumers remain cautious about their spending. CCG was still a profitable business unit for Intel as it generated $520 million, but its operating margin declined to 9%.
"We continue to see a challenging demand environment especially in our consumer and education segments," said David Zisner, chief financial officer of Intel, at the company's earnings call with financial analysts and investors. […] As discussed last quarter, we saw significant inventory burn at our customers in the period. While inventory levels remain elevated, we anticipate the market will be closer to equilibrium as we exit Q2. ASPs were down sequentially due to mix."
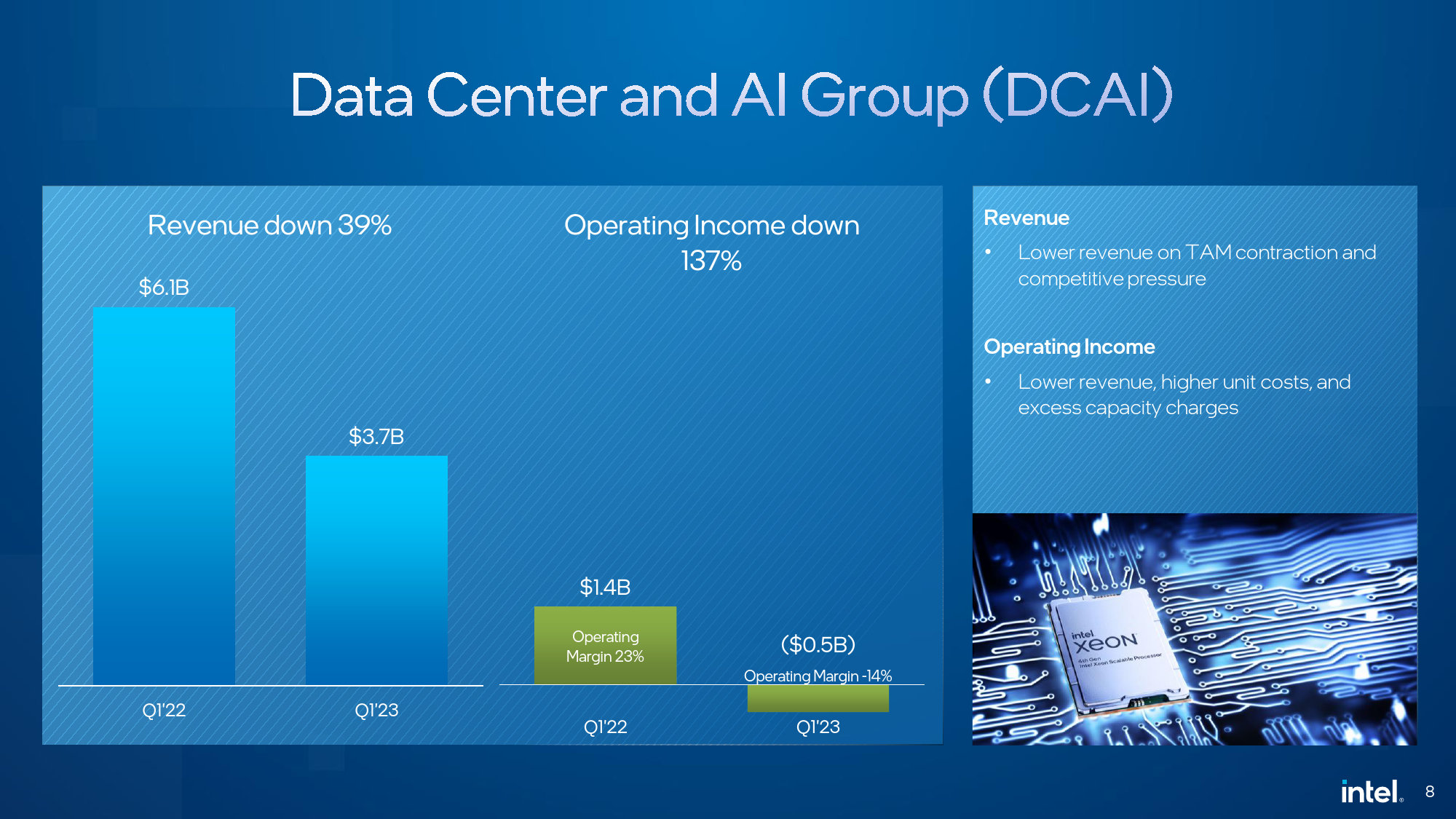
In Q1 2023, Intel's Datacenter and AI Group (DCAI) experienced a whopping 39% year-on-year decrease in sales of data center hardware, with revenue falling from $6.1 billion in Q2 2022 to $3.7 billion last quarter. The unit lost some $580 million as its operating margin collapsed to -14%.
Intel blames poor DCAI results on higher product costs, investment in next-generation products on new process nodes, the merge of the AXG business, and inventory reserves tied to its service system business which the company sold to Mitac earlier this month.
"We saw significant sequential and year-over-year TAM contraction across all CPU market segments and expect demand to remain soft in the second quarter," said Zisner. "We saw stable CPU market share in Q1 and are excited by the broad market ramp of our 4th Generation Xeon Scalable processor 'Sapphire Rapids.'
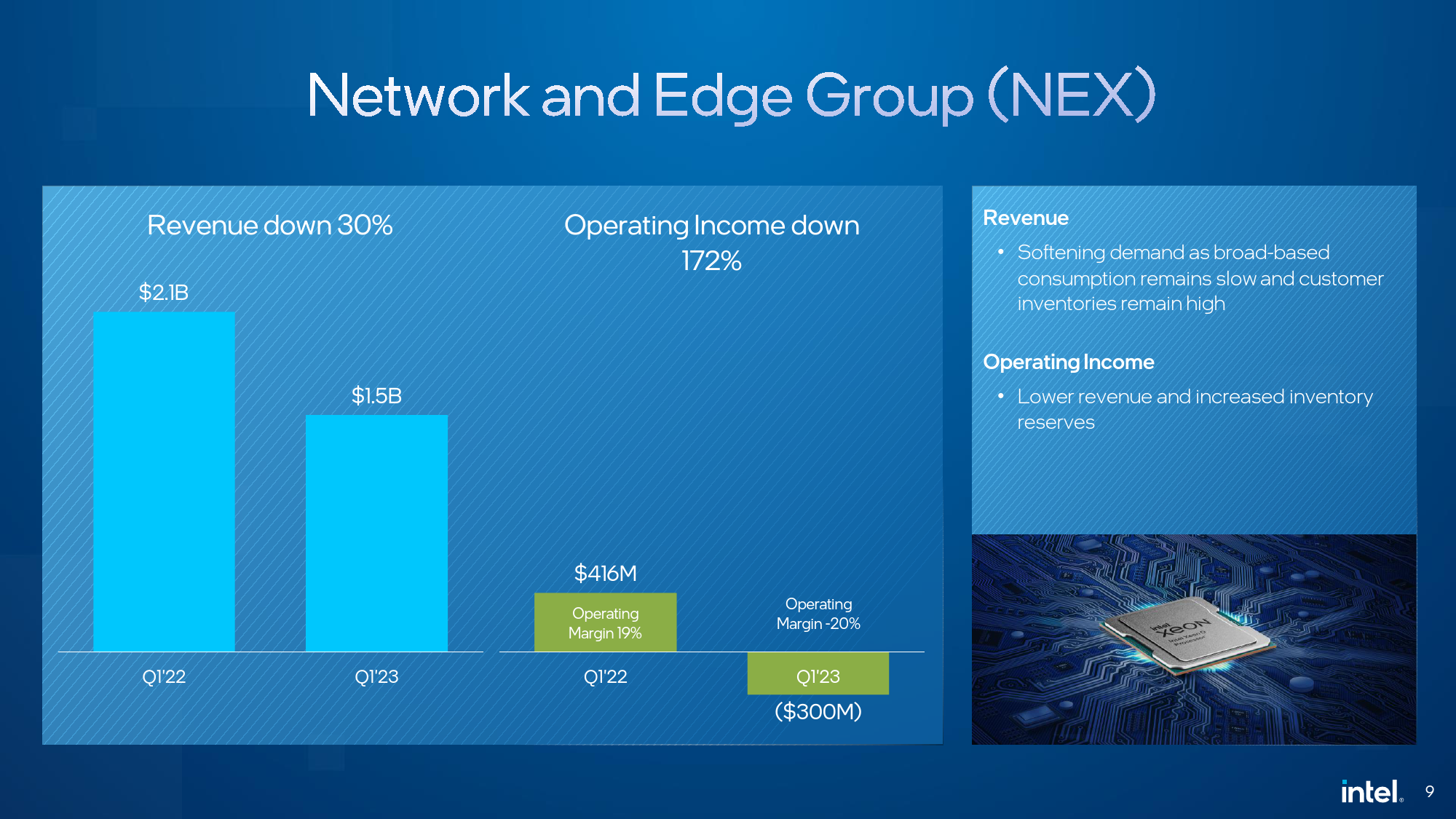
While Intel's Network and Edge Group (NEX) was able to sustain its revenue in recent quarters, in Q1, its sales dropped to $1.5 billion, and it lost $300 million. The gross margin of this business unit decreased to -20%.
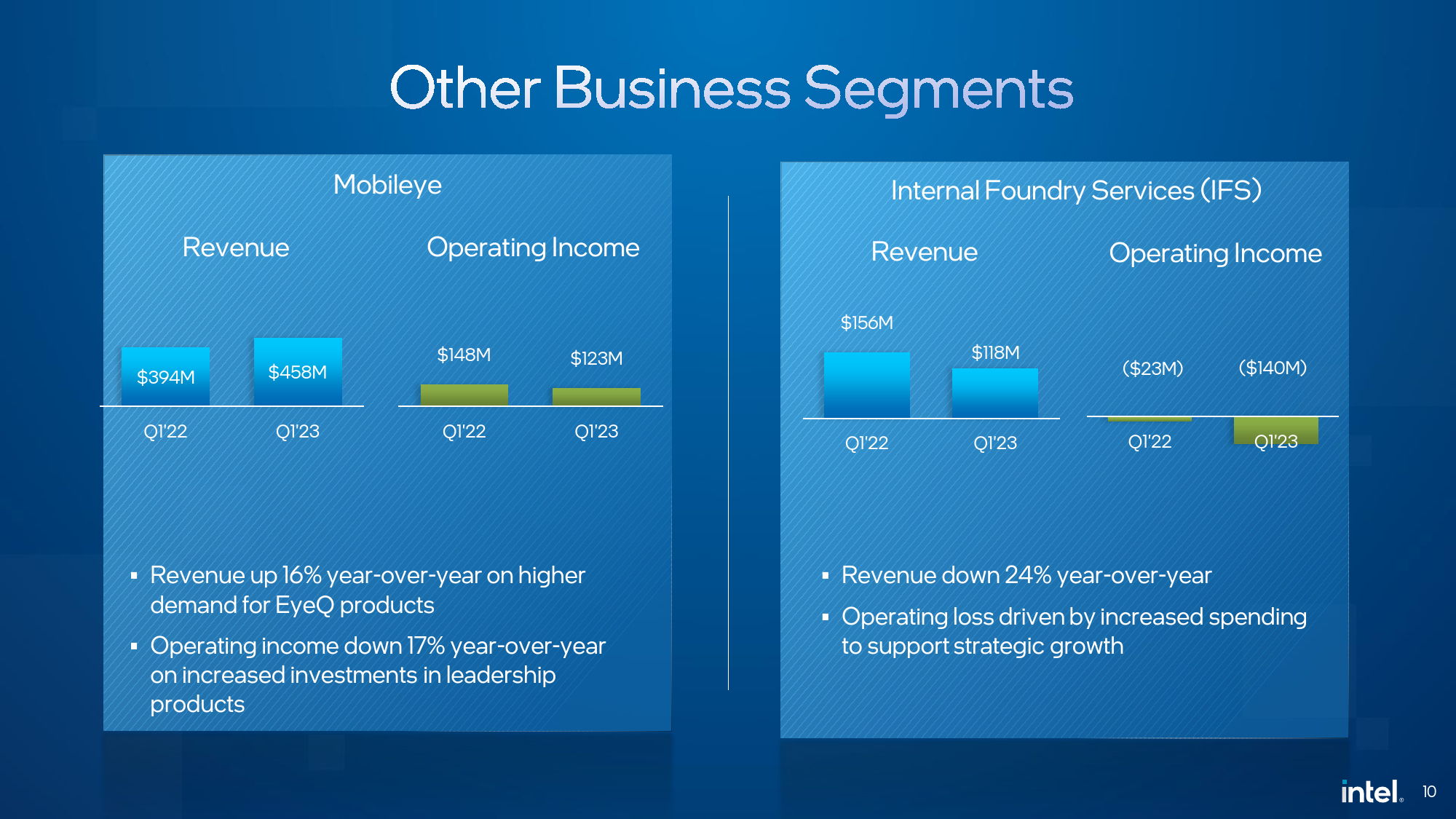
Having earned $458 million in sales in Q1 2023, Intel's Mobileye division was the company's only unit that demonstrated year-over-year revenue growth of 16%. Meanwhile, its operating income declined 17% YoY to $123 million as it increased investments in new products.
As for Intel Foundry Services business, it posted a 24% YoY revenue drop as its sales totaled $118 million, and lost $140 million, more than it earned, because of increasing fab startup costs. But while IFS revenue decreased in general, the company says that the unit posted a 67% sequential growth in packaging revenue. Meanwhile, Intel continues to work with the Chinese authorities to clear its acquisition of Tower Semiconductor in the second quarter.
Pessimistic Outlook for Q2
For the second quarter of FY2023, Intel forecasts its revenue to be between $11.5 billion and $12.5 billion, which represents a significant decline from its earnings in Q4 2022. Moreover, the company is predicting further gross margin decline to 33.2% as well as a loss of $0.62 per share.
While Intel's Q1 results are certainly nothing to brag about, the company remains optimistic as its revenue exceeded its own expectations, which means that the market performs better than it thought several months ago.
"We are encouraged by first quarter revenue and expect growth to improve sequentially through 2023," said Zisner. We are not satisfied with our financial results, and remain focused on what we can control our execution and the prioritization of our owners capital toward our long term goals. We are confident that as we deliver on our roadmap commitments, we will meet and exceed our customers' expectations for our products, and our owners' expectations for strong revenue growth and free cash flow generation."







