Clearwater Forest is turning out to be an entirely different beast. It will incorporate not only the latest goods from Intel Foundry—like Foveros Direct 3D, RibbonFET, PowerVia, and EMIB 3.5D—but also 3D cache, which Intel calls "Local Cache," per an interview with Intel's Florian Maislinger conducted by der8auer and Bens Hardware. And sadly, Team Blue has no plans to introduce AMD 3D V-cache-esque capabilities in its desktop CPUs.
Intel's next-generation E-Core, a Xeon-only series codenamed "Clearwater Forest," will leverage the flagship 18A node on which Pat Gelsinger has staked the entire company's future. Clearwater Forest is expected to use Atom Darkmont cores, succeeding the already-fast Skymont featured in Lunar Lake and Arrow Lake CPUs.
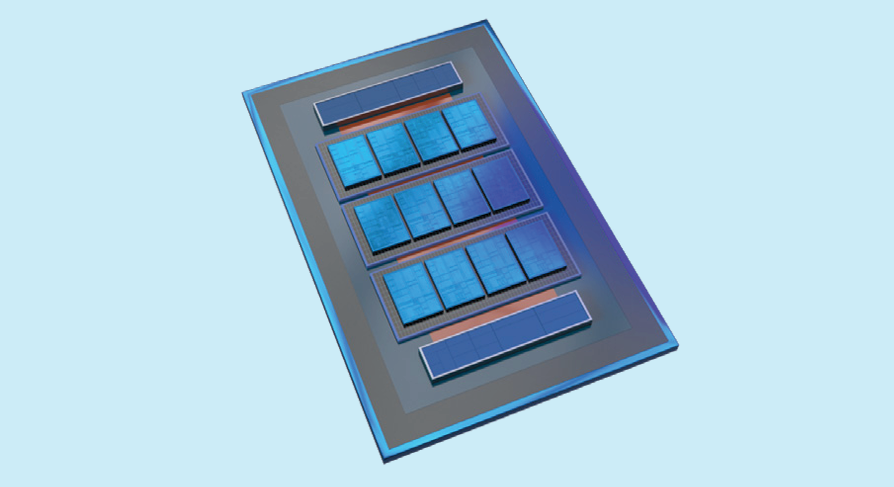
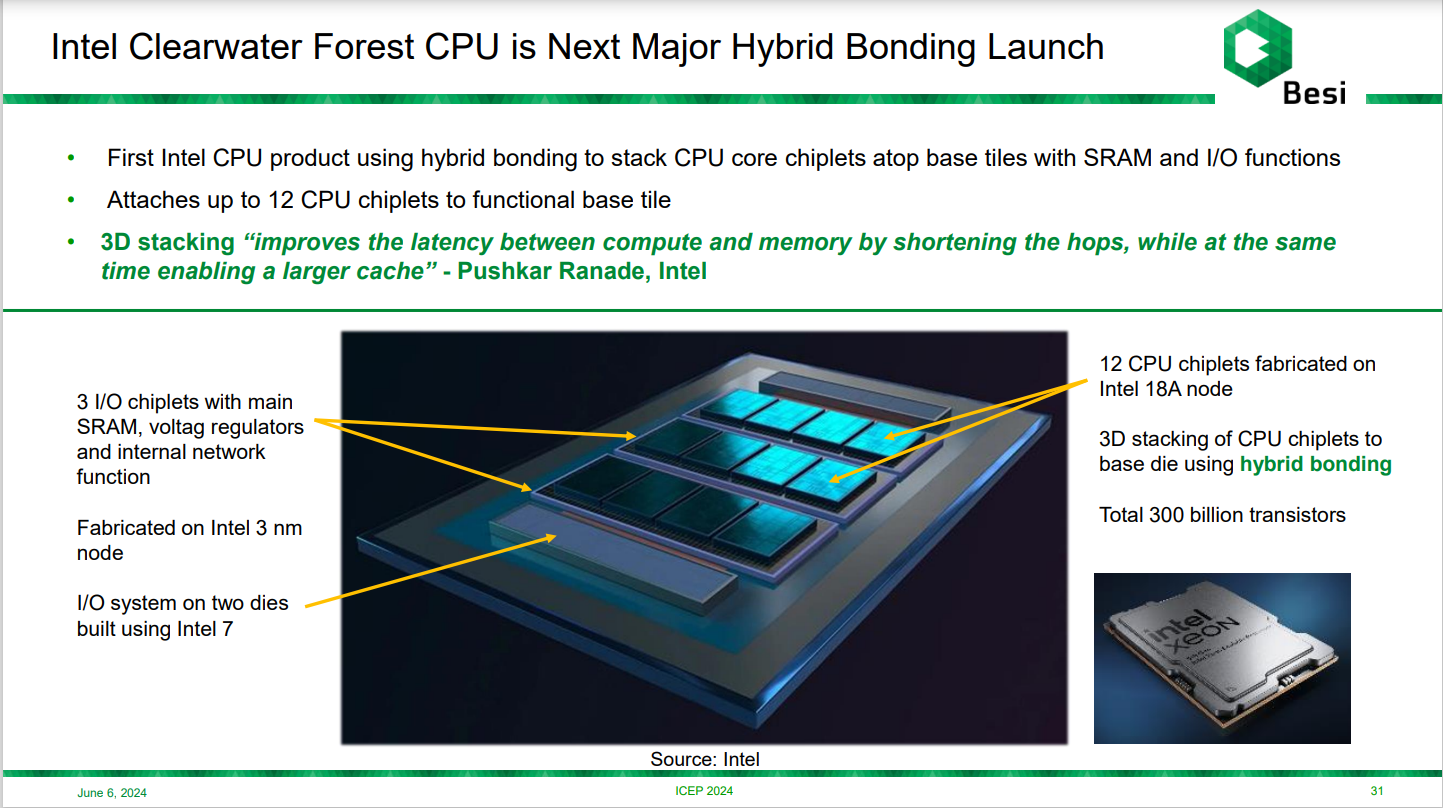
From an architectural and packaging standpoint, Clearwater Forest uses three "active" Base tiles - each hosting four CPU chiplets or tiles for 12 CPU tiles connected via Hybrid Bonding (Foveros 3D Direct). On the outskirts lie two I/O chiplets - connected to the CPU tiles through EMIB 3.5D. The entire package is expected to feature almost 300 billion transistors.
"For us, [gaming] is not an extremely large mass market," Maslinger said. "We sell a lot of CPUs that are not necessarily used for gaming. We still have [3D Stacked Cache] technologically. This means that next year there will be a CPU [Clearwater Forest] for the first time that has a cache tile, but not on desktop."
The interview confirms something we've missed: how the cache is structured. A quick look at Intel's white paper clarifies that the SRAM is packaged into the Base tile, which Intel calls "Local Cache." Until now, even with a disaggregated design, Intel has employed "Compute Tiles" featuring all cores alongside their respective caches linked via the Ring Bus. Clearwater Forest shifts the cache to the Base tile beneath the CPU chiplets, which now only hosts the CPU cores—and the entire assembly acts as a "Compute Module." This is unlike AMD's X3D approach, since the CPU chiplets are mutually dependent on the Base tile.
Afterward, Maislinger asserted that Intel's gaming market is relatively small, and designing an X3D competitor would be pointless if it could not be reused for servers. On a side note, AMD is also looking to introduce 3D V-Cache in Threadrippers.
The conversation shows that Intel (or rather Intel Foundry) does have the technology to combat AMD's 3D V-Cache: Clearwater Forest. But it isn't planning to make that technology mainstream anytime soon.