Intel announced this morning that it was acquiring Tower Semiconductor for $5.4B. To say Intel has been busy the past year with huge IDM 2.0 strategy moves would be an understatement. A mere eight days ago on February 7th, the company launched a $1B foundry innovation fund and an accelerator program with EDA, design, and IP companies, spanning multiple ISAs, including X86, Arm and RISC-V. Three weeks ago on January 21st, Intel announced the planting of two Ohio fabs with a committed $20B investment. Like I said, the announcements are coming fast and furious.
Net-net I think this is a very straightforward acquisition. Intel’s acquisition of Tower Semiconductor is complementary and enables IFS to become an end-to-end foundry, increasing its footprint and capability. I’m also wondering if Intel CEO Pat Gelsinger is setting up IFS as another spin-in possibility like Mobileye and there will be more to come in the future.
Please find the news below followed by my analysis and some thoughts on “what if”.
The news
The following are the deal highlights per the press release and Tower Semiconductor public documents:
- Price: $53 per share in cash
- Enterprise value: $5.4B
- Debt: None. Cash deal.
- Accretion: immediately accretive to non-GAAP EPS
- Expected close: 12 months
- Markets: high-end mobile, high-speed infrastructure, automotive, consumer, medical, industrial and aerospace and defense
- Technologies: RF, BCD (Bipolar-CMOS-DMOS), SOI (silicon on insulator), SiGe (silicon germanium), high performance SiGe, CMOS, MEMS
- Nodes: 250nm, 180nm, 110nm, 65nm
- Foundry locations: U.S., Israel, Italy, and Japan
- Capacity: 2M wafer starts per year
- Structure: IFS and Tower Semiconductor to become a fully integrated foundry business
A straightforward acquisition
To me, Intel’s acquisition of Tower Semiconductor is very straightforward.
When IFS announced its strategy last year, it said it wanted to be an end to end foundry, serving a diverse set of needs. IFS has incredible foundry capabilities based on what Intel needs for its own silicon. It has optimized its technologies and selected bleeding and leading-edge nodes to create the highest performance CPUs, GPUs, FPGAs, and SoCs in the digital domains. These technologies offer extreme compute performance and high leakage. Power draw is important, but performance is more important.
These technologies and nodes are not optimal, though, for lower power applications or analog RF (radio frequency) devices that are prevalent in low power mobile, IoT, power management, sensors, and many automotive applications.
Tower Semiconductor’s markets
Intel and Tower Semiconductor have very different markets. Tower Semiconductor’s business and capabilities to IFS becomes clearer when you look at the Q3 2021 breakdown of its markets:
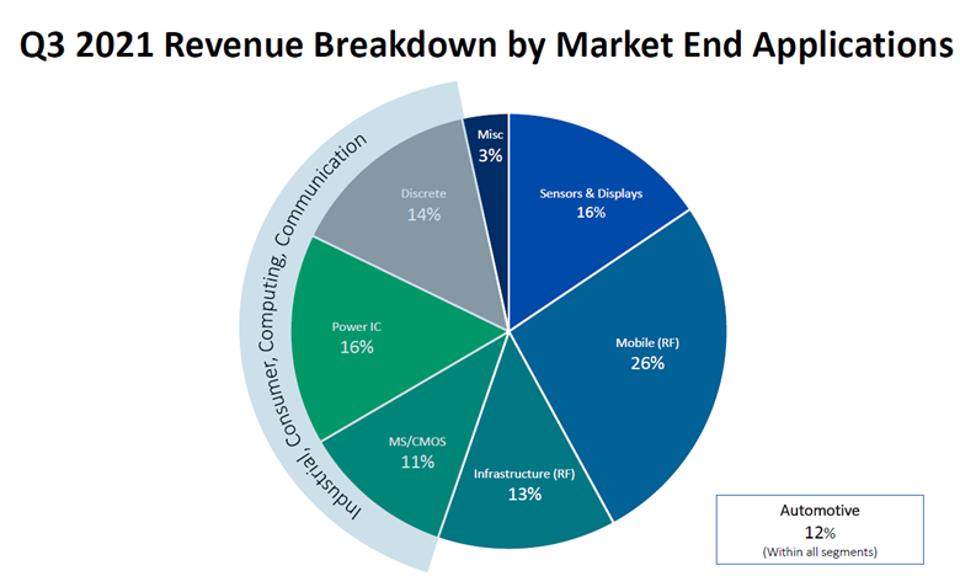
These markets are very different from Intel’s high-performance compute markets. 39% of Tower Semiconductor’s business is RF. Overall, think RF modules for 5G, Bluetooth, and Wi-Fi for PCs, smartphones, smartwatches, smart home devices, automotive and more. 12% of its business is automotive.
The way Tower Semiconductor segments its business units and drilldowns into its automotive business gives us another deeper look at its specialty technologies and nodes.
Analog BU
Its Analog BU is focused on technology for mobile comms, optical infrastructure, and power management. Its RF tech for mobile comms brings two specific technologies to bare, SOI (silicon on insulator) and SigE (Silicon germanium). RF SOI is targeted for RF switches, antenna tuners, and low-noise-amplifiers. RF SigE is for amplifiers for Wi-Fi, Bluetooth and IoT and mmWave for automotive radar and 5G wireless. Tower Semiconductor has capabilities not only for wireless, but for the highest speed optical infrastructure. It offers high performance SigE for 800gbps optical transceivers and silicon photonics with integrated optical, waveguides and modulators. The company offers two processes for power management. It offers 65nm BCD (Bipolar-CMOS-DMOS) for PMICs, load switches, DC-DC converters, LED drivers, motor drivers, battery management, and analog and digital controllers. And it offers 180nm BCD (Bipolar-CMOS-DMOS) for hybrid/EVs capabilities, motor controllers and drivers, LED headlights, and LiDAR. It also services highly efficient data centers and industrial power applications and gate drivers.
Sensors and Displays BU
Tower Semiconductor also has a Sensors and Displays BU which, unsurprisingly focuses on sensor and display technologies. It manufactures CMOS image sensors (CIS) for high-end photography, industrial machine vision, medical/dental x-ray, fingerprint sensors, 3D ToF (time of flight) facial recognition, AR and gaming. It also fabs non-imaging sensors that detect ionizing radiation, remote temperature, magnetic (TMR), UV radiation and gas. On the MEMS side, it builds devices like microphones, speakers, and accelerometers. Finally, the company manufactures displays with micro-LED technology for TVs, laptop displays, and VR headsets.
Automotive vertical
Tower Semiconductor also gives insights into what it vertically offers markets like automotive. The company manufactures power management platforms for motor drivers, DC-DC converters, battery management ICs, PMICs, load switches, voltage regulators, and LED drivers. It builds CMOS image sensors for LiDAR, visual and thermal imaging. And finally, the company manufactures device using high performance SigE, specifically for radar, V2X, and 5G applications.
Tower Semiconductor’s mature nodes
Tower Semiconductor does not require leading or bleeding edge nodes like Intel uses.
In Q3 2021, here’s how Tower Semiconductor broke down its nodes:
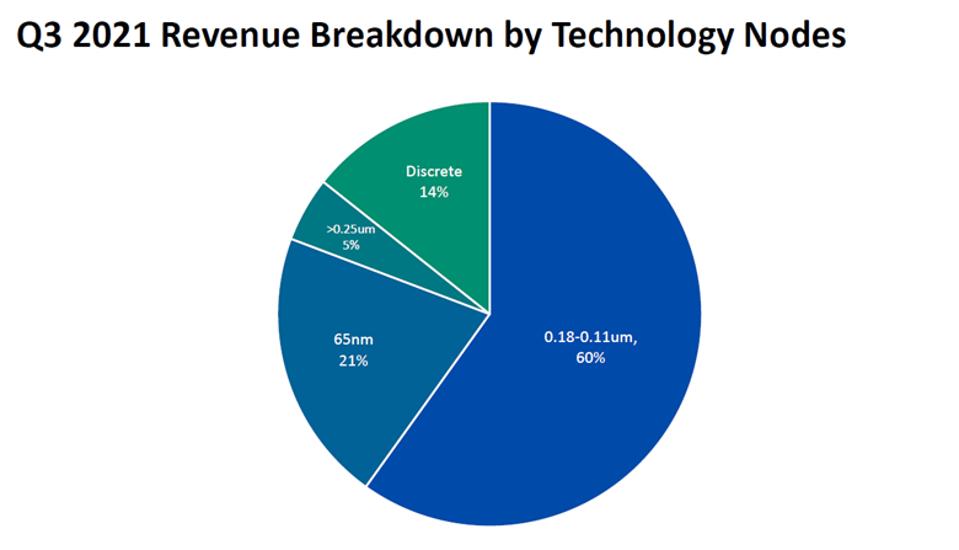
As you can see, these nodes are very different from what Intel is driving for with its bleeding and leading-edge nodes like Intel 10nm, 7, 4, 3 and 20A. We are talking orders of magnitude smaller not to mention sophistication differences with transistor technologies like RibbonFET and PowerVia and multi-patterning EUV techniques.
Summary and Intel’s posture to Wall Street
This is a very straightforward acquisition. Intel’s acquisition of Tower Semiconductor enables IFS to become and end to end foundry, increasing its footprint and capability. It’s as simple as that.
I wouldn’t limit Tower Semiconductor’s capabilities in the current footprint of its fabs. Tower Semiconductor had challenges getting capex to expand and I believe this limited Tower Semiconductor to smaller customers than if it had more capacity. I could see IFS placing Tower Semiconductor technologies inside of its new Ohio fabs. Why not?
I had a final thought on Intel’s posture to the investment community.
Intel already announced that it was going to do an internal spin of Mobileye. This is smart as the market values pure-play auto tech companies like Tesla and Rivian at astronomical values. Mobileye is the pioneer and market share leader in ADAS. This makes a lot of sense.
Now what if Intel takes Tower Semiconductor Semi, combined with IFS, made some investments in it and then spun that? TSMC has a $600B market cap and a 29 PE ratio. Intel is valued at around $200B at a PE ration less that 10.
I think this would be a great time for Intel to look at this. CEO Pat Gelsinger has experience in this with the VMware spin and I’d be shocked if he isn’t thinking about unlocking the value of the company’s assets to get their fair share. Intel would have 6 very distinct business units that are inter-related, but also strong in their own right.
As a tech industry analyst, I don’t do a lot of speculation so consider that a forecast.







