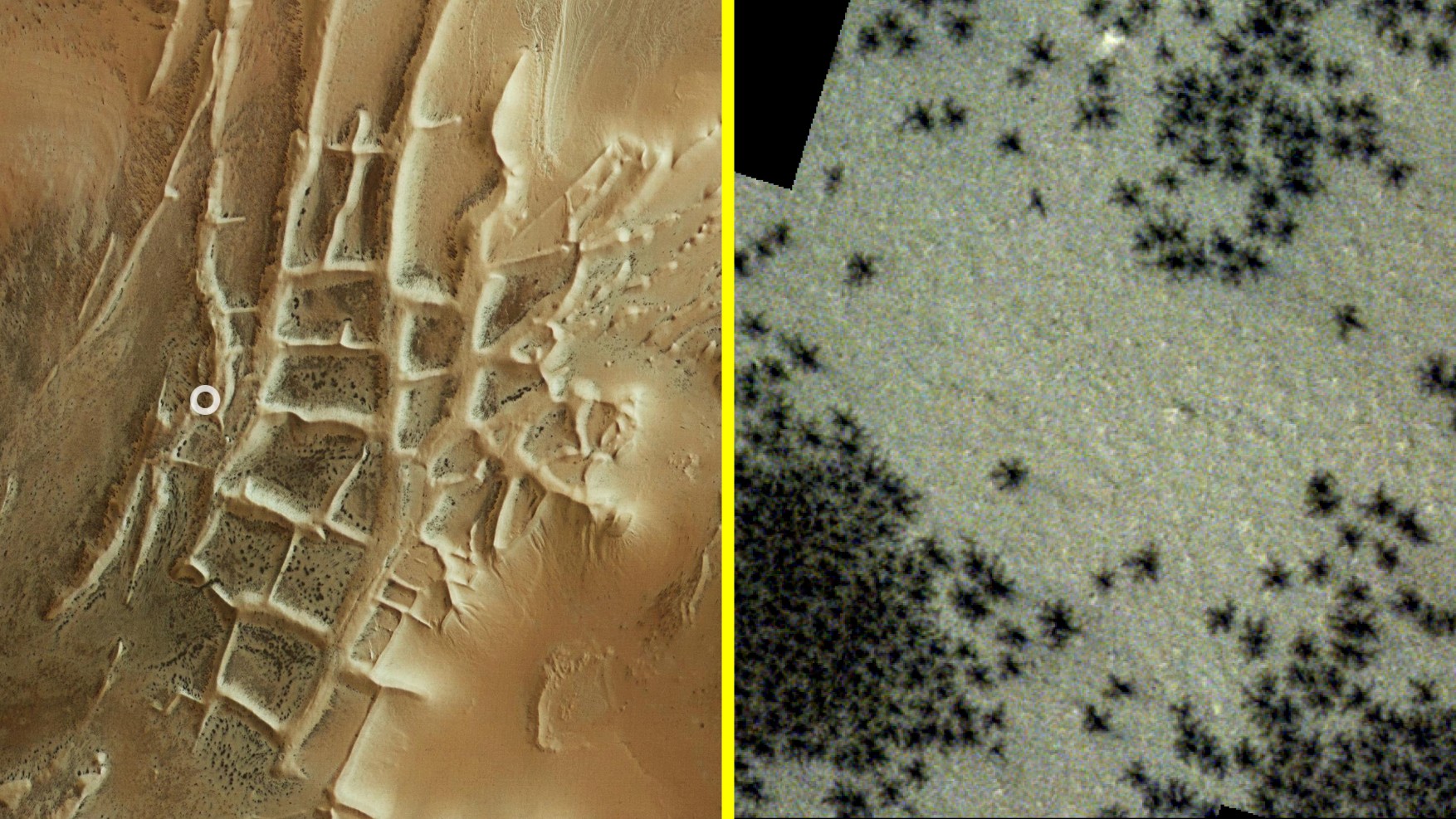
Arachnophobes need not fear: A new European Space Agency (ESA) image of Martian "spiders" actually shows seasonal eruptions of carbon dioxide gas on the Red Planet.
The dark, spindly formations were spotted in a formation known as Inca City in Mars' southern polar region. Images taken by ESA's Mars Express orbiter and ExoMars Trace Gas Orbiter show dark clusters of dots that appear to have teeny little legs, not unlike baby spiderlings huddling together.
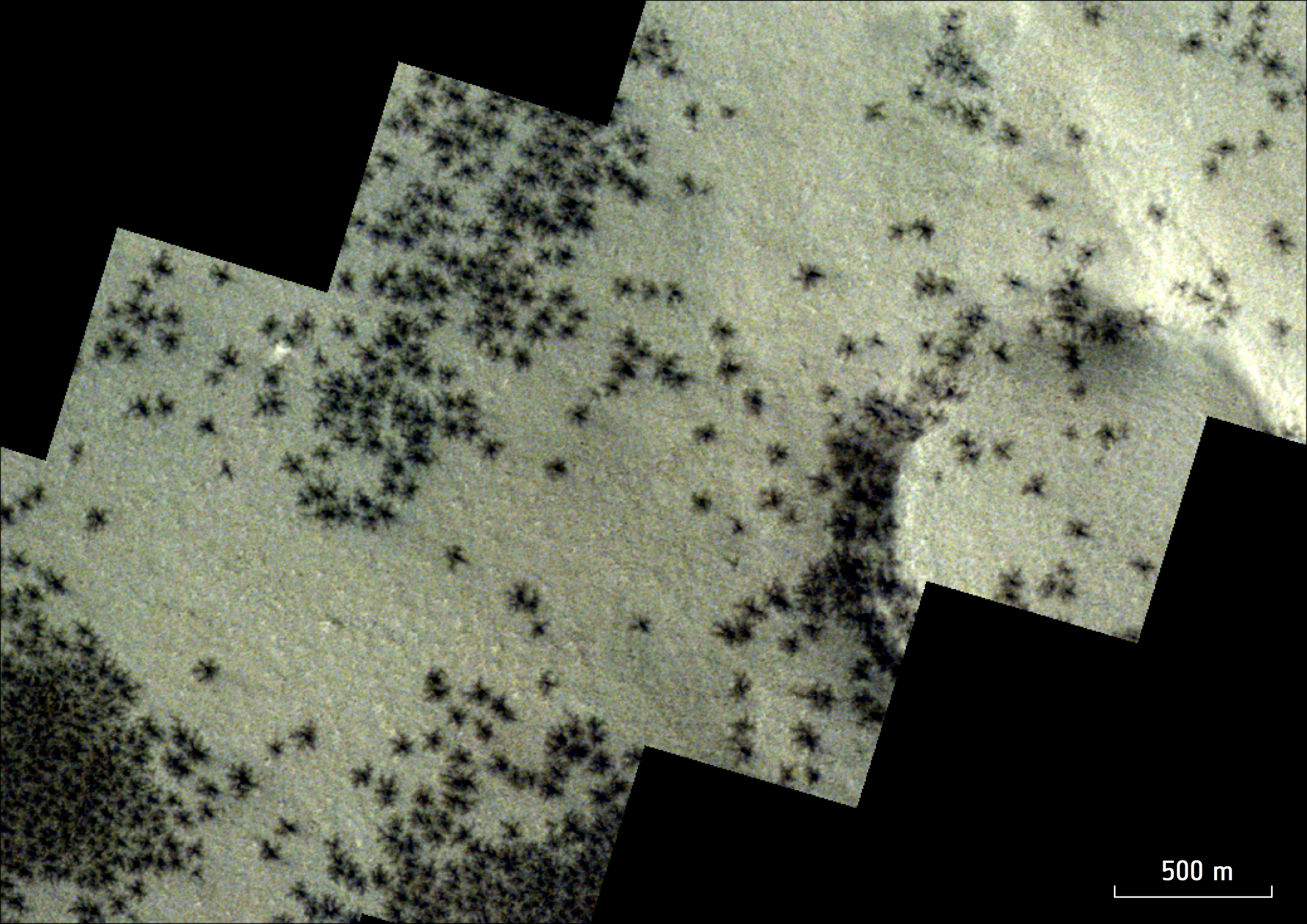
The formations are actually channels of gas measuring 0.03 to 0.6 miles (45 meters to 1 kilometer) across. They originate when the weather starts to warm in the southern hemisphere during Martian spring, melting layers of carbon dioxide ice. The warmth causes the lowest layers of ice to turn to gas, or sublimate.
As the gas expands and rises, it explodes out of the overlying ice layers, carrying with it dark dust from the solid surface. This dust geysers out of the ice before showering down onto the top layer, creating the cracked, spidery pattern seen here. In some places, the geysers burst through ice up to 3.3 feet (1 m) thick, according to ESA.
Related: Single enormous object left 2 billion craters on Mars, scientists discover
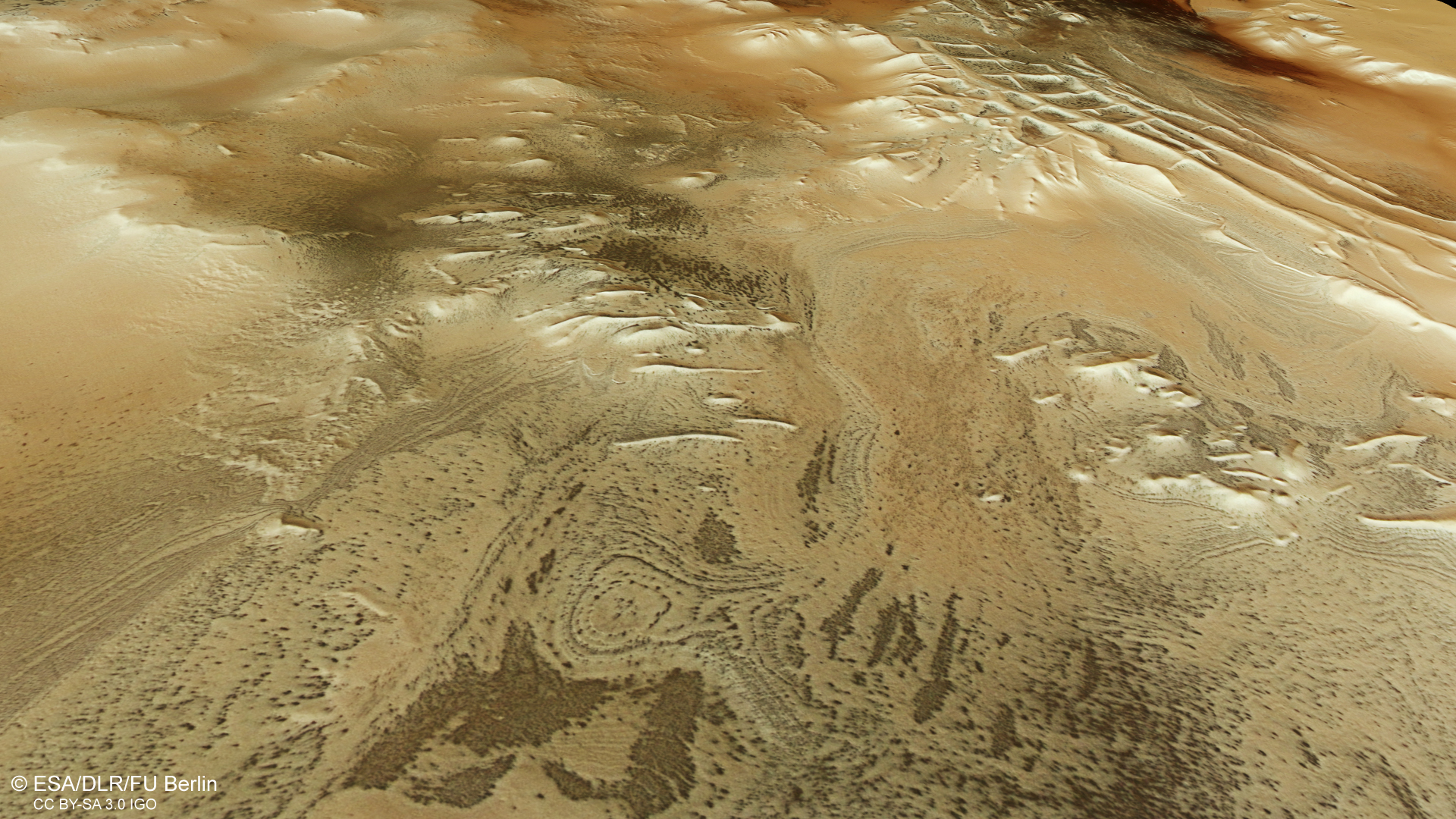
Inca City is also known as Angustus Labyrinthus. It's named for its linear, ruin-like ridgelines, which were once thought to be petrified sand dunes or perhaps remnants of ancient Martian glaciers, which could have left high walls of sediment behind as they retreated.
In 2002, however, the Mars Orbiter revealed that Inca City is part of a circular feature approximately 53 miles (86 km) wide. This feature may be an old impact crater — suggesting that the geometric ridges may be magma intrusions that rose through the cracked, heated crust of Mars after it was hit by a renegade space rock. The crater would have then filled with sediment, which has since eroded, partially revealing the magma formations reminiscent of ancient ruins.







