In theory, the name of a chord should describe its content, especially if it differs from the root-3rd-5th of a standard major chord. In guitar circles, describing a chord as ‘G’ without any other information would usually mean a G major chord.
Once we get into minor chords (with a b3) and 5 chords – often called powerchords and which don’t have a 3rd at all – it’s necessary to include these extra details to make sure everyone is on the same page (sometimes literally!).
Just as ‘G’ is often slang for G major, other terms that refer to extended and/or altered chords have developed over time. C7, for instance, means a C major chord with a b7th (Bb).
C9 (see Example 3) contains the b7th plus the 9th (D), so there’s more going on than many may suspect. Cadd9 (see Example 4) on the other hand simply adds the 9th to an existing C major (or minor) chord.
I’ve included a few more commonly misunderstood chords in the examples.
Example 1. Dsus4
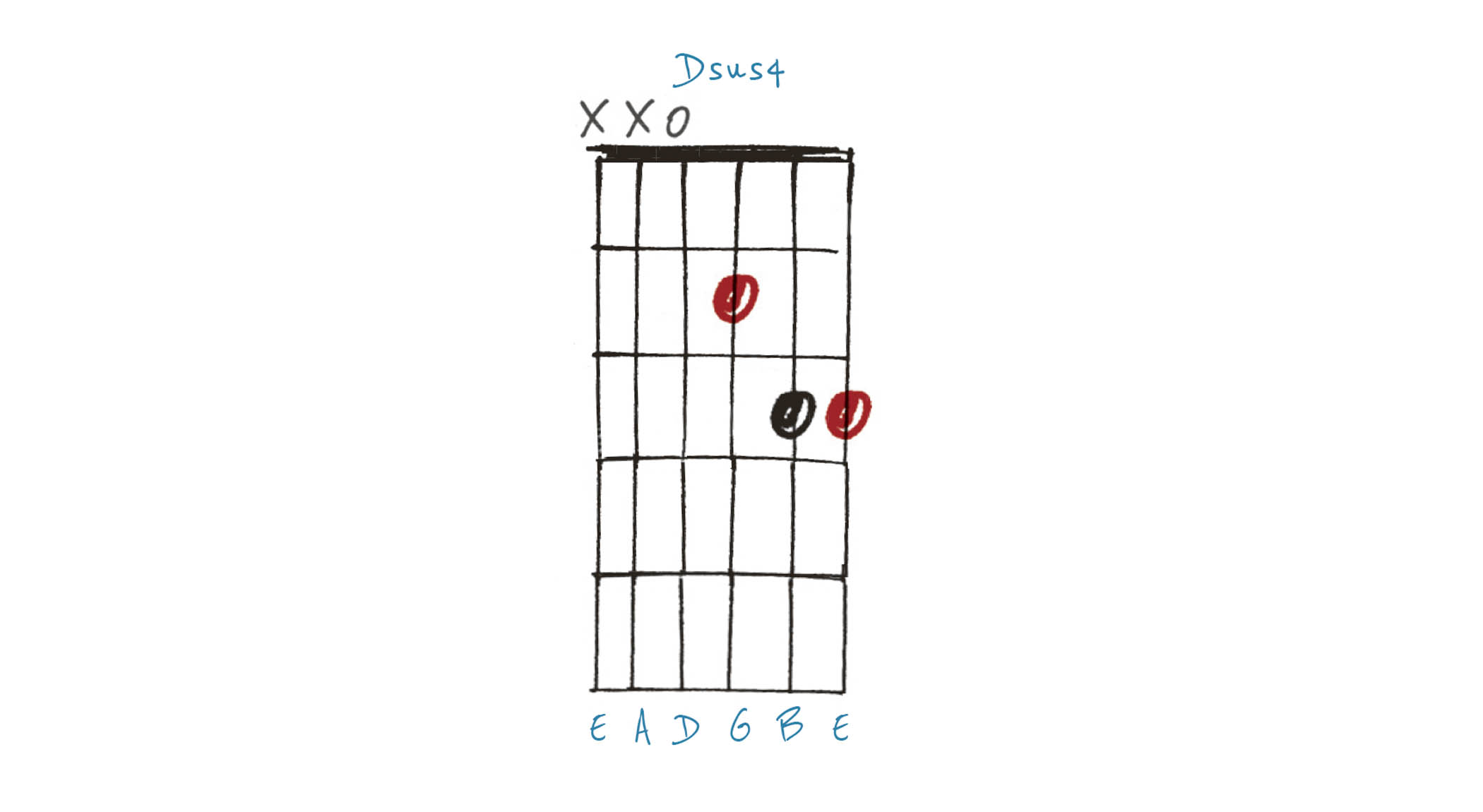
Dsus4 is an abbreviated way of saying D suspended 4th. The 4th in this case is G, the 4th of the D major scale. The G replaces the 3rd (F#), meaning sus chords are neither major nor minor; it’s all about which chord you resolve to afterwards (that’s where the ‘suspended’ part comes from).
Resolving to D major sounds a bit like The Who, while resolving to D minor sounds a bit like Bach.
Example 2. Dadd4
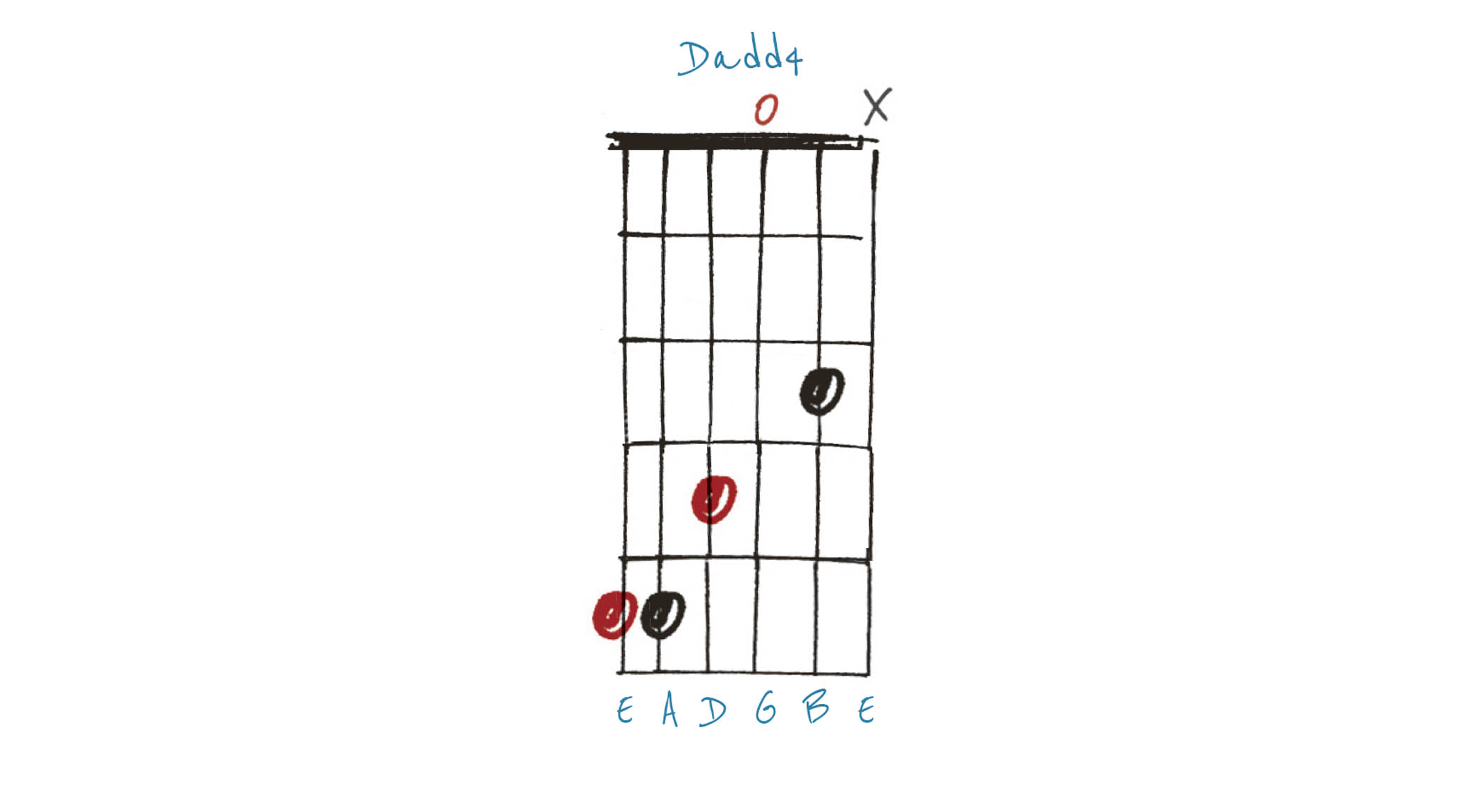
Here’s another D chord containing the 4th (G). This time, the 3rd (F#) is also retained, giving us what is called a Dadd4.
This is a major chord, but it retains a certain suspended quality by containing the 3rd and 4th a semitone apart. If you can stretch to making the F# an F natural on the 3rd fret of the fourth string, you’ll have Dm(add4).
Example 3. C9
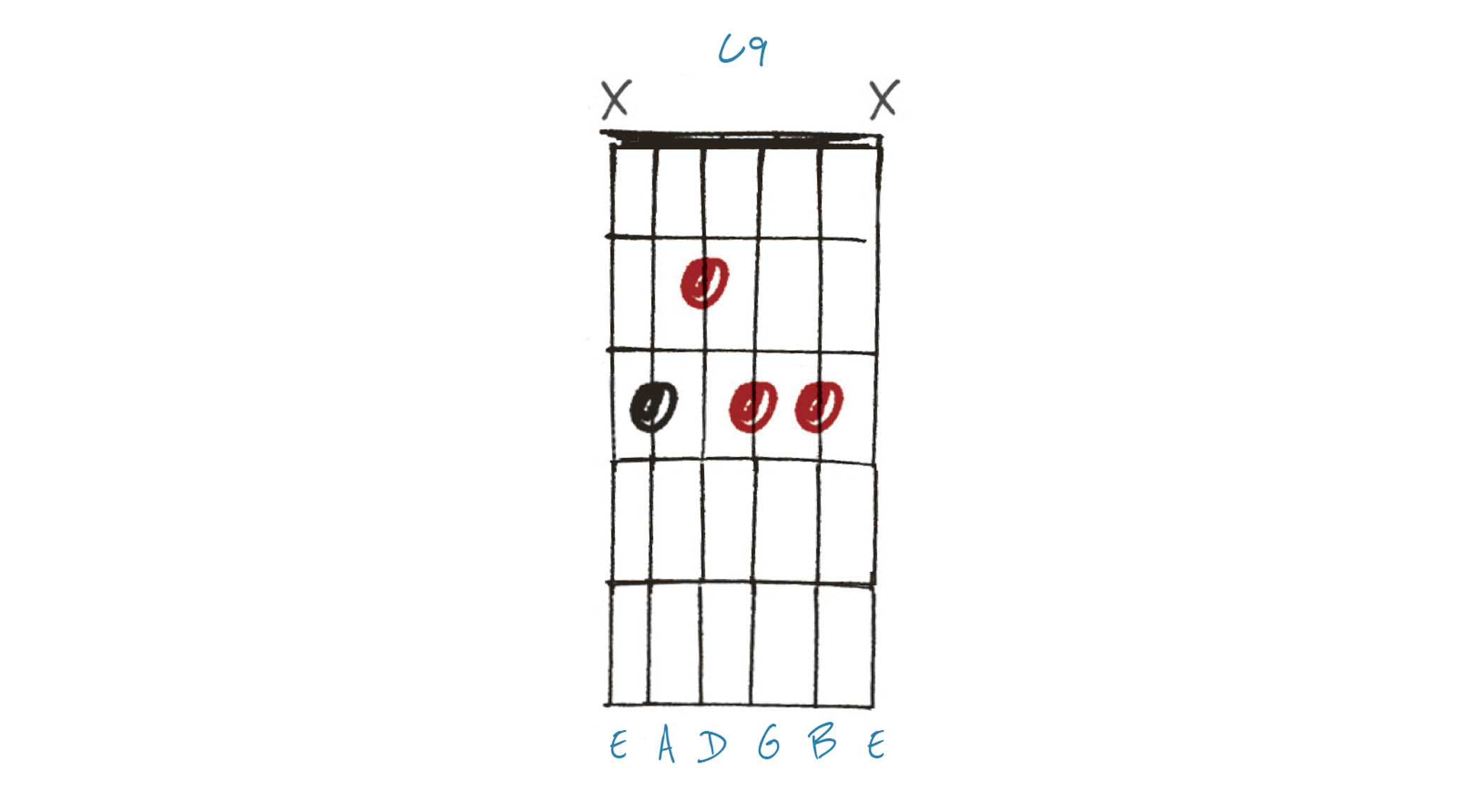
When we extend a chord beyond the 7th, we start adding the names/numbers from a second octave of the major scale. The 9th (D) is nine notes above the original root when we play a two-octave C major scale. This, plus the inclusion of the b7 (Bb), is why this chord is called C9, instead of Cadd9.
Example 4. Cadd9
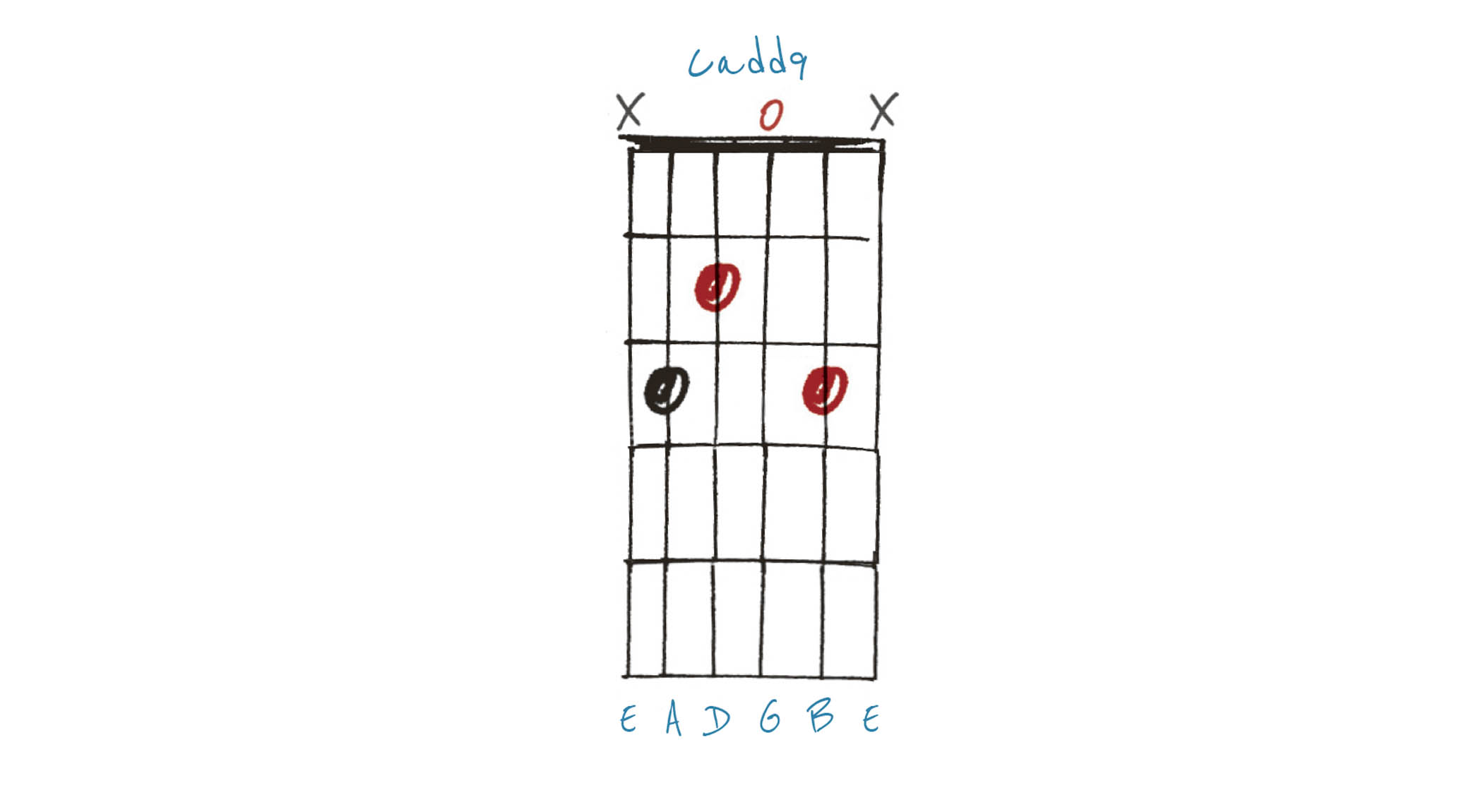
Further to Example 3, here is a Cadd9 in the same position. There is no b7 th, just the root-3rd-5th (C-E-G) plus the 9th (D) added on top.
On an instrument such as the guitar where chords don’t always oblige by appearing in scale order, there can sometimes be confusion about what is a 2nd and what is a 9th (both D in this key!). I’ll attempt to clarify in Example 5…
Example 5. Asus2
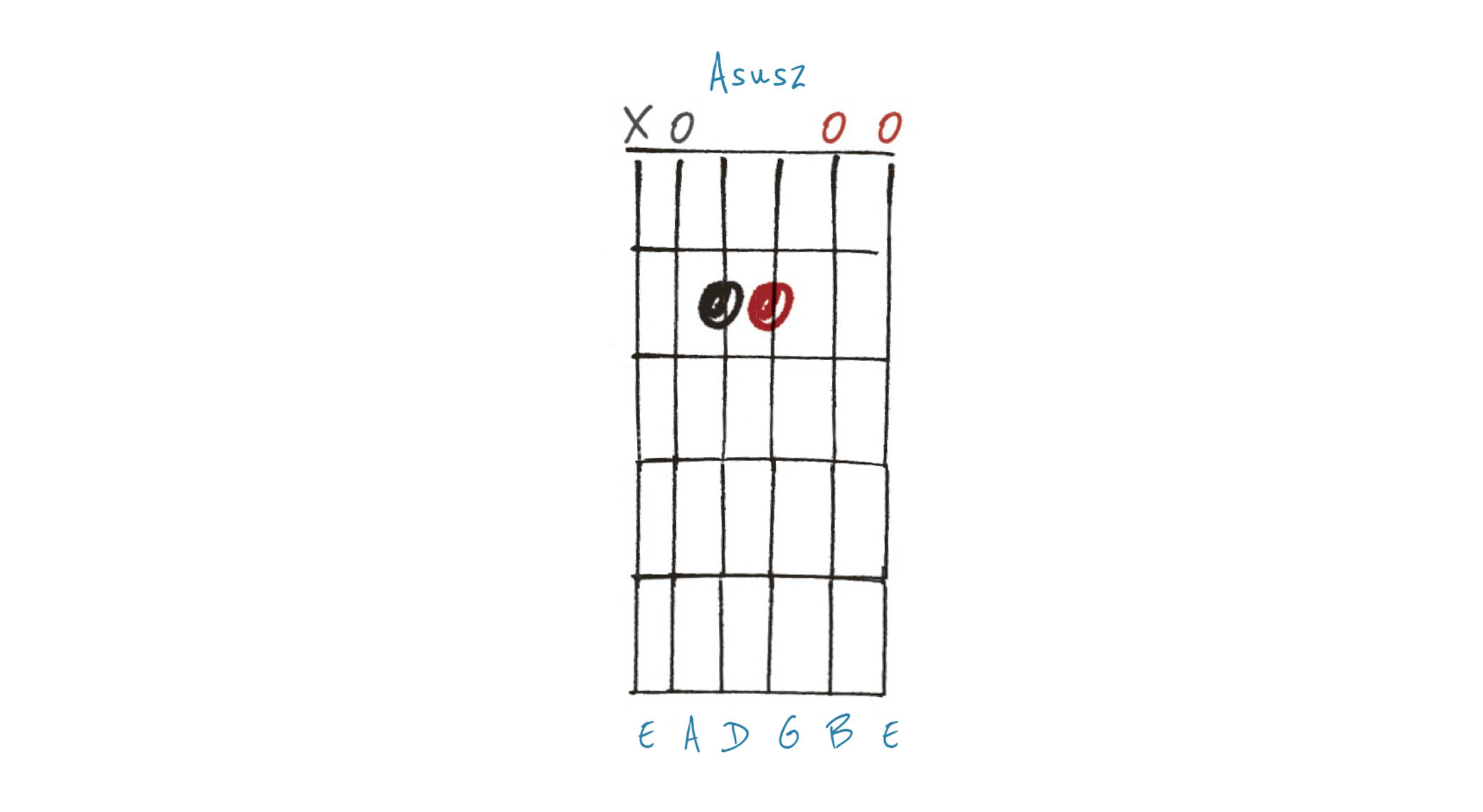
This Asus2 chord features the 2nd (B), a full nine notes above the root (A) on the open fifth string – but as the 2nd replaces the 3rd (C#), here the octave becomes irrelevant.
This is similar to the triad (E-A-C#) that forms the A major chord at the 2nd fret of the fourth, third and second strings (in that order). Like sus4, sus2 is neither major nor minor. Try mixing this with Asus4, A major and A minor.







