Although Microsoft offers Windows 11 as a free upgrade for devices already running Windows 10, this does not mean that your hardware configuration is compatible. The device also needs to have one of the supported processors, in addition to requiring a trusted platform module (TPM) 2.0 chip.
As part of the minimum system requirements, Windows 11 is supported only on 64-bit (x64) processors and only in specific chips from Intel, AMD, and Qualcomm, leaving many older computers without the possibility to upgrade. For example, from Intel, the operating system officially supports only the 8th Gen and newer processors and some of the Celeron, Atom, Pentium, and Xeon chips. And from AMD, Windows 11 supports third-generation Ryzen and newer processors, including some second-generation Ryzen 7 CPUs and some Athlon and EPYC processors.
If you plan to switch to Windows 11 but are unsure whether the processor is supported, there are several quick ways on Windows 10 to confirm whether it's on the list of supported hardware, including using the Settings app, Command Prompt, or the PC Health Check app.
In this how-to guide, we will walk you through the easy steps to confirm whether your computer's processor is supported to run Windows 11.
How to check CPU compatibility using Settings
To check whether the processor installed on your device supports Windows 11, use these steps:
- Open Settings.
- Click on System.
- Click on About.
- Check the processor make and model under the "Device specifications" section.
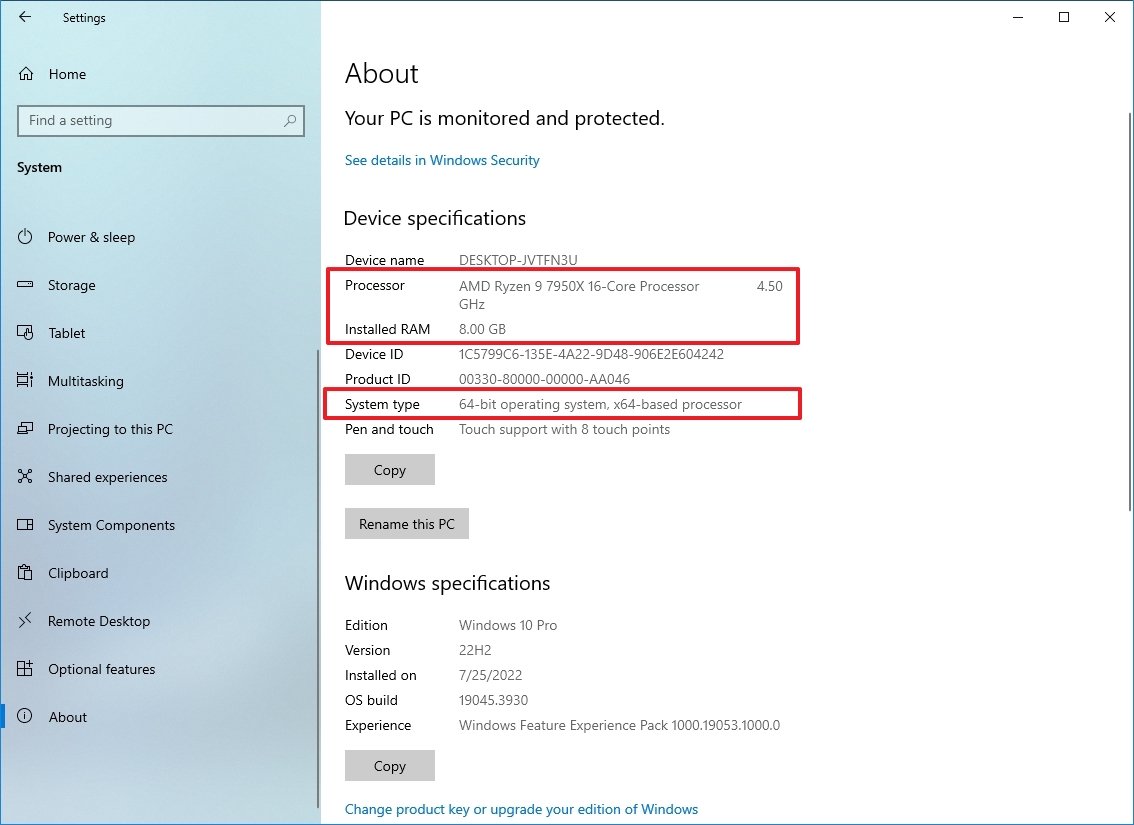
- Confirm the System type reads "64-bit operating system, x64-based processor."
- If you have an Intel processor, check this Microsoft support page to determine if the chip is on the compatibility list to run Windows 11.
- If you have an AMD processor, check this Microsoft support page to determine if the chip is on the compatibility list to run Windows 11.
Once you complete the steps, you will find out whether the processor is compatible. You can also use these steps to check your device's full technical specifications.
How to check CPU compatibility using commands
- Open Start.
- Search for Command Prompt, right-click the top result, and select the Run as administrator option.
- Type the following command to find out the processor make and model and press Enter: wmic cpu get name
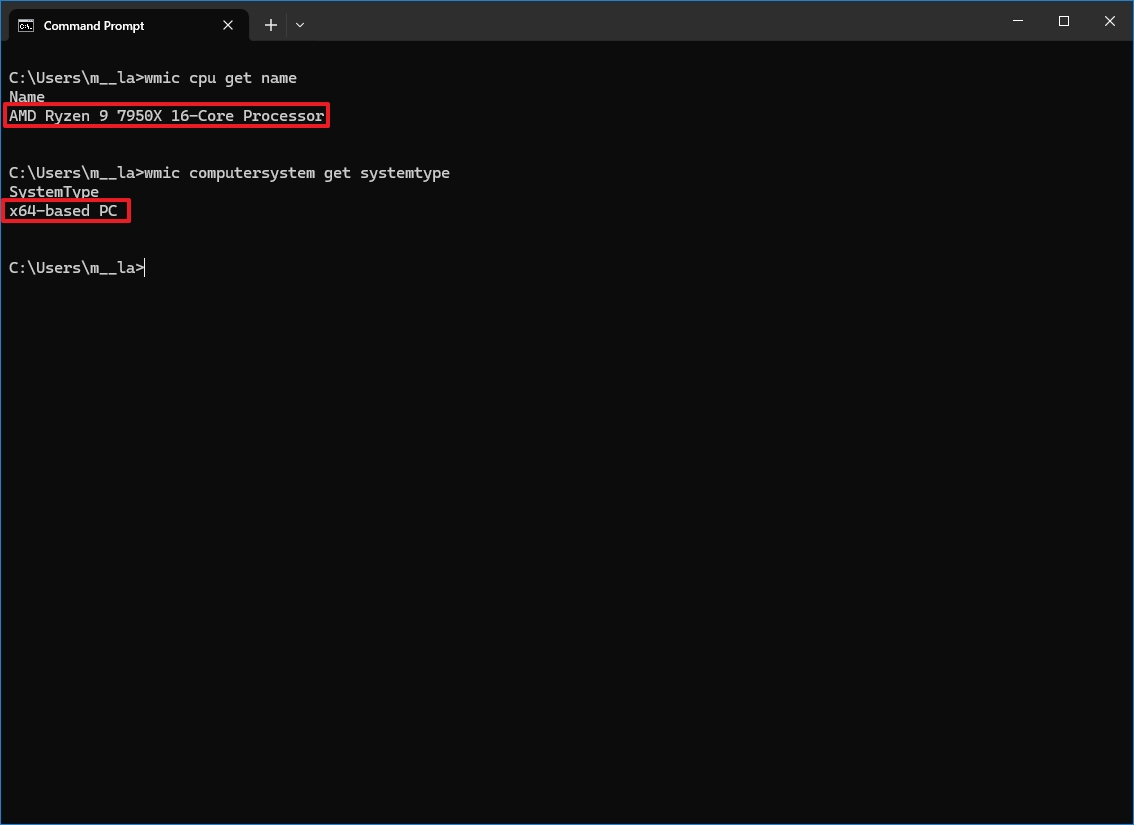
- Type the following command to determine if the system is 64-bit and press Enter: wmic computersystem get systemtype
- If you have an Intel processor, check this Microsoft support page to determine if the chip is on the compatibility list.
- If you have an AMD processor, check this Microsoft support page to determine if the chip is on the compatibility list.
After you complete the steps, you will confirm if the processor may prevent you from upgrading to the next version of the operating system.
How to check CPU compatibility using PC Health Check
Alternatively, you can also use the PC Health Check to determine if your processor is compatible with Windows 11. The only caveat using this app is that it will only tell you if your hardware configuration will support the new operating system, but it will not show any details about the processor available on your device.
To use the PC Health Check app to confirm a processor is compatible, use these steps:
- Quick note: The app should already be installed on your computer, but if it's not, you can download it using the Microsoft support link.
- Search for the PC Health Check and click the top result to open the app
- Click the Check now button.
- Click the "See all results" button to display the final report.
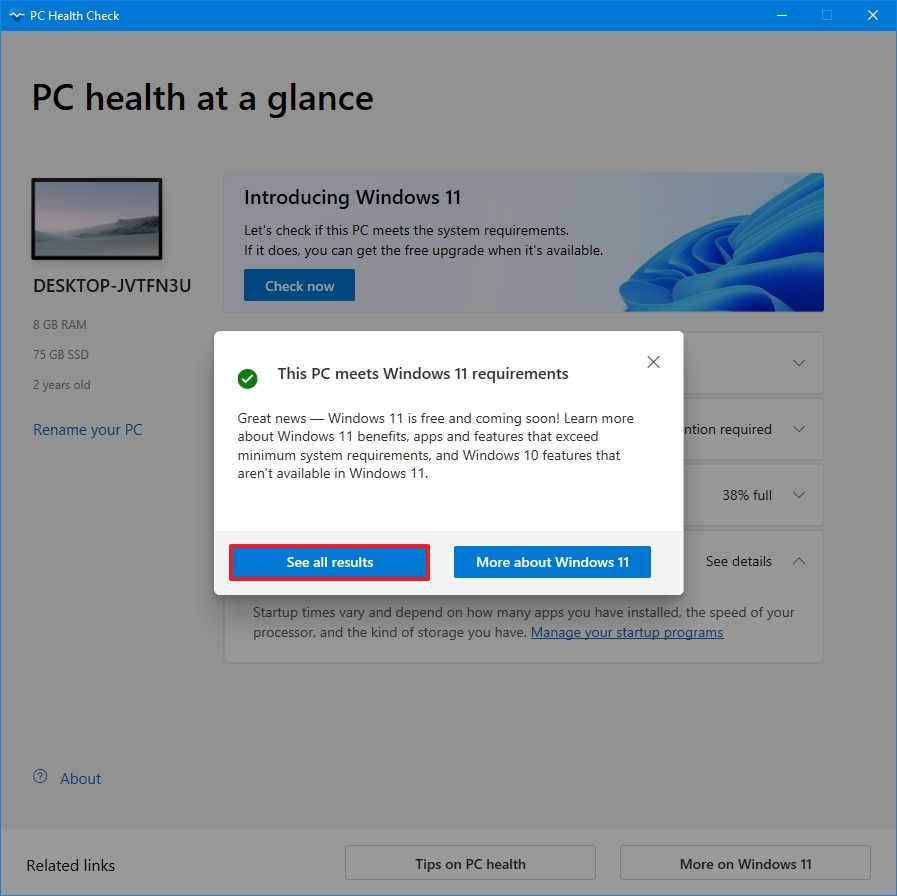
Once you complete the steps, the app will determine whether the processor and other components, such as memory and storage, are compatible with Windows 11.
It's important to note that if you want to upgrade to version 24H2, the processor will also need support for "SSE4.2" on Intel or "SSE4A" on AMD (which also includes the POPCNT instruction). Although these methods won't directly reveal if your processor features the required instructions, most chips released after 2008 contain these instructions. You can verify your device's compatibility by checking the list of supported processors on the Microsoft support pages as shown above.
More resources
For more in-depth insights, troubleshooting tips, and the latest updates on Windows 11 and 10, be sure to explore these resources:







