On 8 April 2024, a total solar eclipse will sweep across North America, providing an astronomical experience in many alluring locations.
Only a tiny proportion of humanity has ever witnessed a total eclipse – but tens of millions of people will be able to experience one as the “path of totality” sweeps from the Pacific to the Atlantic during the course of that magical Monday.
Here’s what you need to know about why you should see it and where to be.
What happens during a total solar eclipse?
The greatest show on earth comes courtesy of the lifeless moon. Normally the orbiting lunar lump merely provides earth with tides, moonlight and somewhere to aim space rockets. But roughly once a year the natural satellite aligns with the sun and, thanks to a geometric miracle, blots out the hub of the solar system to create a total eclipse.
“Even though the moon is 400 times smaller than the sun, it’s also about 400 times closer to earth than the sun is,” says Nasa. “This means that from earth, the moon and the sun appear to be roughly the same size in the sky.”
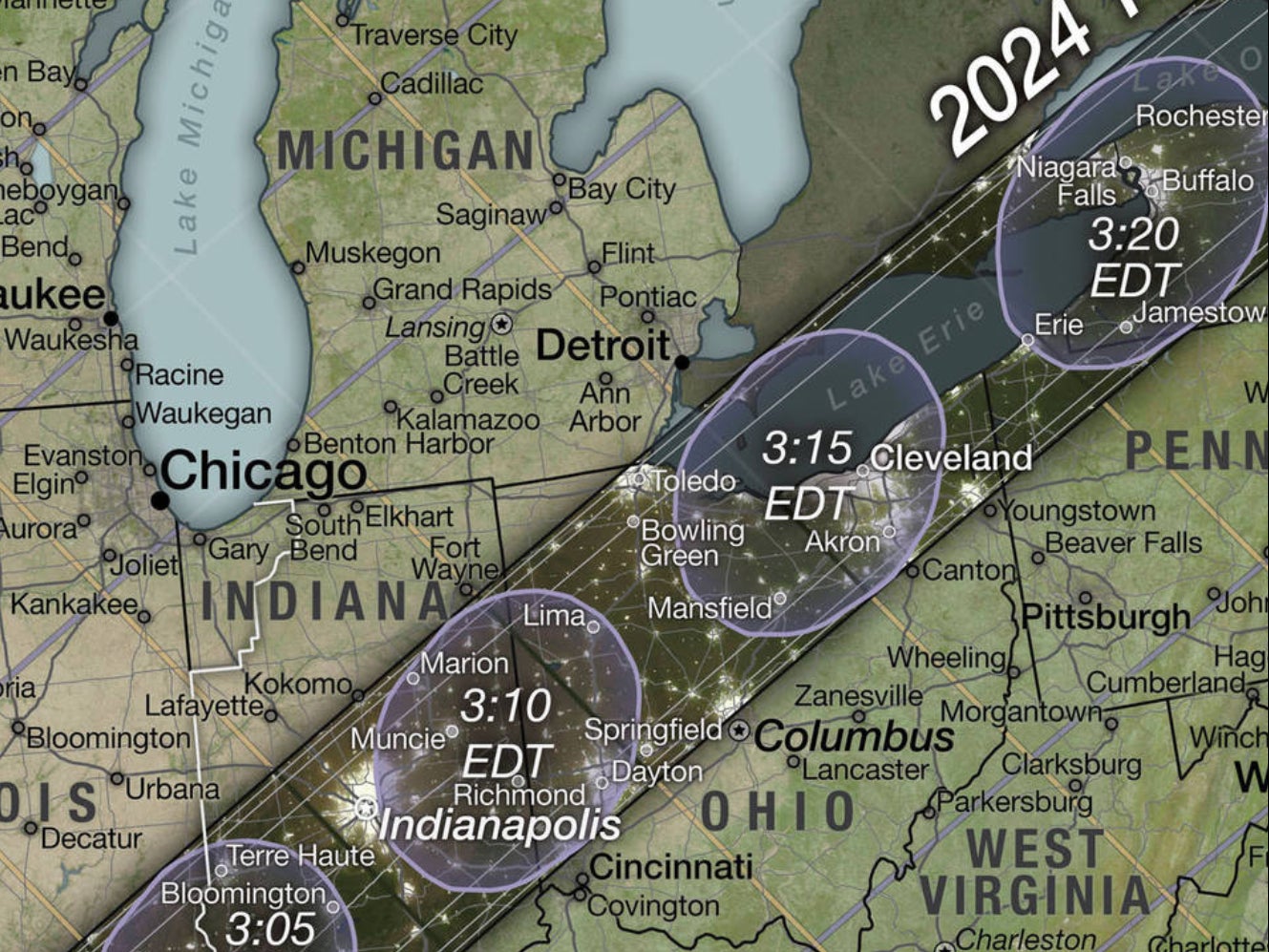
A narrow band marking the “path of totality” carves an arc of darkness across the surface of our planet. If you are somewhere on that line at the predicted time, and you have clear skies, then the experience will become a lifelong memory.
The closer you are to the centre of the path of totality, the longer the total eclipse will last. The astronomer Dr John Mason, who has guided dozens of eclipse trips (and will be doing so again in 2024), says: “People down in southwest Texas will get about four minutes 20 seconds, and that reduces to about three minutes 20 seconds up in the northeast. That’s a pretty good, long total eclipse.”
What’s so good about seeing an eclipse?
In the days leading up to the eclipse, locations in the path of totality acquire something of a carnival atmosphere as astronomical tourists converge in excited anticipation.
On the day, the cosmological performance begins with a warm-up lasting more than an hour, during which the moon steadily nibbles away at the surface of the sun.
Suddenly, you experience totality. The stars and planets appear in the middle of the day. The air chills.
To testify to the heavenly fit between our two most familiar heavenly bodies, faint diamonds known as Baily’s beads peek out from behind the moon. They actually comprise light from the sun slipping through lunar valleys.
A sight to behold – so long as you can see the moon blotting out the sun and appreciate the mathematical perfection of nature in our corner of the galaxy.
Eclipses are entirely predictable: we know the stripes that the next few dozen will paint upon the surface of the Earth. But the weather is not. Cloud cover, which blighted the Cornwall eclipse in 1999, downgrades a cosmological marvel to an eerie daytime gloom.
Almost as predictable as the eclipse is that traffic towards the path of totality will be heavy on the morning of 8 April 2024.
Accommodation rates are astronomical: even humdrum motel rooms in Niagara, central in the path of totality, are selling for C$600 (£350) for the night of 7-8 April 2024.

Where will the great American eclipse 2024 be visible?
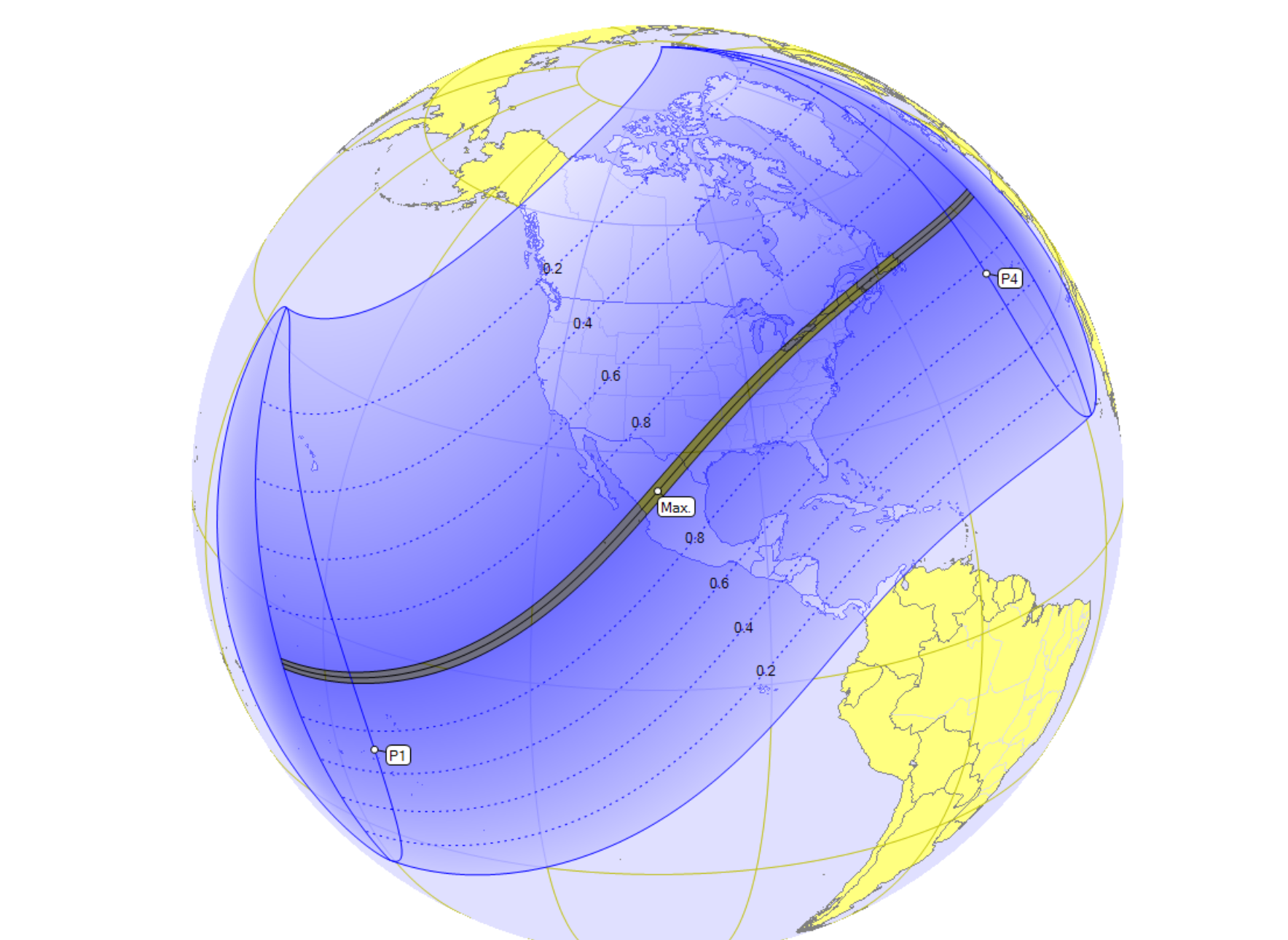
The path of totality makes landfall from the Pacific at Mazatlan on Mexico’s Pacific Coast and sweeps northeastwards to reach the US-Mexican border at Piedras Negras.
In the US, three big Texan cities – San Antonio, Austin and Dallas – are on the extremes of the path of totality; many citizens are likely to drive to locations near the centre of the line.
Arkansas will be an attractive place to see the eclipse, with both Texarkana (on the border with Texas) and Little Rock within the path of totality.
In the Midwest, Indianapolis and Cleveland share the distinction of being fairly central in the path of totality. In upstate New York, Buffalo and nearby Niagara Falls (shared with Canada) could be extremely attractive – though prone in early April to cloudy skies.
In Canada, Montreal is just touched by the path of totality. The line then reverts to the US, passing across northern Maine – which promises to be a superb with clear skies. Then back to Canada’s Maritime Provinces, with New Brunswick, Prince Edward Island and Newfoundland all in the line of darkness.
Will I be able to see a partial eclipse from the UK?
Yes. The eclipse ends with the sunset in the eastern Atlantic, about 600 miles off the coast of Cornwall, before it reaches the UK and Ireland. But on the island of Ireland and western parts of Great Britain, a partial eclipse may be visible with the sun low in the sky.
If skies are clear and you have an open view to the west, it will start at around 7.55pm in Cardiff, Liverpool, Manchester, Edinburgh and Glasgow.
BBC Weather presenter Simon King said: “With the partial solar eclipse occurring late in the day UK time, the Sun will be low to the horizon and will actually set before the spectacle is over.”
Can I combine an exciting city with a partial eclipse?
Boston, New York and Chicago are among the big cities that will see a sizeable chunk of the sun blotted out. Viewer as far apart as Alaska and the far north of Colombia and the Caribbean will, if skies are clear and they use the correct eye protection, see a partial eclipse. But there is nothing to compare with a total eclipse.
Eclipse guru Dr Mason sums up the difference between a 99 per cent partial eclipse and a total eclipse as far apart as “a peck on the cheek and a night of passion”.
“There will be people who will look at the map and say, ‘I live in Cincinnati or I live in Columbus [Ohio] and I’m just outside the zone of totality. But I’m going to get a 99 per cent-plus eclipse, so maybe I won’t bother to travel’.
“What they don’t realise is there an enormous difference between 99 per cent and 100 per cent. And there’s a range of phenomena that they won’t see if they put up with 99 per cent.”
You must use special eclipse safety glasses or viewers when viewing a partial eclipse or during the partial phases of a total solar eclipse.

Where should I be for the total experience?
There are no guarantees of clear skies: all you can do is play the odds based on the record of cloud cover for the corresponding date in previous years.
Dr Mason says the average expected cloud cover amounts increase from around 40-45 per cent on the Mexico/Texas border to over 80 per cent in Maine, New Brunswick and Newfoundland.
Three particularly tempting locations:
- Southern Texas, close to San Antonio or Austin. Besides clear skies being more likely than not, access is easy with direct flights to Austin. Importantly there is much to explore in the region before and after the eclipse, from Big Bend National Park on the Rio Grande to Space Center Houston – an excellent place to continue the cosmological theme.
- Northern Arkansas, a picturesque part of the state, with the added attraction of Memphis just a couple of hours away.
- Niagara Falls: the dramatic border between the US and Canada could be an eclipse washout due to clouds. But the natural surroundings are impeccable – and there is plenty of accommodation, which will avoid the risk of being caught in severe traffic congestion on the freeways from Toronto and locations in New York State.
However, the most recent forecasts for cloud cover suggest that the Midwest around Indianapolis and the northeastern state of Maine could have the best prospects.
When are the next total solar eclipses?
Summer 2026 – Wednesday 12 August, to be precise – should bring a spectacular eclipse visible in northern Spain at the height of the European holiday season. The path of totality begins in the Arctic and crosses Greenland and Iceland before arriving in the northern half of Spain. The stripe of darkness will traverse the great cities of Bilbao, Zaragoza and Valencia in mainland Spain before arriving in Palma de Mallorca.
The following summer (2 August 2027), the southern tip of mainland Spain is in the path of totality for an eclipse that will sweep across North Africa and the Arabian peninsula: going east from the Strait of Gibraltar, it will encompass Morocco, Algeria, Tunisia, Libya, Egypt, the northeasternmost corner of Sudan, Saudi Arabia and Yemen.
Just under 12 months later, on 22 July 2028, Outback Australia will be the place to be. A total eclipse will make landfall in northern Western Australia, sweep across the Northern Territory and part of southwest Queensland – then clean across New South Wales, with Sydney in the middle of the path of totality.
Winter cloud cover could disrupt the experience in Australia’s largest city – and is very likely in the southern portion of New Zealand’s South Island where the eclipse reaches a finale.
Australia also features in the cosmological plans on 25 November 2030. This is early summer in the southern hemisphere, and likely to be good conditions for viewing in Namibia, Botswana and South Africa (Durban is on the path of totality) as well as South Australia.







