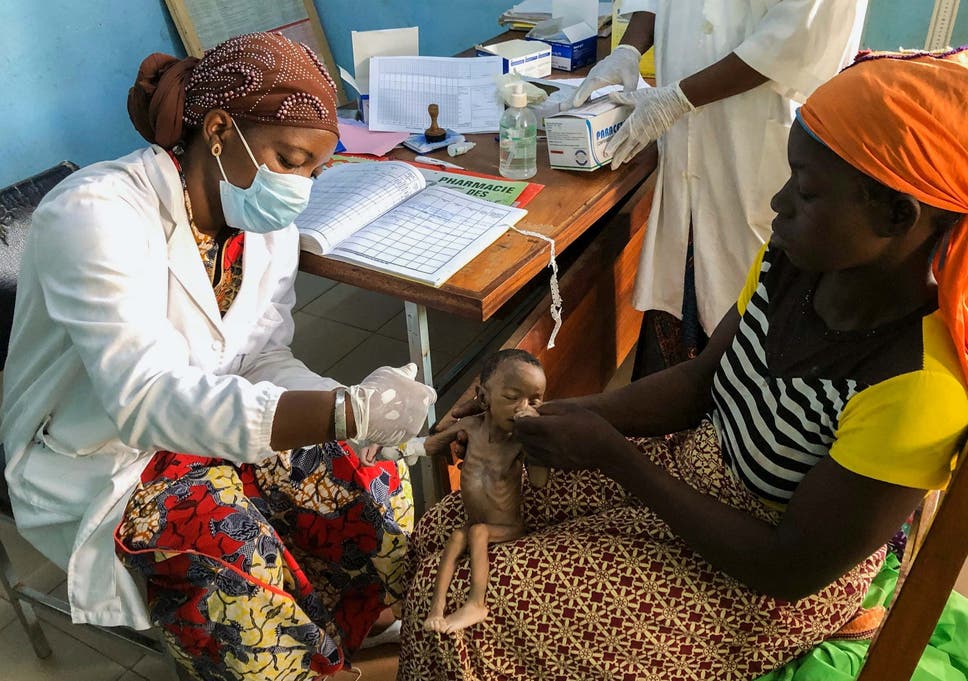
The lean season is coming for Burkina Faso‘s children. And this time, the long wait for the harvest is bringing a hunger more ferocious than most have ever known.
That hunger is already stalking Haboue Solange Boue, an infant who has lost half her former body weight of 5.5 pounds (2.5 kilograms) in the last month. With the markets closed because of coronavirus restrictions, her family sold fewer vegetables. Her mother is too malnourished to nurse her.
“My child,” Danssanin Lanizou whispers, choking back tears as she unwraps a blanket to reveal her baby’s protruding ribs. The infant whimpers soundlessly.
All around the world, the coronavirus and its restrictions are pushing already hungry communities over the edge, cutting off meagre farms from markets and isolating villages from food and medical aid. Virus-linked hunger is leading to the deaths of 10,000 more children a month over the first year of the pandemic, according to an urgent call to action from the United Nations shared with the Associated Press ahead of its publication in the Lancet medical journal.
Further, more than 550,000 additional children each month are being struck by what is called wasting, according to the UN — malnutrition that manifests in spindly limbs and distended bellies. Over a year, that’s up 6.7 million from last year’s total of 4.7 million. Wasting and stunting can permanently damage children physically and mentally, transforming individual tragedies into a generational catastrophe.
“The food security effects of the Covid crisis are going to reflect many years from now,” said Dr Francesco Branca, the World Health Organisation (WHO) head of nutrition. “There is going to be a societal effect.”
In Burkina Faso, for example, one in five young children is chronically malnourished. Food prices have spiked, and 12 million of the country’s 20 million residents don’t get enough to eat.
Ms Lanizou’s husband, Yakouaran Boue, used to sell onions to buy seeds and fertiliser, but then the markets closed. Even now, a 50-kilogram bag of onions sells for a dollar less, which means less seed to plant for next year.
“I’m worried that this year we won’t have enough food to feed her,” he said, staring down at his daughter over his wife’s shoulder. “I’m afraid she’s going to die.”
From Latin America to South Asia to sub-Saharan Africa, more families than ever are staring down a future without enough food. The analysis published on Monday found about 128,000 more young children will die over the first 12 months of the virus.
In April, World Food Program head David Beasley warned that the coronavirus economy would cause global famines “of biblical proportions” this year.
There are different stages of what is known as food insecurity — famine is officially declared when, along with other measures, 30 per cent of the population suffers from wasting.
The agency estimated in February that one in every three people in Venezuela was already going hungry, as inflation rendered many salaries nearly worthless and forced millions to flee abroad. Then the virus arrived.
“The parents of the children are without work,” said Annelise Mirabal, who works with a foundation that helps malnourished children in Maracaibo, the city in Venezuela thus far hardest hit by the pandemic. “How are they going to feed their kids?”
These days, many new patients are the children of migrants who are making long journeys back to Venezuela from Peru, Ecuador or Colombia, where their families became jobless and unable to buy food during the pandemic. Others are the children of migrants who are still abroad and have not been able to send back money for more food.
“Every day we receive a malnourished child,” said Dr. Francisco Nieto, who works in a hospital in the border state of Tachira. He added that they look “like children we haven’t seen in a long time in Venezuela”, alluding to those in famines in parts of Africa.
In May, Dr Nieto recalled, after two months of quarantine in Venezuela, 18-month-old twins arrived at his hospital with bodies bloated from malnutrition. The children’s mother was jobless and living with her own mother. She told the doctor she had only been able to feed them a simple drink made with boiled bananas.
“Not even a cracker? Some chicken?” he asked.
“Nothing,” the children’s grandmother responded.
When doctors tried to treat them, one of the boys developed “refeeding syndrome”, where food can result in metabolic abnormalities. Eight days later, he died.
Dr Nieto said aid groups have provided some relief, but their work has been limited by Covid-19 quarantines. A home set up in Tachira to receive malnourished children after they are released from the hospital is no longer in operation. So now children are sent directly back to their families, many of whom are still unable to feed them properly.
“It’s very frustrating,” Dr Nieto said. “The children get lost.”
The rise in child deaths worldwide would reverse global progress for the first time in decades. Deaths of children younger than 5 years old had declined steadily since 1980, to 5.3 million around the world in 2018, according to a UNICEF report. About 45 per cent of the deaths were due to undernutrition.
The leaders of four international agencies —the WHO, UNICEF, the World Food Program and the Food and Agriculture Organisation — have called for at least $2.4bn (£1.9bn) immediately to address hunger. Even more than the money, restrictions on movement need to be eased so that families can seek treatment, said Victor Aguayo, the head of UNICEF’s nutrition program.
“By having schools closed, by having primary health care services disrupted, by having nutritional programmes dysfunctional, we are also creating harm,” Mr Aguayo said. He cited as an example the near-global suspension of Vitamin A supplements, which are a crucial way to bolster developing immune systems.
In Afghanistan, restrictions on movement prevent many families from bringing their malnourished children to hospitals for food and aid just when they need it most. The Indira Gandhi hospital in the capital, Kabul, has seen only three or four malnourished children, said specialist Nematullah Amiri.
“Transportation between Kabul and the provinces was not allowed regularly and also people were afraid of coronavirus,” Mr Amiri explained. Last year, 10 times as many malnourished children filled the ward. The same is true of hospital beds in multiple countries, according to Medecins Sans Frontieres.
Afghanistan is now in a red zone of hunger, with severe childhood malnutrition spiking from 690,000 in January to 780,000 — a 13 per cent increase, according to UNICEF. Food prices have risen by more than 15 per cent, and a recent study by Johns Hopkins University indicated an additional 13,000 Afghans younger than five could die.
Four in 10 Afghan children are already stunted. Stunting happens when families live on a cheap diet of grains or potatoes, with supply chains in disarray and money scarce. Most stunted children never catch up, dampening the productivity of poor countries, according to a report released this month by the Chatham House think tank.
In Yemen, restrictions on movement have also blocked the distribution of aid, along with the stalling of salaries and price hikes. The Arab world’s poorest country is suffering further from a fall in remittances and a huge drop in funding from humanitarian agencies.
Yemen is now on the brink of famine, according to the Famine Early Warning Systems Network, which uses surveys, satellite data and weather mapping to pinpoint the places most in need. A UNICEF report predicted that the number of malnourished children could reach 2.4 million by the end of the year, a 20 per cent increase.
Days after seven-month-old baby Issa Ibrahim left a medical centre in the impoverished northern district of Hajjah, he succumbed to severe acute malnutrition. His mother found his body on 7 July, lifeless and cold.
Fatma Nasser, a 34-year-old mother of seven, is among three million displaced people in Yemen who don’t have enough money to feed themselves or their children. She lives on one meal a day. Ibrahim Nasser, the father, lost his only source of income, fishing, after roads to the sea were closed because of the coronavirus.
The mother’s milk dried up, and the baby lived on formula. But doctors say families tend to use less milk powder to save money, and babies don’t usually get enough nutrition.
“It’s God’s will,” the mother said. “We can say nothing.”
AP







