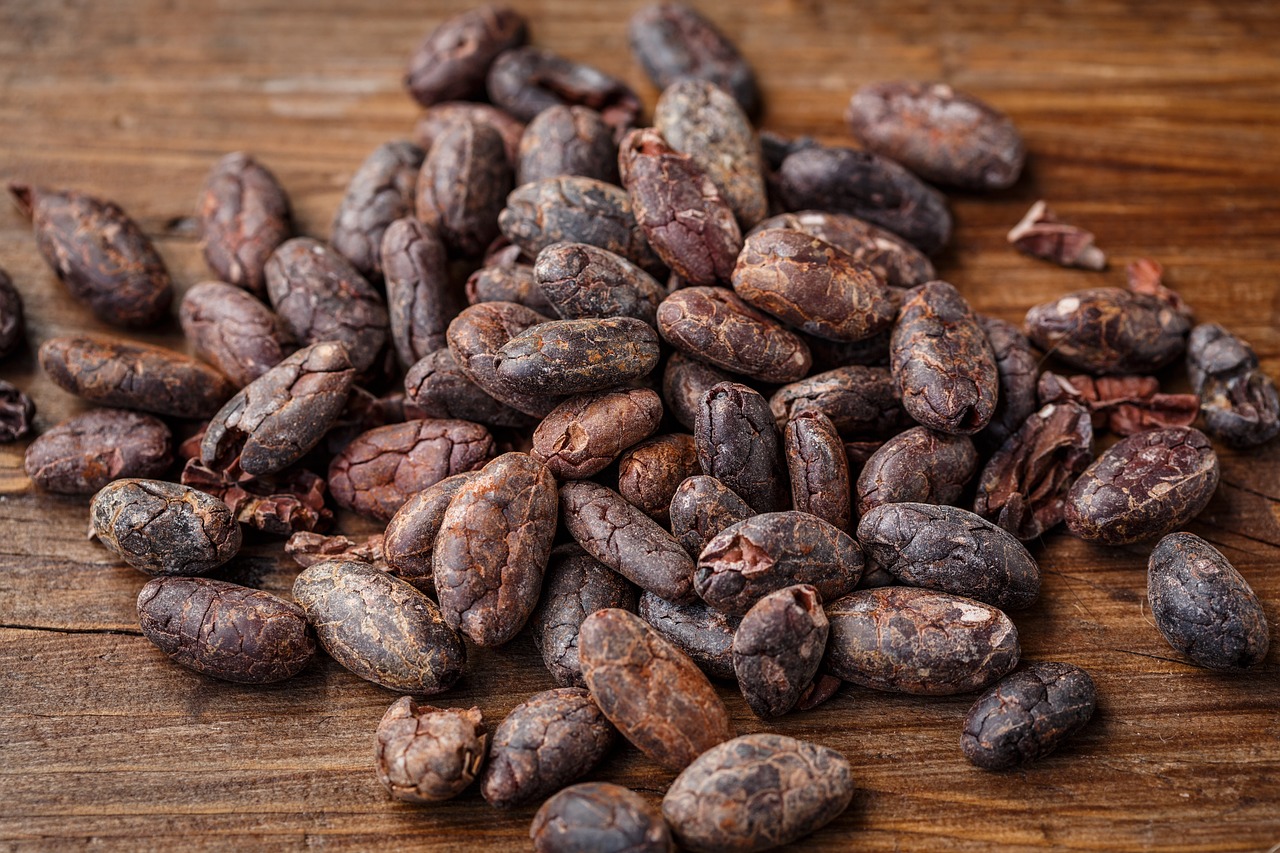
December ICE NY cocoa (CCZ24) Friday closed down -321 (-4.13%), and December ICE London cocoa #7 (CAZ24) closed down -243 (-4.18%).
Cocoa prices plunged to 1-week lows on Friday and closed sharply lower on the outlook for a larger Ivory Coast cocoa crop. On Friday, Ivory Coast regulator Le Conseil Cafe-Cacao raised its Ivory Coast 2024/25 cocoa production estimate by as much as 10% to 2.1 MMT to 2.2 MMT from a June forecast of 2.0 MMT.
Recent global cocoa demand has been mixed. The National Confectioners Association reported Thursday that North American Q3 cocoa grindings rose +12% y/y to 109,264 MT. Also, the Cocoa Association of Asia reported that Q3 Asian cocoa grinding rose +2.6% y/y to 216,998 MT. However, the European Cocoa Association reported that European Q3 cocoa grindings fell -3.3% y/y to 354,335 MT.
On Tuesday, NY cocoa climbed to a 2-week high as heavy rain in West Africa caused flooding and kept cocoa farmers out of their fields, delaying the harvest. Also, the heavy rain makes it harder to dry harvested cocoa beans, lowering their quality.
Lower cocoa production in the Ivory Coast, the world's largest producer, is a bullish factor for cocoa prices. Government data Monday showed that Ivory Coast farmers shipped 100,264 MT of cocoa to ports from October 1 to October 13, down -12% from 114,000 MT shipped the same time last year.
Shrinking global cocoa stockpiles are also bullish for prices. ICE-monitored cocoa inventories held in US ports have been trending lower for the past 15 months and fell to a 15-year low Thursday of 1,948,190 bags.
Earlier this month, NY cocoa fell to a 4-3/4 month nearest-futures low after the European Commission postponed an anti-deforestation law for one year. The legislation, previously scheduled to go into effect December 30, is aimed at curbing forest clearance in countries that send products, including cocoa, to the EU. The postponement of the law allows certified cocoa stockpiles held at European warehouses to be used to satisfy contracts, reducing concerns that the new law would lead to the decertification of the cocoa and limiting existing cocoa supplies.
Cocoa also had support after Ghana's Cocoa Board (Cocobod) on August 20 cut its 2024/25 Ghana cocoa production estimate to 650,000 MT from a June forecast of 700,000 MT. Due to bad weather and crop disease, Ghana's 2023/24 coca harvest sank to a 23-year low of 425,000 MT. Ghana is the world's second-biggest cocoa producer, and its 2024/25 cocoa harvest begins in October.
An increase in cocoa production by Cameroon, the world's fifth-largest cocoa producer, is bearish for cocoa prices. On August 21, Cameroon's National Cocoa and Coffee Board reported that 2023/24 (Aug/July) Cameroon cocoa production rose +1.2% y/y to 266,725. Also, Nigeria's August cocoa exports rose by +6.8% y/y to 14,984 MT. Nigeria is the world's sixth-largest cocoa producer.
In a bullish factor, the International Cocoa Association (ICCO) on August 30 raised its 2023/24 global cocoa deficit estimate to -462,000 MT from May's -439,000 MT, the largest deficit in over 60 years. ICCO also cut its 2023/24 cocoa production estimate to 4.330 MMT from May's 4.461 MMT. ICCO projected a 2023/24 global cocoa stocks/grindings ratio of a 46-year low of 27.4%.
On the date of publication, Rich Asplund did not have (either directly or indirectly) positions in any of the securities mentioned in this article. All information and data in this article is solely for informational purposes. For more information please view the Barchart Disclosure Policy here.