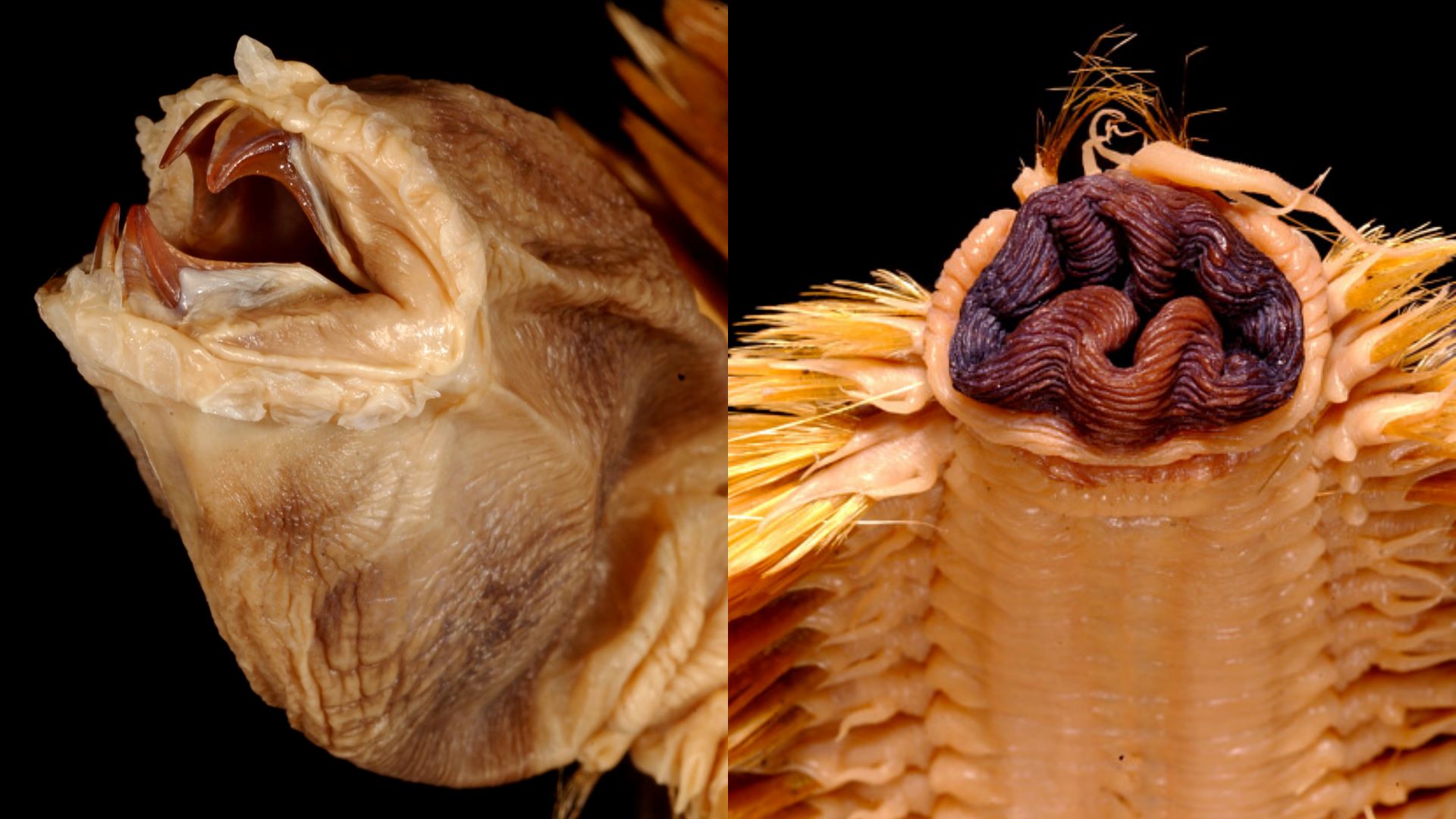
Name: Antarctic scale worm (Eulagisca gigantea)
Where it lives: Below 1,640 (500 meters) deep in Antarctica's Southern Ocean
What it eats: Unknown. Probably other animals and/or organic debris.
Why it's awesome: With their shimmering golden coats, these worms almost look glamorous — until you see their horrifying jaws, which resemble the mouth of the xenomorph from "Alien."
The worms are named after the scales (known as elytra) that cover their bodies. These scales look a bit like human teeth, adding to the worms' dazzling-yet-gruesome appearance.
Growing up to 8 inches (20 centimeters) long, Antarctic scale worms are a type of ocean-dwelling polychaete, or bristle worm (polychaete is Latin for "many bristles"). Related to earthworms and leeches, there are over 8,000 named polychaete species.
They have segmented bodies, with loads of little bristles sticking out of each section.
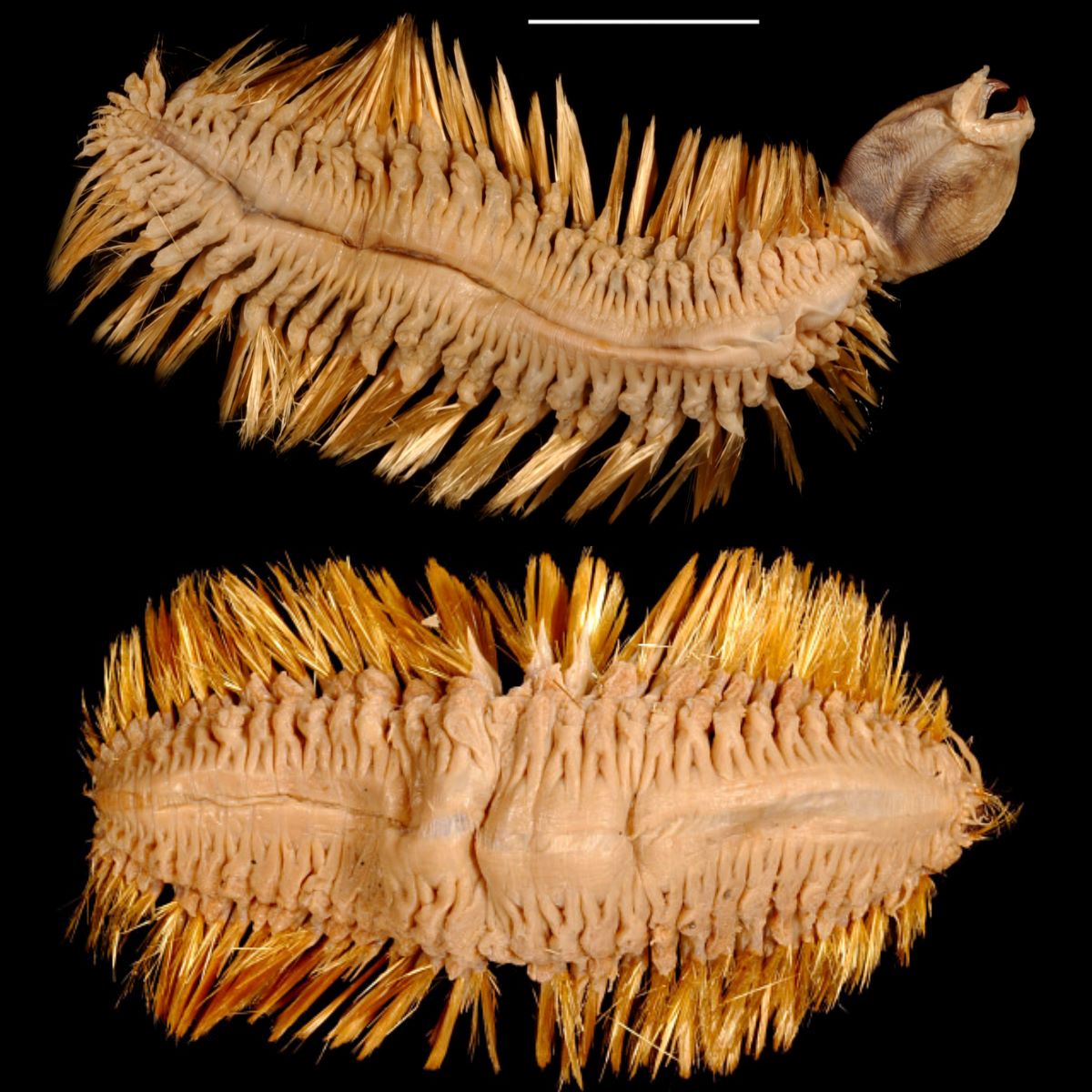

Different polychaete species use their bristles for different purposes, according to the Monterey Bay Aquarium Research Institute (MBARI). In this case, Antarctic scale worms' shimmering golden hairs could help them crawl or swim through the water, or defend themselves from threats. It's unclear why their bristles are golden.
Related: Ghostly white giant worms appear to be reproducing under the seafloor where tectonic plates meet
Their most remarkable body part, however, is often hidden. Their purplish "head" isn't actually a head at all but a retractable mouth they keep tucked away until they're ready to feast. The worms unfurl this proboscis to reveal a set of jaws almost 3 inches (7 cm) wide complete with large, sharp teeth, according to Australian Geographic.
We don't know exactly what they eat, but according to "The Illustrated Encyclopaedia of 'Ugly' Animals" (Wren & Rook, 2020) their large teeth mean they are likely "quick and aggressive hunters."
Although it was discovered in 1939, very little is known about this deep-sea species. Like other bristle worms, it probably plays an important role in keeping the ocean healthy. Bristle worms "are fabulous recyclers and builders, creating massive reef structures and tangles of tubes that house a myriad of other animals including crabs, snails, and (of course!) other worms," MBARI representatives wrote.