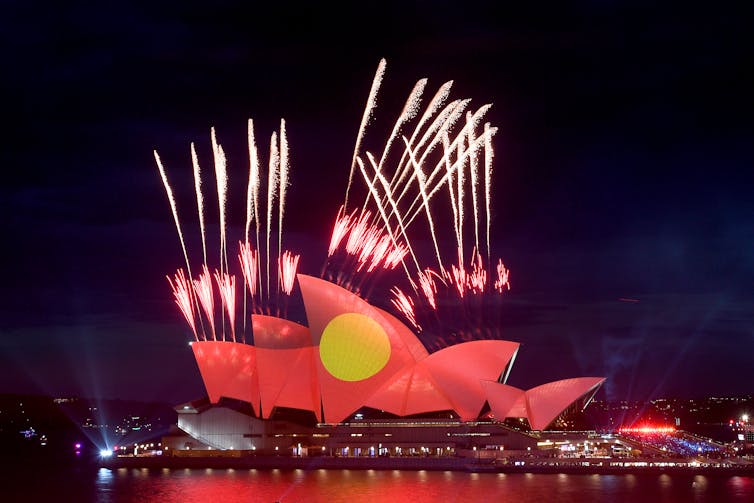
The issue of when or whether to celebrate Australia Day seems to have become stuck in a loop of fierce debate without resolution.
There are those who want to mark January 26 as the start of modern Australia, while others view it as the start of systematic dispossession of Indigenous Australians.
What does the broader public think? A new national survey shows at the moment, the majority of Australians want the day left as it is. But it also suggests a groundswell for change is in the works.
Our study
During November 2021, we polled a representative, random sample of more than 5,000 Australians as part of the Deakin Contemporary History Survey.

In contrast to previous surveys, which have focused on what to call Australia Day, we asked a more general question – is January 26 the right date for something called Australia Day?
We also asked other questions about respondents’ knowledge of and interest in Australian history. Our collective understanding of history can explain why some stories seem more important than others. For example, consider how frequently, and in how many different forms, we learn of Australian military history due to ANZAC Day.
Our findings
Overall, 60% of our respondents want to continue celebrating “Australia Day” on January 26.
But the generational differences are significant. More than half (53%) of millennials (those born between 1986 and 2002) think we should not celebrate Australia Day on January 26.
By contrast, 74% of those over 75 said “disagree” or “strongly disagree” to any change with 70% of baby boomers (born 1946–65) also against change. The generation X cohort (born 1966–1985) was also decisively against change (64%), revealing a gulf between millennials and the rest of those surveyed.
One possible explanation for this is older people being more resistant to change. Their familiarity with Australia Day as an established end-of-summer day for social gathering is possibly stronger than their interpretation of the day’s historical significance or a political stance on the debate.
What does this mean?
These results also mirror other polls (with smaller sample sizes of about 1,200), including one by Roy Morgan in January 2021 and another by CoreData released over the weekend.
Younger Australians are more readily accepting of marriage equality, gender diversity and other kinds of progressive social change.
Recognising and responding to past injustices or complicated histories is familiar terrain for them. Rap group A.B. Original’s call-out of Australia Day, “January 26th,” came 16th place in Triple J’s Hottest 100 songs of 2016.
In 2018, the Hottest 100 was moved from the traditional January 26, after listeners expressed discomfort with holding the celebration on this date.
Other differences
Beyond generational differences, we also found gender and geography matter when it comes to attitudes about Australia Day.
Women were significantly more likely than men to want to change the date of Australia Day (43% compared to 33% men).
This is in keeping with studies showing women are more progressive than men.
Meanwhile, about 66% of those living outside capitals cities were opposed to changing Australia Day. This reduces to 60% opposed to change in capitals. This is driven by boomers in regional areas, who are significantly more opposed than boomers in cities.
More history, please
Importantly for the Australia Day question, we also asked about Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander history. More than 80% of those polled agreed more of this history should be taught in schools. Here there is less of a generation gap: almost 90% of millennials want more of this education, for boomers, it is nearly 80%.
Women and non-binary interviewees were still more likely to agree than men, by eight percentage points, and those in cities were six points ahead of those in regions.
But Australians are relatively united in their enthusiasm for greater teaching of Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander history.
Change is coming
We suggest our findings indicate a slow burn to change the date, based on strong foundations. While there remain differences among Australians, the combination of younger generational desire for change to Australia Day and strong enthusiasm among the broader population for more Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander history may suggest that change is not so far off.
Read more: Why Australia Day survives, despite revealing a nation's rifts and wounds
This slow pace for change probably suits the major political parties (but not so much the Greens).
A growing appetite for change may also indicate a discomfort with celebrating “Australia Day” at all. Luke Pearson, Gamilaroi man and founder of media organisation IndigenousX opposes simply changing the date. As he explained in 2019, there is still too little recognition of the harmful impact of colonisation and too little justice for Indigenous peoples for there to be any day to celebrate.
So, change the country first and then we can talk about a date.
David Lowe receives funding from the Australian Research Council.
Andrew Singleton receives funding from the Australian Research Council and the Gandel Foundation.
Joanna Cruickshank receives funding from the Australian Research Council.
This article was originally published on The Conversation. Read the original article.