What if I told you that the US military once launched a campaign called “Operation Toenails”? They aimed to capture a group of islands from the Japanese during World War II, and they succeeded. Feel free to look it up.
You’ll also find it on this list of weird government projects implemented worldwide over the years. While Operation Toenails was a success, many others weren’t. Like when India punished COVID-19 protocol violators by making them write “I’m sorry” 500 times.
Regardless of how they turned out, we now consider them some of the oddest governmental pursuits in human history. Enjoy these bits of trivia.
#1 Tourists In Rishikesh Punished With 'Sorry' 500 Times For Lockdown Breach
In a bizarre and controversial enforcement of India’s COVID-19 lockdown, foreigners caught violating restrictions in Rishikesh, a popular tourist destination, were ordered to write "I'm sorry" 500 times as punishment. This unusual penalty came after authorities found several tourists flouting the lockdown orders by strolling around the city, which had strict movement restrictions in place. The local police decided on this unusual form of discipline rather than imposing a fine or arrest, aiming to enforce the seriousness of adhering to public health regulations. The incident drew mixed reactions, with some seeing it as an over-the-top measure and others as a humorous, albeit unconventional, solution.

Image credits: Adam Withnall
#2 Operation Chaos
Operation CHAOS was a covert CIA program launched in the 1960s and continuing into the 1970s, aimed at monitoring and infiltrating anti-Vietnam War groups and domestic activist organizations within the United States. The operation sought to gather intelligence on individuals and groups that the government suspected of being sympathetic to or involved with communist movements. It involved extensive surveillance, wiretapping, and the infiltration of peace groups, student organizations, and civil rights movements. The operation was controversial for its violation of civil liberties and was eventually exposed by the Church Committee in 1975, leading to public outcry and government reforms on intelligence gathering.

Image credits: Wikipedia
#3 People In Home Quarantine In Karnataka Directed To Send Selfies Every Hour
In an attempt to enforce COVID-19 quarantine measures, the government of Karnataka introduced a policy requiring individuals in home quarantine to send selfies every hour. The move was designed to ensure compliance with isolation orders and prevent the spread of the virus. Those in quarantine were expected to send proof of their location and adherence to the rules through regular selfies, which were monitored by health authorities. While the initiative aimed to enhance public safety, it sparked concerns about privacy and surveillance. Nonetheless, it highlighted the challenges governments faced in managing quarantine during the pandemic.

Image credits: The Economic Times
Since we’re discussing oddly named government operations, we would be remiss if we didn’t include “Operation Chattanooga Choo-Choo.” In 1944, US and British fighter planes worked to limit Germany’s access to locomotives and reinforcements during the Second World War.
The operation was also a success, as hundreds of trains were destroyed, giving the Allied Forces a considerable advantage.
#4 Malaysian Government Lockdown Tips
In 2020, the Malaysian Ministry of Women, Family, and Community Development sparked controversy with a set of lockdown tips that included advice for women to wear makeup, dress neatly, and avoid nagging their husbands. The guidance, intended to help families cope with the stress of home confinement, was widely mocked for being outdated and reinforcing gender stereotypes. Critics, particularly women’s rights groups, condemned the tips as patronizing and out of touch with the realities of quarantine life. In response to the backlash, the ministry issued a public apology, acknowledging the tone was inappropriate for the situation.

Image credits: The Guardian
#5 Operation Northwoods
Operation Northwoods was a declassified Cold War-era proposal drafted in 1962 by the U.S. Department of Defense. The plan called for false flag attacks on American soil, including staged terrorist acts and fabricated civilian casualties, to justify military intervention against Cuba. Suggested tactics included sinking boats of Cuban refugees, orchestrating bombings in U.S. cities, and hijacking planes—all designed to blame Fidel Castro’s government and gain public support for war. The proposal was ultimately rejected by President John F. Kennedy, but it remains one of the most shocking examples of Cold War psychological warfare strategies.

Image credits: Wikipedia
#6 Operation Gold
Operation Gold was a covert Cold War-era intelligence operation led by the CIA and British intelligence in the early 1950s. The mission aimed to tap into East German and Soviet military communications by digging a tunnel under Berlin to intercept Soviet signals. The tunnel was equipped with advanced listening devices, and the plan was to secretly access the Soviet-controlled zone and gather vital intelligence on military activities. Unfortunately for the operation, the Soviets discovered the tunnel in 1956, but not before the CIA and MI6 had gathered a significant amount of intelligence. The operation's exposure led to major diplomatic tensions, but it also provided valuable insights into Soviet operations.
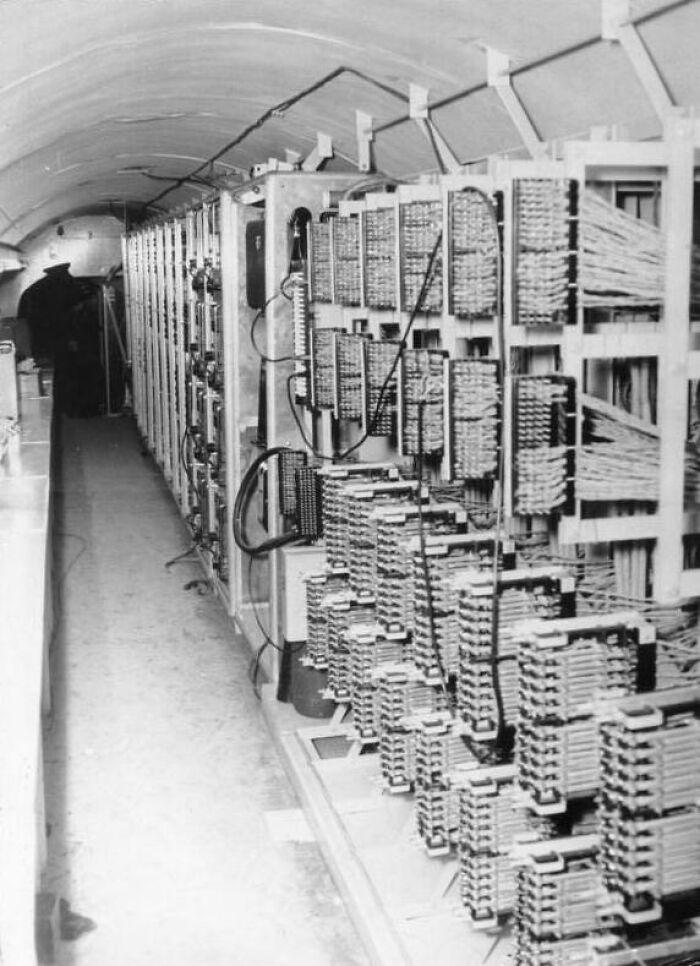

Image credits: Wikipedia
“Operation Menu” (a.k.a “Operation Breakfast”) happened on March 18th, 1969, when then United States President Richard Nixon ordered a secret carpet bombing in Cambodia. Their targets were bases controlled by Vietcong forces, as the US-Vietnam War was in full swing.
The US dropped more than 2,000 tons of bombs, a resounding success that prompted the American government to launch more missions, aptly named Operations Lunch, Snack, Dinner, and Dessert.
#7 Operation Plumbbob
Operation Plumbbob was a series of nuclear tests conducted by the U.S. government between 1957 and 1958 at the Nevada Test Site. The operation consisted of 29 tests, including both atmospheric and underground explosions. One of the most infamous aspects of Plumbbob was the “Smoky” test, which was a high-altitude detonation that led to radioactive fallout affecting nearby areas. The operation also included human radiation experiments, where soldiers and civilians were exposed to nuclear tests to study their effects. Though it helped advance nuclear weapons development, Operation Plumbbob faced criticism for its impact on human health and the environment, and it remains a dark chapter in Cold War history.
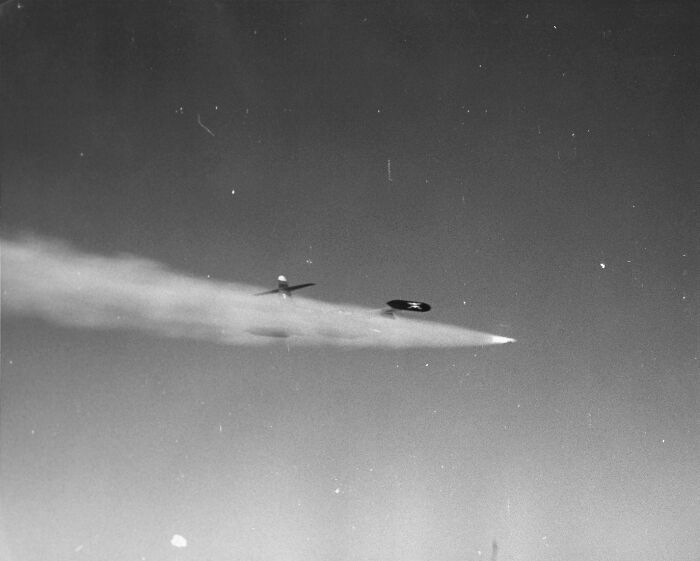

Image credits: Wikipedia
#8 Infecting Children With Hepatitis At The Willowbrook State School For Children
In the 1950s and 1960s, the Willowbrook State School in Staten Island, New York, became infamous for conducting controversial and unethical medical experiments on children with intellectual disabilities. One of the most notorious studies involved deliberately infecting children with the hepatitis virus to study the progression of the disease. Researchers believed this would help develop a vaccine, but the children were not informed or given consent. The experiments were led by Saul Krugman, a pediatrician who justified the research on the grounds of its potential benefits. The scandal was revealed in the 1970s, sparking public outrage and leading to major reforms in medical ethics.
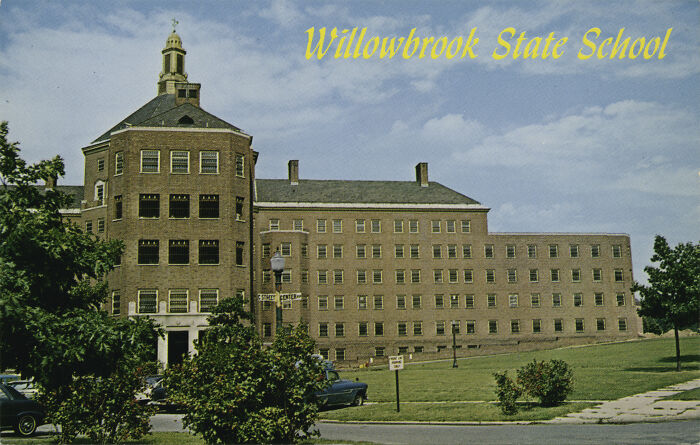

Image credits: Wikipedia
#9 Operation Midnight Climax
Operation Midnight Climax was a secret CIA experiment during the 1950s, part of the larger MKUltra program, focused on mind control. The operation involved setting up "safe houses" in San Francisco, where agents secretly lured unsuspecting civilians into rooms, where they were dosed with LSD without their knowledge. The goal was to study the effects of the drug on behavior and extract information. The experiment was controversial and ethically dubious, as it violated individuals' rights. When the operation was exposed, it sparked public outrage, contributing to growing distrust in government covert activities during the Cold War era.
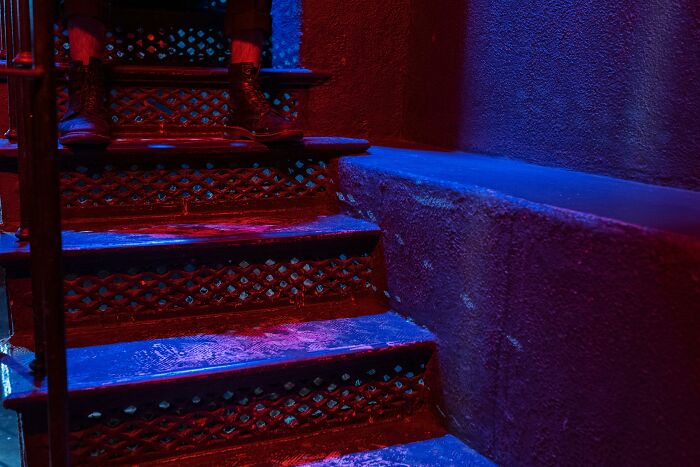

Image credits: Wikipedia
In 1967, then-FBI director J. Edgar Hoover came up with a surveillance program aimed to curb the destruction brought about by race riots. He named this project the “Ghetto Informant Program,” where he involved African-Americans whom he deemed reliable in reporting unrest in poor neighborhoods.
The operation ultimately failed as the FBI’s inspection expressed their concerns about the possible dangers of using African-Americans as informants. The bureau ultimately pulled the plug in 1972.
#10 The Poop Plane
The XF-84H, also known as the "Poop Plane," was a prototype aircraft developed by the U.S. Air Force in the 1950s. It was a modified version of the F-84 Thunderjet, designed to test a turbo prop engine. However, the plane earned its nickname due to the incredibly loud and disturbing noise produced by its engine, which was so intense it caused a physical vibration that made it nearly impossible for pilots to fly without ear protection. The deafening sound was often compared to the smell of feces, which led to its unfortunate nickname. Due to its unmanageable noise, the project was eventually canceled.
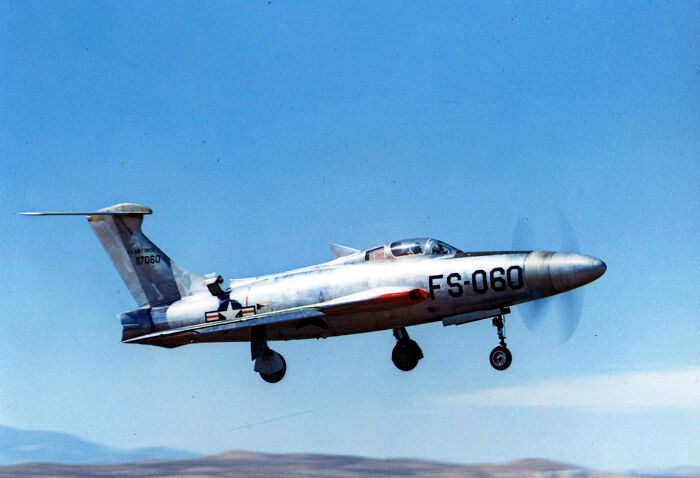

Image credits: Stephan Wilkinson
#11 Danish Police Asked For Proof Of Relationship From Visitors
In a compassionate move, Denmark allowed couples separated by borders to reunite during the COVID-19 pandemic, but with a catch: they had to prove they had been in a relationship for at least six months. This policy, aimed at reuniting "sweethearts" who had been kept apart by travel restrictions, required couples to provide evidence of their relationship through photos, messages, and other documentation. While the rule was celebrated by many, it also sparked debates about privacy and fairness. Nevertheless, the decision reflected Denmark's efforts to prioritize emotional connections while balancing public health concerns.
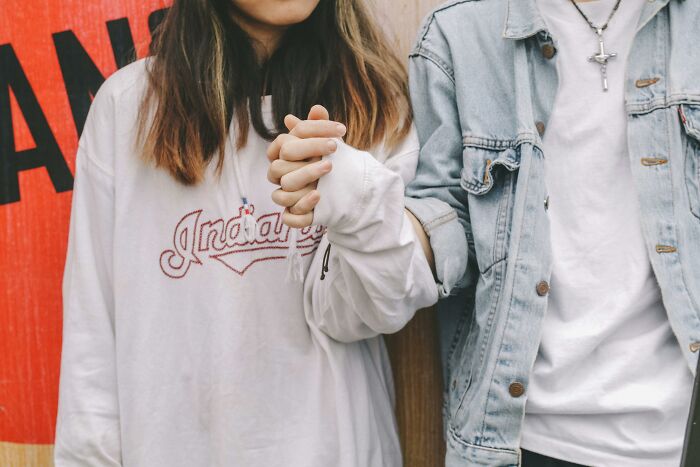

Image credits: Lauren Kent
#12 Project Sunshine
Project SUNSHINE was a secret Cold War-era study conducted by the U.S. government in the 1950s to assess the effects of nuclear fallout on human tissue. The project involved collecting bones and tissue samples, often from deceased infants and young children, to measure radioactive contamination caused by nuclear tests. In many cases, these samples were taken without parental consent, sparking ethical outrage when the program was later exposed. The findings helped scientists understand the dangers of strontium-90, a radioactive isotope, but the project remains infamous for its disturbing methods and lack of transparency.
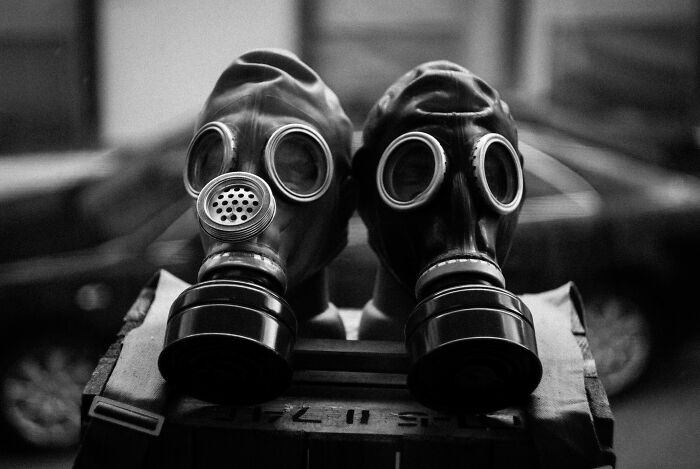

Image credits: Wikipedia
The late great Muhammad Ali had been vocal about his stance against America’s efforts during the Vietnam War in the 1960s. Apart from losing his world title and three prime years of his fighting career, the National Security Agency (NSA) also tapped into his overseas phone calls.
These spying efforts were part of Operation Minaret, which targeted critics of the Vietnam War. Along with Ali, the NSA also monitored the phone calls of Martin Luther King Jr. and other government officials.
#13 Project 112
Project 112 was a series of secret U.S. military experiments conducted in the 1960s and 1970s to test the effects of chemical and biological agents on military personnel and equipment. The project involved a wide range of testing, including exposure to nerve agents, biological toxins, and environmental contamination from chemical weapons. One of the most notorious sub-projects under Project 112 was Project SHAD (Shipboard Hazard and Defense), which tested the vulnerability of Navy ships and their crews to chemical and biological agents in simulated battlefield conditions. Many of the tests were conducted without proper warnings or consent from the individuals involved. The project remained classified for decades, and only in the 1990s were the details revealed, leading to public outcry and concerns over the health effects on the participants.
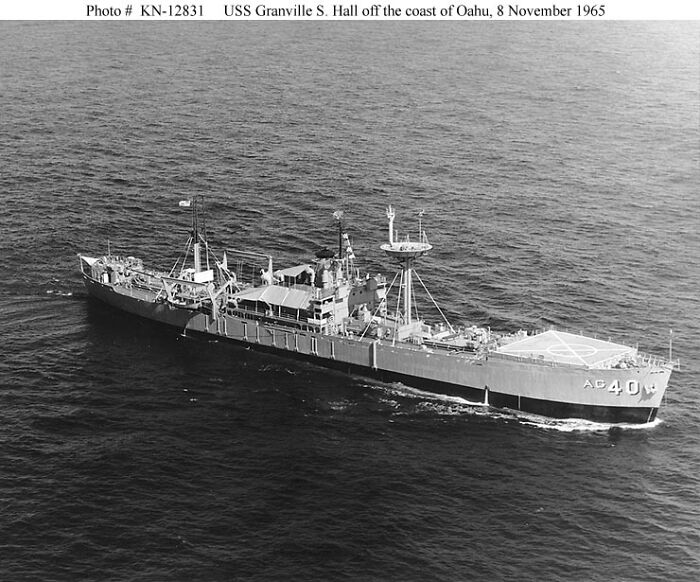

Image credits: Wikipedia
#14 Manhattan Project
The Manhattan Project was a top-secret U.S. research and development initiative during World War II (1942-1946) aimed at creating the first nuclear weapons. Spearheaded by the U.S., with support from the UK and Canada, the project culminated in the successful development of the atomic bomb. The project brought together some of the world’s brightest scientists, including J. Robert Oppenheimer, who led the Los Alamos laboratory. The first test of a nuclear weapon, known as the Trinity Test, took place in 1945 in New Mexico. The bombs created under the Manhattan Project were used on Hiroshima and Nagasaki, leading to Japan’s surrender.

Image credits: Wikipedia
#15 La Paz Traffic Zebras
The traffic zebras of La Paz, Bolivia, are a unique and heartwarming initiative aimed at improving pedestrian safety. In this program, young people, often dressed in zebra-striped costumes, act as traffic guides at busy intersections. They help pedestrians cross streets safely, assist drivers in managing traffic, and raise awareness about road safety. The traffic zebras have become a beloved part of the city’s culture, symbolizing both community involvement and the importance of safety in a fun and engaging way. This creative solution has been praised for its impact on both reducing accidents and fostering a sense of civic responsibility.
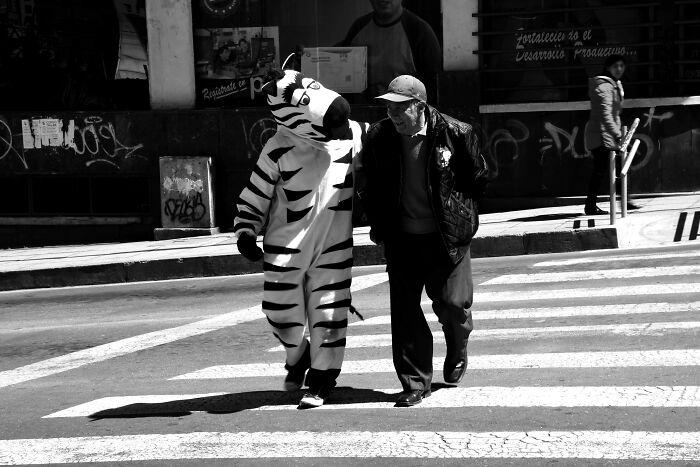

Image credits: Wikipedia
We’d also like to hear your thoughts, dear readers. Which of these weird government operations did you find most intriguing? Share your thoughts in the comments, and feel free to add to this list!
#16 Super Bowl Ad
In an expensive effort to boost participation, the U.S. Census Bureau spent $2.5 million on a Super Bowl ad in 2010. The commercial aimed to raise awareness about the importance of the census and encourage Americans to respond. However, the ad received widespread criticism for being vague and unmemorable, with many questioning whether it justified its massive price tag. Lawmakers and watchdog groups accused the Census Bureau of wasting taxpayer money on ineffective outreach. Despite the backlash, officials defended the expenditure, arguing that an accurate count was crucial for federal funding and representation.

Image credits: CBS News
#17 Operation Paperclip
Operation Paperclip was a secret U.S. intelligence program that recruited over 1,600 German scientists, engineers, and technicians—many of whom had worked for Germany—after World War II. The goal was to leverage their expertise in rocketry, aerospace, and weapons technology to gain an advantage in the Cold War, particularly against the Soviet Union. Among the recruits was Wernher von Braun, who played a key role in developing NASA’s Saturn V rocket. While the program contributed to U.S. technological advancements, it was highly controversial, as many of the scientists had direct ties to war crimes and human experimentation under the Nazi regime.
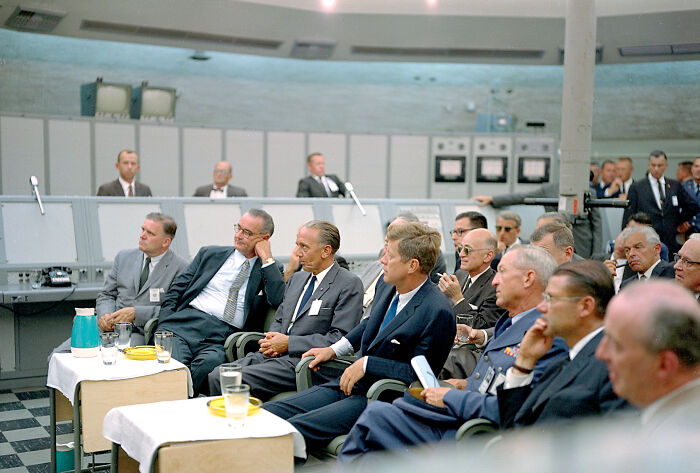

Image credits: Wikipedia
#18 Project Azorian
Project Azorian was a secret U.S. government operation in the early 1970s, designed to recover a Soviet submarine that had sunk in the Pacific Ocean. The submarine, known as the K-129, was lost in 1968 with all hands aboard. The CIA, in partnership with a private company, designed a specialized ship called the Glomar Explorer to retrieve the sub and its valuable intelligence, including nuclear missile technology. The operation was highly classified, and its existence was kept secret until it was revealed in 1975. Although the operation was only partially successful, it remains one of the most ambitious and secretive efforts in Cold War espionage.

Image credits: Wikipedia
#19 Operation Big Itch
Operation Big Itch was a U.S. military biological warfare experiment conducted in 1954. The operation aimed to test the effectiveness of aerosolized fleas as a potential biological weapon. The military released infected fleas over a desert area in Utah, with the goal of studying how easily they could spread diseases like plague. The experiment involved dropping fleas from planes, allowing them to land in the target area. Though the operation was not intended to target civilians, it raised ethical concerns and questions about the use of biological agents. The operation's details remained classified for many years, contributing to the controversy surrounding its execution.
Image credits: Wikipedia
#20 Operations Dew I And Dew II
Operations DEW I and DEW II were top-secret U.S. military operations in the early 1950s, designed to test the capabilities of the Distant Early Warning (DEW) Line, a system of radar stations set up across the Arctic to detect incoming Soviet bombers during the Cold War. DEW I focused on the initial construction of the radar stations across Canada and Alaska, intended to provide early warning of potential air attacks from the Soviet Union. DEW II, launched shortly after, involved improving the system’s technology and ensuring its effectiveness by conducting tests under extreme cold weather conditions. These operations were crucial in bolstering the U.S.'s defense strategy during the Cold War and formed the backbone of North America's early missile defense systems.
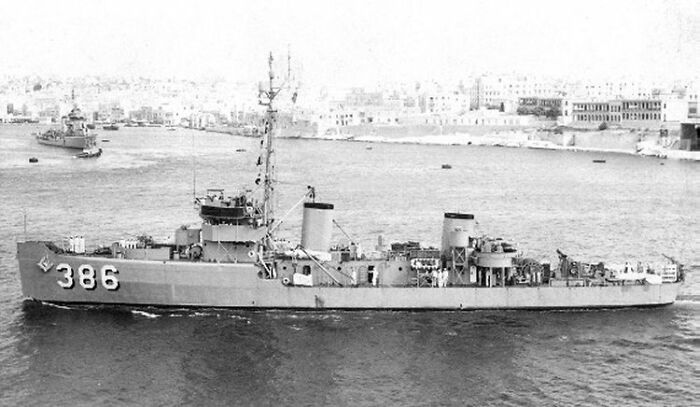

Image credits: Wikipedia
#21 Operation Toenails
Operation Toenails was a 1943 U.S. military campaign during World War II, aimed at capturing the New Georgia Islands in the Solomon Islands from Japanese forces. The operation involved U.S. Marines and Army units, who faced fierce resistance in dense jungle terrain. The primary objective was to secure the islands for future Allied operations and disrupt Japanese control over crucial Pacific sea routes. Despite the challenges of jungle warfare and heavy casualties, the operation succeeded in weakening Japanese positions and was a key step in the Allied push toward the eventual liberation of the Solomon Islands.

Image credits: Wikipedia
#22 Recovered From Coronavirus
In a controversial move during the COVID-19 pandemic, the Chilean government faced criticism for counting individuals who had died from the virus as "recovered" in official statistics. The government explained that the deaths were counted as recoveries because they had occurred more than 28 days after a positive test, a method based on technical definitions used for reporting purposes. However, this approach led to widespread confusion and concerns about the accuracy of the country’s COVID-19 data. Critics argued that it misrepresented the true scale of the pandemic's impact, highlighting the challenges of managing public health data amid a global crisis.

Image credits: Vincent Barone
#23 Hawaii Is Paying To Get People Off The Island
In a bold move to combat overcrowding, the Hawaii Tourism Authority began paying tourists to leave the islands. The initiative was launched to alleviate the pressure on local resources, reduce environmental strain, and ensure a more sustainable travel experience. Tourists who overstayed their welcome or booked long stays during peak seasons were offered financial incentives to return home earlier. This unusual program aims to balance tourism with the needs of the local community, preserving the islands' natural beauty and improving quality of life for residents. The initiative received mixed reactions but highlights Hawaii’s unique approach to managing tourism.

Image credits: Andy Rose and Leah Asmelash
#24 Tunisia Deployed Robot To Enforce Lockdown
To enforce its strict COVID-19 lockdown measures, Tunisia deployed a "robocop" style robot in the streets to monitor and control movement. The robotic enforcer, designed to check individuals' IDs and ensure compliance with lockdown orders, was part of a broader strategy to reduce human-to-human contact while maintaining order. The robot was equipped with surveillance technology, including cameras and speakers, to issue warnings and remind citizens of the importance of staying indoors. While the move attracted attention for its futuristic approach, it also raised questions about privacy and the use of technology in public safety during a health crisis.

Image credits: The Guardian
#25 Venezuela Created Orwellian Ministry Of Supreme Social Happiness
In a move that raised concerns about government overreach, Venezuela introduced the Ministry of Supreme Social Happiness, a new governmental body focused on ensuring the "happiness" of its citizens. The Orwellian-sounding ministry's mandate included overseeing social programs, managing the public's well-being, and promoting a sense of national unity and happiness. Critics quickly pointed out the potential for abuse of power and the risk of using the ministry as a tool for political control, with its vague and broad mission. Supporters argued it could help address the country’s social issues, though many remained skeptical about its true intent.

Image credits: Emily Thomas
#26 Party In Vegas
In a scandalous move, the General Services Administration (GSA) was revealed to have thrown an extravagant $800,000 party in 2010, funded by taxpayer money. The event, held in Las Vegas, included lavish accommodations, entertainment, and other costly indulgences, sparking outrage when the details were exposed. Critics slammed the GSA for its wasteful spending at a time when the country was grappling with economic challenges. The incident led to widespread public backlash and congressional hearings, ultimately forcing several GSA officials to resign. The party became a symbol of government excess and mismanagement, leaving taxpayers with the hefty bill.

Image credits: Courtney Subramanian
#27 Let's Stockpile Toilet Paper!
In 2011, following the catastrophic earthquake and tsunami in Japan, citizens began stockpiling toilet paper in response to widespread panic. Concerns about supply chain disruptions and rumors suggesting that toilet paper could become scarce led people to flood stores, purchasing large quantities. This phenomenon was fueled by anxiety over the ongoing crisis, even though there were no actual shortages. The Japanese government and retailers quickly reassured the public that toilet paper supplies were unaffected, but the hoarding continued for weeks. The event became a notable example of how fear can sometimes lead to irrational consumer behavior during times of crisis.

Image credits: BBC
#28 Operation Christmas
Operation Christmas, launched by the Colombian military in December 2010, was a unique and heartwarming campaign aimed at encouraging FARC guerrillas to demobilize. The military strategically placed nine 75-foot Christmas trees along paths frequently used by insurgents. Each tree was adorned with festive lights and displayed a message inviting the guerrillas to come home and rejoin society. This symbolic gesture, set against the backdrop of the holiday season, aimed to appeal to the insurgents’ humanity, offering a peaceful alternative to continuing the armed conflict. The campaign reflected Colombia's creative approach to promoting peace and reconciliation during a challenging time.

Image credits: Wikipedia
#29 $28m' Camouflaged Uniforms
In a costly misstep, the Pentagon spent $28 million on camouflage uniforms for the Afghan military that were poorly suited for the country's terrain. The uniforms featured a "forest" pattern, despite Afghanistan being largely desert and mountainous. The decision was based on a preference expressed by an Afghan official rather than strategic necessity. Since the pattern was privately owned, the U.S. also had to pay licensing fees. A government watchdog later criticized the spending as wasteful, highlighting it as an example of mismanagement in U.S. efforts to equip Afghan forces during the war.

Image credits: BBC
#30 Mistake That Costed $4 Million
In a controversial move, the U.S. government paid CGI Federal, the same contractor responsible for the flawed launch of HealthCare.gov, an additional $4 million to fix the very issues it had created. The healthcare website, a key component of the Affordable Care Act, was plagued by technical failures upon its 2013 debut, preventing millions from accessing insurance enrollment. Despite its initial failures, CGI Federal was awarded more funds to repair the site, sparking criticism over government mismanagement and lack of accountability. The incident became a symbol of bureaucratic inefficiency in handling major public projects.

Image credits: John Tozzi
#31 Star Trek Parody Went Wrong
In a bizarre misuse of taxpayer funds, the IRS produced a "Star Trek" parody video in 2010, costing an estimated $60,000. The five-minute video, intended as a training tool, featured IRS employees in Starfleet uniforms aboard a poorly designed USS Enterprise set. Meant to educate staff on tax procedures, it was widely criticized as an unnecessary waste of government resources. After public backlash and congressional scrutiny, the IRS admitted the video was a mistake. The controversy became a symbol of government excess, raising questions about how federal agencies allocate taxpayer money for internal projects.

Image credits: Kelly Phillips Erb
#32 Operation Mockingbird
Operation Mockingbird was a covert CIA program launched in the late 1940s aimed at influencing media and controlling public perception during the Cold War. The agency secretly recruited journalists from major news outlets—including The New York Times, The Washington Post, and Time—to spread pro-American propaganda, suppress unfavorable stories, and shape public opinion. The operation also funded student organizations, cultural programs, and foreign media to counter Soviet influence. Though the CIA officially ended direct media manipulation in the 1970s, revelations about Operation Mockingbird fueled concerns about government control over the press and the ethics of state-sponsored disinformation.

Image credits: Wikipedia
#33 Project Greek Island
Project Greek Island was a top-secret U.S. government initiative during the Cold War to construct a massive underground bunker designed to shelter Congress in the event of a nuclear attack. Built beneath The Greenbrier, a luxury resort in West Virginia, the facility was equipped with dormitories, a cafeteria, meeting rooms, and a fully functional legislative chamber. The project remained classified for over 30 years until it was exposed by a journalist in 1992, rendering it obsolete. Though never used for its intended purpose, the bunker symbolized Cold War-era preparations for continuity of government in case of catastrophe.

Image credits: Wikipedia
#34 Operation Merlin
Operation Merlin was a covert CIA operation that took place in the late 1990s, aimed at disrupting Iran's efforts to develop nuclear weapons. The operation involved providing Iran with flawed blueprints for a key component of a nuclear weapon, the detonation system. The intention was to mislead Iranian scientists and sabotage their nuclear program. However, the operation became highly controversial after the flawed plans were delivered, and it was later revealed that the operation was compromised. The flaws in the design were not immediately recognized by the Iranians, but eventually, the operation’s exposure raised serious questions about its effectiveness and the risks involved in such operations.

Image credits: Wikipedia
#35 Project Artichoke
Project Artichoke was a CIA-led operation in the 1950s, focused on researching methods of mind control and interrogation techniques. It was part of a broader set of experiments exploring the use of drugs, hypnosis, and psychological manipulation to extract information from subjects. The project predated the more infamous MKUltra program and involved experiments with substances like LSD, alongside other forms of coercion, on both willing participants and unwitting civilians. The goal was to develop ways of controlling individuals' thoughts and behaviors, particularly for use in espionage and interrogation. The project's existence remained secret until the 1970s, leading to public outrage and congressional hearings on the CIA’s covert activities.

Image credits: Wikipedia
#36 Operation Paul Bunyan
Operation Paul Bunyan was a U.S. military operation in 1976, designed to defuse tensions along the Korean Demilitarized Zone (DMZ) after the Axe Murder Incident, where two U.S. soldiers were killed by North Korean troops. In response, the U.S. launched Operation Paul Bunyan, which was primarily a show of strength rather than a military confrontation. The operation involved the cutting down of a large poplar tree in the DMZ, which was the site of the attack. To ensure the operation's safety, the U.S. deployed a heavily armed convoy of soldiers and aircraft. Despite its name, which humorously referenced the folklore lumberjack, the operation demonstrated the U.S.'s readiness to act forcefully in defense of its interests, without direct military escalation.
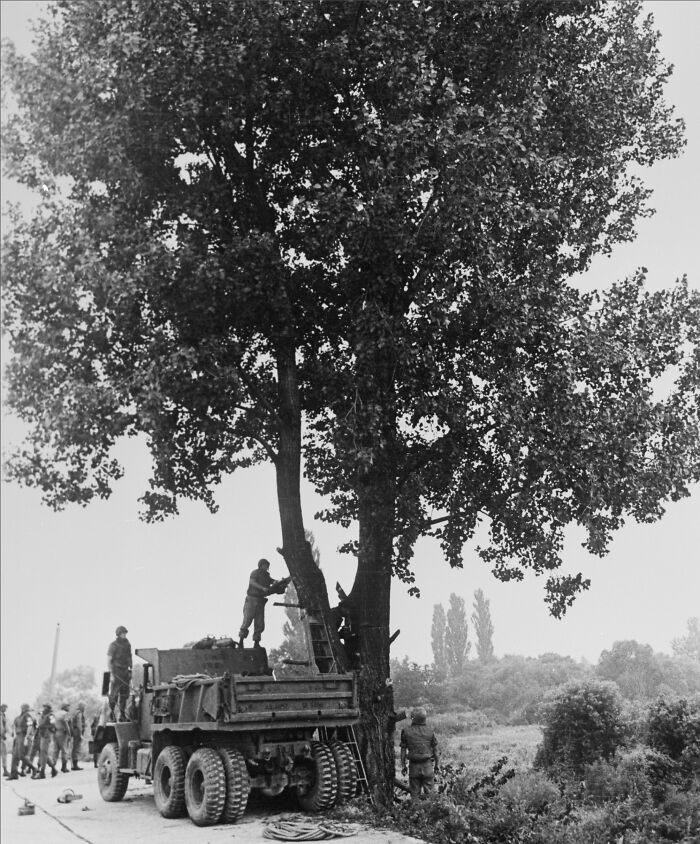

Image credits: Wikipedia
#37 Operation Acoustic Kitty
Operation Acoustic Kitty was a CIA project in the 1960s that aimed to use cats as surveillance devices. The idea was to implant microphones and transmitters into live cats, turning them into covert listening agents that could eavesdrop on Soviet or enemy conversations. The CIA’s plan was to train these cats to infiltrate specific locations, like embassies, and spy on high-ranking officials. However, the operation quickly encountered challenges: the first field test ended disastrously when the cat was hit by a car. The program was eventually deemed a failure and discontinued, making it one of the more bizarre and unsuccessful espionage efforts of the Cold War.

Image credits: Wikipedia
#38 Qattara Depression Project
The Qattara Depression Project was an ambitious engineering initiative in Egypt during the mid-20th century. The idea was to harness the Qattara Depression, one of the lowest points in Africa, to generate hydroelectric power and alleviate water shortages. The plan involved using seawater to flood the depression, creating a massive lake, and then using the height difference to drive turbines for power generation. Despite its bold vision, the project faced major technical, environmental, and financial challenges and was ultimately abandoned. Today, the Qattara Depression remains an intriguing symbol of unfulfilled potential in large-scale engineering.

Image credits: Wikipedia
#39 Päntsdrunk
"Päntsdrunk" is a peculiar and unofficial government initiative that emerged in Finland as part of a broader cultural and wellness campaign aimed at reducing stress and promoting mental health. The project, although informal, encouraged citizens to embrace relaxation at home by drinking alcohol in the comfort of their own space—preferably in pajamas. The idea was to combat the pressures of modern life by fostering a laid-back, stress-free environment where individuals could unwind without social obligations. While not an officially funded government program, the concept of "Päntsdrunk" became widely discussed as a reflection of Finland's approach to balancing work-life stress and leisure.

Image credits: Rosie Fitzmaurice
#40 Stargate Project
The Stargate Project was a secret U.S. government program initiated in the 1970s and focused on exploring psychic phenomena, particularly "remote viewing"—the ability to perceive or describe distant locations without using the traditional five senses. Funded by the CIA and later transferred to the Defense Intelligence Agency (DIA), the project involved training individuals to use these purported abilities for military and intelligence purposes. Despite some intriguing results, the project was eventually declassified in the 1990s, leading to skepticism and controversy. Although it was officially closed in 1995, the Stargate Project became the subject of popular interest, inspiring books, films, and conspiracy theories.

Image credits: Wikipedia
#41 Facebook Likes
An Inspector General report revealed that the U.S. State Department spent $630,000 between 2011 and 2013 to boost its Facebook presence by purchasing "likes." The campaign aimed to increase engagement on pages promoting American policies and diplomacy, but much of the engagement came from users who had no real interest in the content. Critics slammed the spending as wasteful, arguing that organic engagement—not paid popularity—should be the priority. The report highlighted concerns about inefficient use of taxpayer funds, prompting calls for the State Department to reconsider its social media strategy and spending habits.

Image credits: Josh Hicks
#42 Madrid Open-Air Cinema
In response to the COVID-19 lockdowns, Madrid staged a unique open-air cinema experience for locals who were confined to their homes. The initiative aimed to bring a sense of normalcy and entertainment to residents during the strict stay-at-home orders. Outdoor screenings were set up across the city, allowing people to enjoy movies from the safety of their balconies, windows, or nearby public spaces while adhering to social distancing measures. The project was seen as a creative solution to combat isolation and provide a collective cultural experience during a time of uncertainty, offering a bit of joy in an otherwise challenging period.
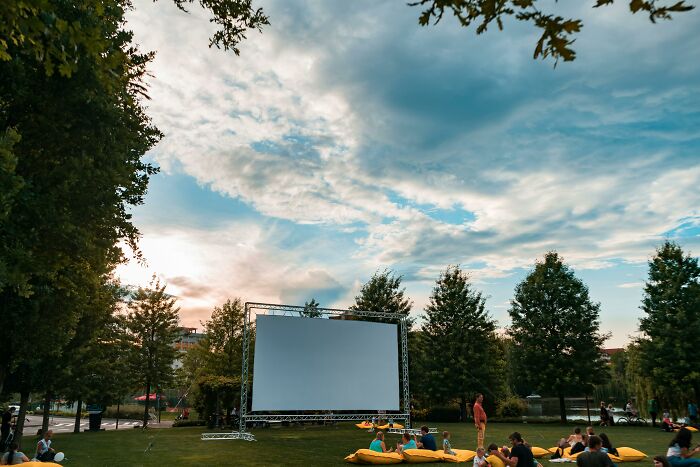

Image credits: Euronews
#43 Australia Is Moving Homeless People Into Five-Star Hotels
In a surprising and compassionate move during the COVID-19 pandemic, Australia’s government decided to move homeless individuals into five-star hotels to help protect them from the virus. With many shelters unable to meet social distancing requirements, the government arranged temporary accommodations in luxury hotels, providing safe and comfortable living conditions for those in need. The initiative was praised for its innovative approach, offering homeless individuals a rare opportunity for stability and privacy. It also helped reduce the risk of virus transmission in overcrowded shelters, highlighting a proactive response to public health and social welfare challenges.

Image credits: Andy Gregory
#44 Press Conference For Children
In a heartwarming move during the COVID-19 pandemic, Finnish Prime Minister Sanna Marin held a press conference specifically aimed at children. The event was designed to provide young people with clear, age-appropriate information about the pandemic and the government's measures to keep them safe. Marin’s approach, focusing on empathy and communication, addressed common questions children might have about the virus, school closures, and social distancing. It was seen as a refreshing and responsible way to engage younger generations in the midst of a global crisis, ensuring they felt informed and reassured during uncertain times.

Image credits: this is Finland
#45 AI Matchmaker
In response to Japan's ongoing demographic crisis, the government has decided to fund AI-based matchmaking services to help boost the country's declining birth rate. The initiative will use artificial intelligence to pair singles based on compatibility, with the goal of encouraging more marriages and family growth. Japan’s aging population and low fertility rate have been significant challenges, and this high-tech solution is seen as a way to modernize matchmaking efforts. By integrating AI, the government hopes to offer tailored match suggestions, making it easier for individuals to connect and form lasting relationships.

Image credits: BBC







