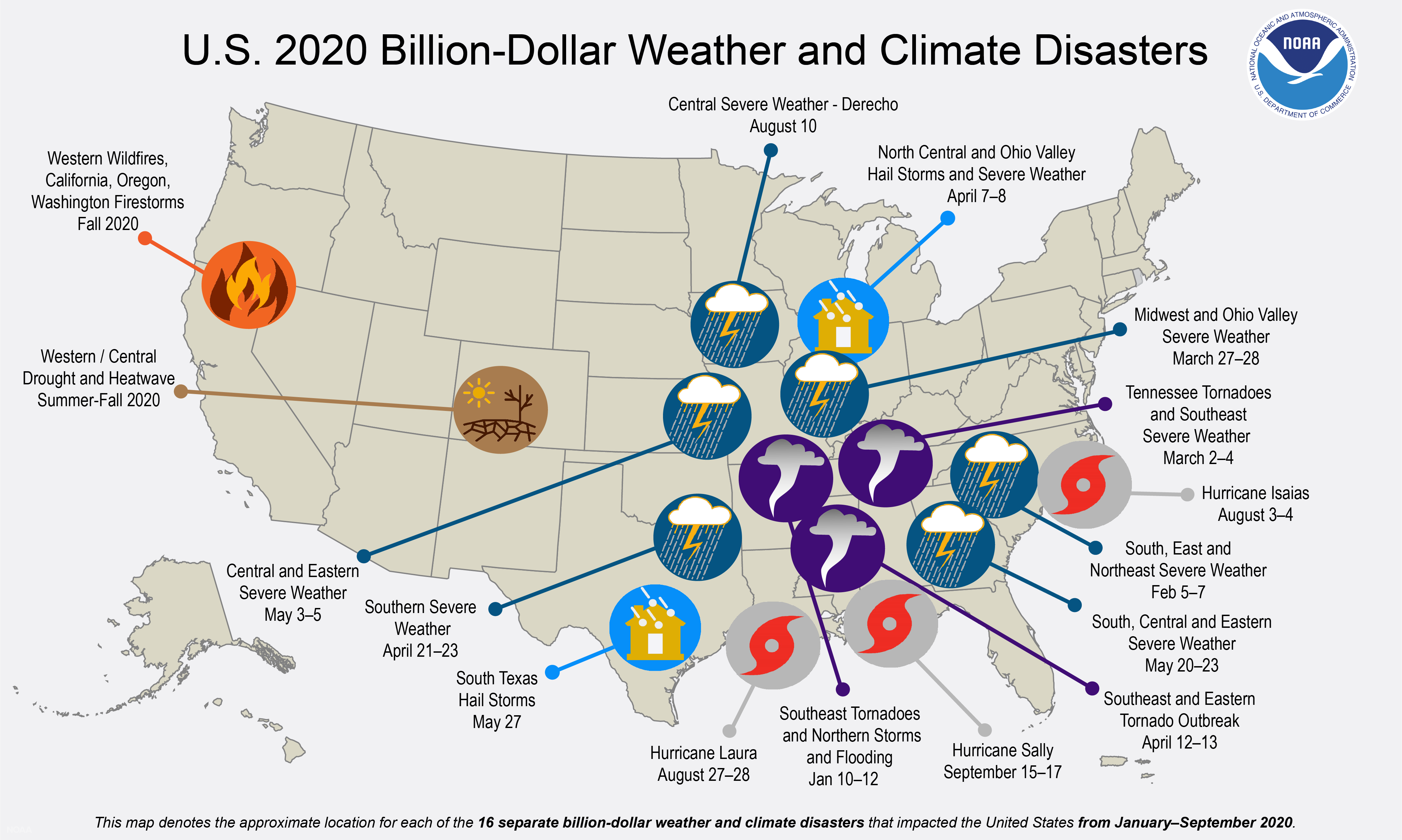
The number of climate change-driven disasters and extreme weather events costing in excess of a billion dollars, has beaten the annual US record in the first nine months of 2020 - with another two months of wildfire and hurricane season still to come.
The price tag of the disasters was totted up by scientists at the National Centers for Environmental Information (NCEI), part of the federal National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA).
Six of those events - unprecedented wildfires in the American West, a drought and heatwave across the west and central belt, a Midwest derecho, then Hurricanes Sally, Laura and Isaias - have all happened in the past three months.
The first nine months of 2020 are already tied with the annual record of 16 events that occurred in 2011 and 2017.

2020 is also the sixth year in a row where the US has experienced ten or more billion-dollar weather and climate disasters, NCEI reported.
As of 7 October, each of the events had losses exceeding $1bn - one drought, 11 severe storms, three tropical cyclones, and the wildfires. The disasters have resulted in 188 deaths.
Many of the costs are still to be determined, notably in western states where wildfires are still raging and have consumed more than 4 million acres in California alone since the beginning of the year.
Meanwhile in the Gulf of Mexico, Hurricane Delta has strengthened to a category-2 and is forecast to make landfall in Louisiana on Friday.
The billion-dollar weather and climate disasters of 2020
Fall: Wildfires in California, Oregon, Washington
41 Deaths
Total Estimated Costs: TBD
The wildfires this fall spread rapidly and destroyed several small towns in California, Oregon and Washington.
Since mid-August historic wildfires have burned more than 4 million acres in California, more than doubling the statewide record from 2018. Five of the six largest wildfires on record in California burned in the past two months.
The August Complex, which began as 37 separate wildfires has now been classified as a “gigafire” after burning through more than a million acres. More than 8,500 structures have been destroyed across California.
In Oregon, historic wildfires have burned more than 2,000 structures. Dense wildfire smoke has also produced hazardous air quality affecting millions of people for weeks.
Summer-Fall 2020: Western/Central Drought and Heatwave -Widespread
Deaths: TBD
Total Estimated Costs: TBD
Continuous drought and record heat affected more than a dozen Western and Central states for much of the summer and early fall. Death Valley recorded a temperature of 130F - what is believed to the highest temperature ever record.
Los Angeles county recorded a record high of 121F. There may be a significant fatality total resulting from persistent, excessive heat over large population centers. The drought and heat also helped to dry out vegetation across the West that contributed to the Western wildfire potential and severity.
September 2020: Hurricane Sally - Florida Panhandle, Alabama, Georgia
5 Deaths
Total Estimated Costs: TBD
A category 2 hurricane at landfall with winds up to 100 mph and 20-30 inches of rainfall.The storm caused considerable flood and wind damage across the panhandle of Florida, into Alabama and Georgia. Many homes and businesses in downtown Pensacola, Florida were impacted by storm surge and heavy rainfall. 2020 is now the fourth consecutive year (2017-2020) that the U.S. has been impacted by a slow moving tropical cyclone that produced extreme rainfall and damaging floods, following Harvey, Florence, Imelda and Sally.
August 2020: Hurricane Laura - Louisiana, Texas, Mississippi, Arkansas
42 deaths
Total Estimated Costs: $14bn
The powerful category-4 made landfall at Cameron Parish, in southwestern Louisiana bringing winds up to 150 mph and storm surge in excess of 15 feet. There was catastrophic damage along the coast as well as inland to the city of Lake Charles. Broken water systems and severely damaged electrical grid in the region will slow the recovery process. Laura also had highest landfall wind speed to impact the US since Hurricane Michael in 2018
August 2020: Derecho - most affected - South Dakota, Iowa, Illinois, Minnesota, Indiana and Ohio
4 deaths
Total Estimated Costs: $7.5bn
A powerful derecho traveled from southeast South Dakota to Ohio, a path of 770 miles in 14 hours producing widespread winds greater than 100 mph. It caused widespread damage to farming operations including millions of acres of corn and soybean crops across central Iowa. There was also severe damage to homes, businesses and vehicles particularly in Cedar Rapids, Iowa. In addition, there were 15 tornadoes across northeastern Illinois several affecting Chicago metropolitan area
August 2020: Hurricane Isaias - North Carolina, New York, New Jersey, Pennsylvania
16 deaths
Total Estimated Costs: $4.5bn
Isaias made landfall in southeastern North Carolina as a category 1, then accelerated up the East Coast. There was also considerable inland flooding particularly in Pennsylvania. In addition, 34 tornadoes developed across North Carolina, Virginia, Maryland, Delaware and New Jersey. Many tornadoes were weaker with scattered damage to agriculture, structures and residences. Isaias also produced several EF-2 tornadoes and one EF-3 tornado that caused damage in coastal North Carolina and Virginia
May 2020: Hail storms - South Texas
0 deaths
Total Estimated Costs: $1.4bn
Golf-ball sized hail pounded several cities. The highest concentration of hail damage to homes, businesses and vehicles occurred across the northern portion of the San Antonio. There was also significant damage east of San Marcos, southeast of Waco and to the west and south of Bryan and College Station
May 2020: Thunderstorms, wind, hail and tornadoes - Southern, Central and Eastern states
2 deaths
Total Estimated Costs: $1.6 Billion
The states most affected included Texas, Illinois and North Carolina with damage to homes, businesses and vehicles. Oklahoma, Arkansas, Indiana, Tennessee, Alabama, Georgia, Florida and South Carolina.
May 2020: Severe weather - Central and Eastern states including Kansas, Missouri, Arkansas, Tennessee and South Carolina
2 deaths
Total Estimated Costs: $2.1bn
High winds and hail slammed southern Missouri and western to central Tennessee
April 2020: Severe Weather - many Southern states
3 deaths
Total Estimated Costs: $1.4bn
High winds, hail and tornadoes blasted Texas, Oklahoma, Louisiana, Mississippi, Alabama, Georgia, Florida and Virginia. The states with the highest damage totals for the event were Oklahoma, Louisiana and Texas
April 2020: Tornado outbreak - southeast and eastern states
35 deaths
Total Estimated Costs: $3.5bn
At least 140 tornadoes tore through states from Texas to Maryland. Highly destructive to many homes, vehicles and businesses
April 2020: Hail Storms and Severe Weather - Illinois, Iowa, Indiana, Ohio, Michigan, Wisconsin and Missouri
0 deaths
Total Estimated Costs: $2.9bn
More than 20 tornadoes across southern Indiana and Ohio. Widespread high wind damage to homes, vehicles and businesses in many other surrounding states
March 2020: Severe weather - mainly Midwest and Ohio Valley
0 deaths
Total Estimated Costs: $2.6bn
A combination of high winds and hail blasted Missouri, Ohio and Arkansas. There were also two dozen tornadoes across Iowa, Illinois, Indiana and Arkansas causing additional damage
March 2020: Tornadoes, severe weather - Tennessee, Alabama, Kentucky, Mississippi and Missouri
25 Deaths
Total Estimated Costs: $2.4bn
EF-3 and EF-4 tornadoes cause considerable damage across Nashville and several counties to the east. This damage included many homes, businesses, vehicles, 90 planes and numerous buildings at the Nashville airport
February 2020: Severe Weather -Many South, East and Northeastern states
3 deaths
Total Estimated Costs: $1.3bn
More than 20 tornadoes clustered across central Mississippi into Tennessee. High wind damage reports from Florida to New Jersey, with the Carolinas and Florida receiving the most costly damage
January 2020: Tornadoes and flooding - many southeastern states
10 deaths
Total Estimated Costs: $1.1bn
More than 80 tornadoes caused significant damage in the southeast but northern states including Michigan, Wisconsin and New York were also slammed by severe storms. Significant damage occurred along Lake Michigan to roads, the foundation of homes and to Port Milwaukee. Powerful waves were generated by high winds and a lack of seasonal ice cover







