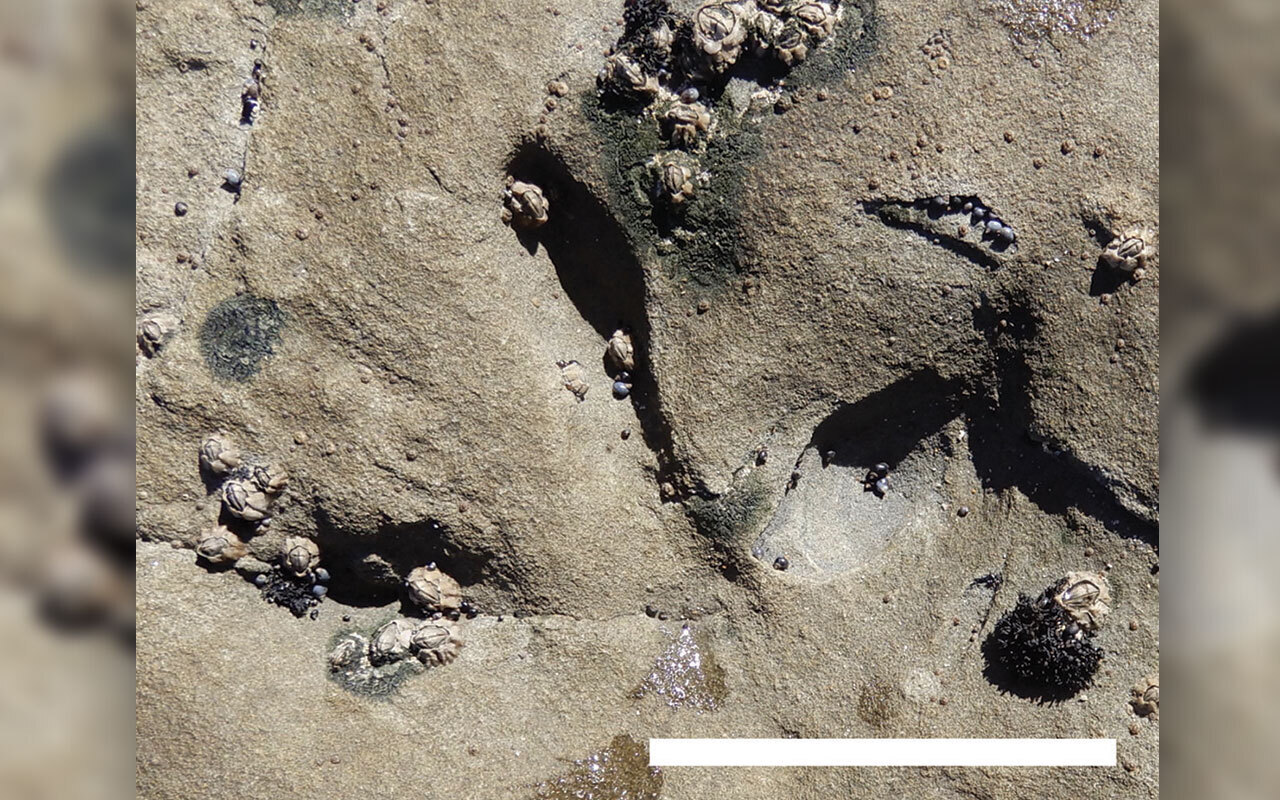
Researchers have discovered the earliest bird footprints ever found in Australia, showing that these early birds once lived in southern polar regions on the supercontinent Gondwana.
Palaeontologists unearthed the bird tracks in Wonthaggi Formation in Victoria, Australia, that date back to around 120 million years ago, during the Early Cretaceous (145 million to 100.5 million years ago).
Prior to these findings, there has been minimal evidence of Early Cretaceous birds in Australia — consisting of limited skeletal material, feathers and two tracks. At that time, what is now Australia was part of Gondwana and was further south, sitting near the South Pole.
"These bird tracks are scientifically important for several reasons. For one, they’re the oldest in Australia, telling us that birds have been living in Australia for at least 120 million years. But they’re also the oldest bird tracks in the Southern Hemisphere, which covers a lot more of the Cretaceous world," study co-author author Anthony Martin, a paleontologist at Emory University in Atlanta, Georgia, told Live Science.
"These tracks are from when this part of Australia was still connected to Antarctica and close to the South Pole then. So this makes them the oldest bird footprints from formerly polar environments."
Related: Extinct 'Lord of The Rings' eagles had a 10-foot wingspan and probably could have carried a hobbit
Researchers say the tracks give insight into how early birds dispersed across landmasses and biomes. Cretaceous bird fossils are extremely rare in southern regions — unlike in the northern continents, where a diverse range of early bird fossils have been found. The study, published Nov. 15 in the journal PLOS ONE, describes 27 bird footprints of varying sizes and shapes, which are evidence that several ancient bird species lived in the region, including some of the largest known birds from the Cretaceous.
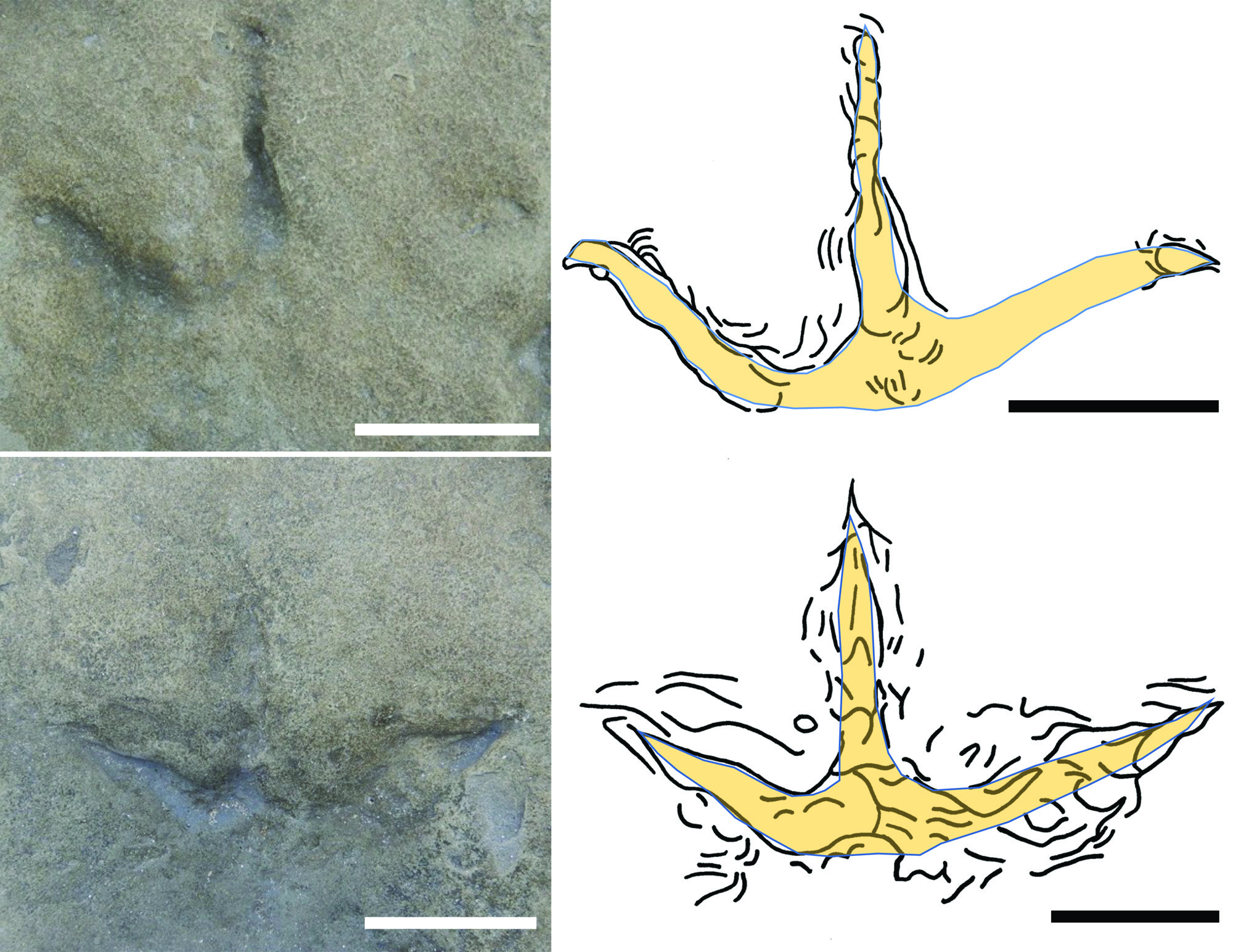
The researchers identified the tracks as belonging to avian animals because they were tridactyl (meaning they had three digits on a foot), with thin digits and sharp claws.
The bird tracks were discovered on marine outcrops that would once have been an ancient polar floodplain, suggesting that the area could have been part of a migratory route during polar summers, the researchers suggest in the study.
The authors suggest the fossilized tracks are evidence of seasonal behaviors, as the birds would have walked across the surface of the beds after the weather thawed in the spring season. It also suggests that Early Cretaceous birds might have flown to what is now Australia from northern regions of Gondwana during Southern Hemisphere springs.
"Because these bird tracks were made in polar environments at least 120 million years ago, and they were preserved on what were then river floodplains, we think this shows that birds were living in these places during the summers there, after spring thaws," Martin said. "That further implies that they probably aren't living there during cold, dark winters, so they may have migrated seasonally to and from other environments."
The researchers hope the new finds will inspire others to look for more evidence of Cretaceous birds in the Southern Hemisphere. "We can then better understand where birds dispersed early in their evolutionary history, and about when they started changing the world," Martin said.







