This article is being processed for speech. This might take a few seconds. You can listen to other articles in the mean time and comeback later if you don't want to wait.
Your current playlist has ended. Remember you can listen to any article on inkl. Why not listen to the morning edition if you have not already.
-
{{ item.publisher_name }}{{ item.title }}
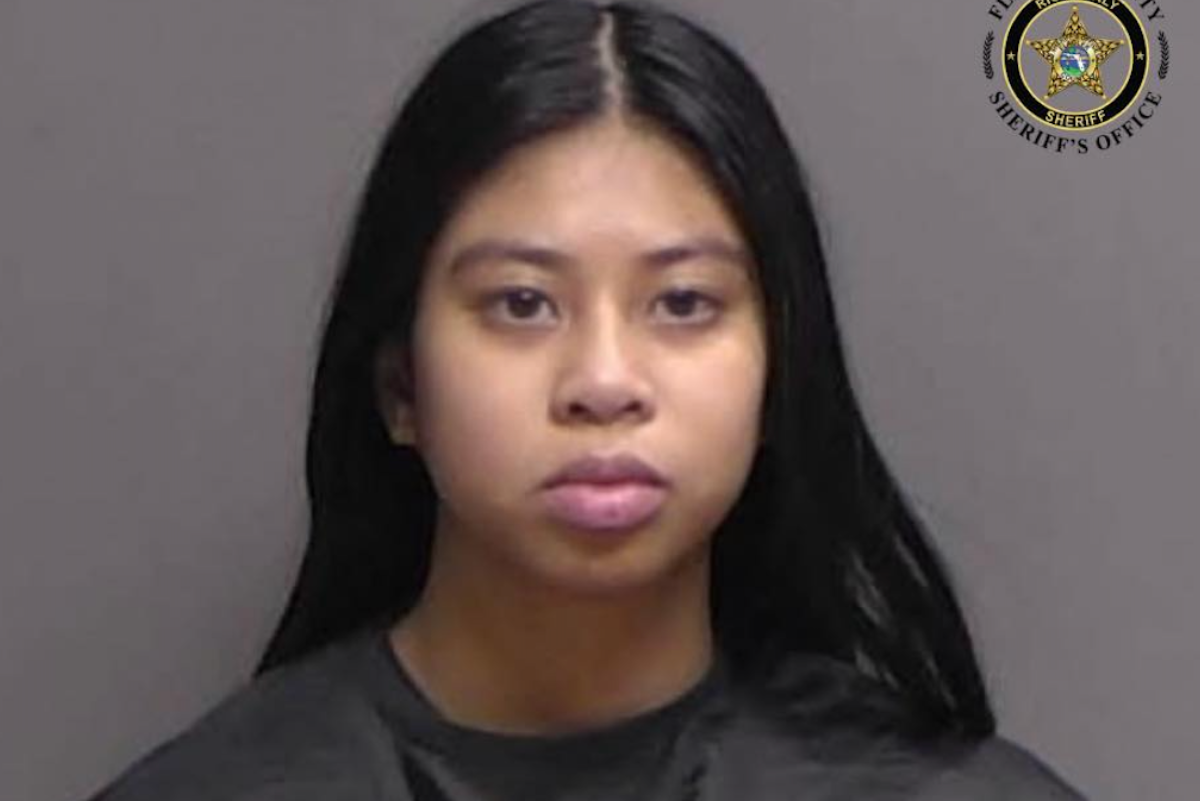
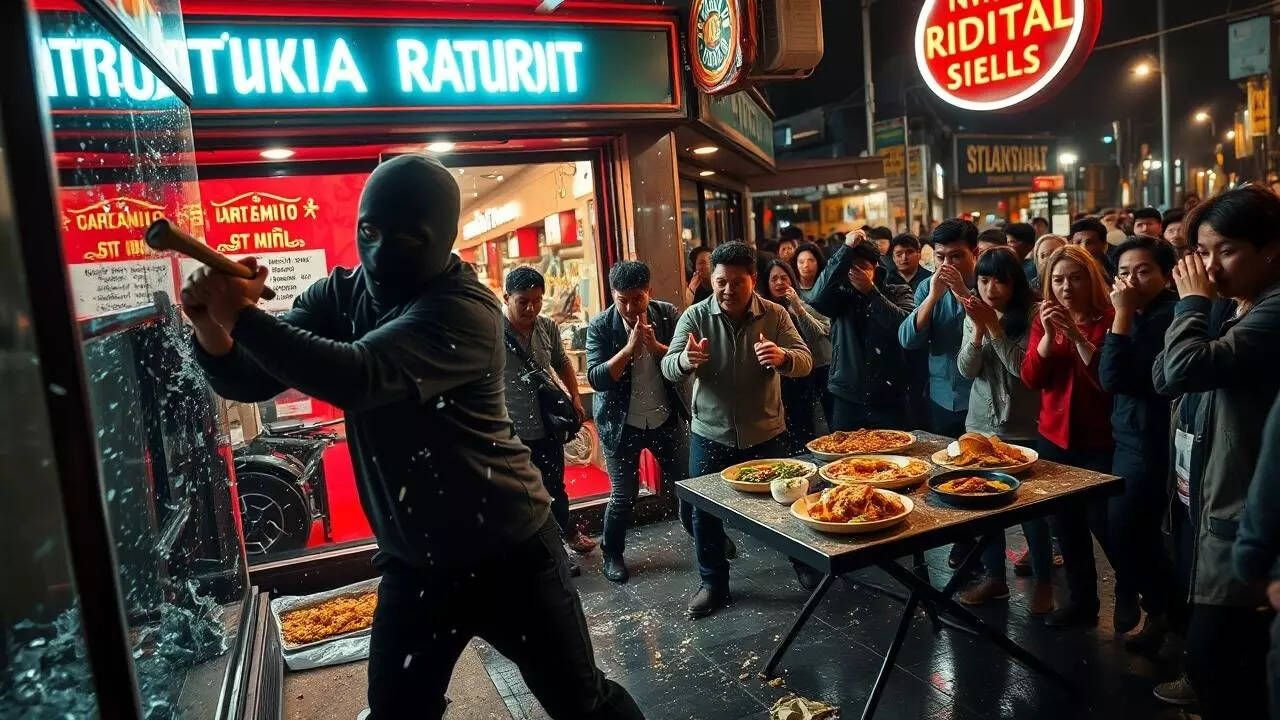
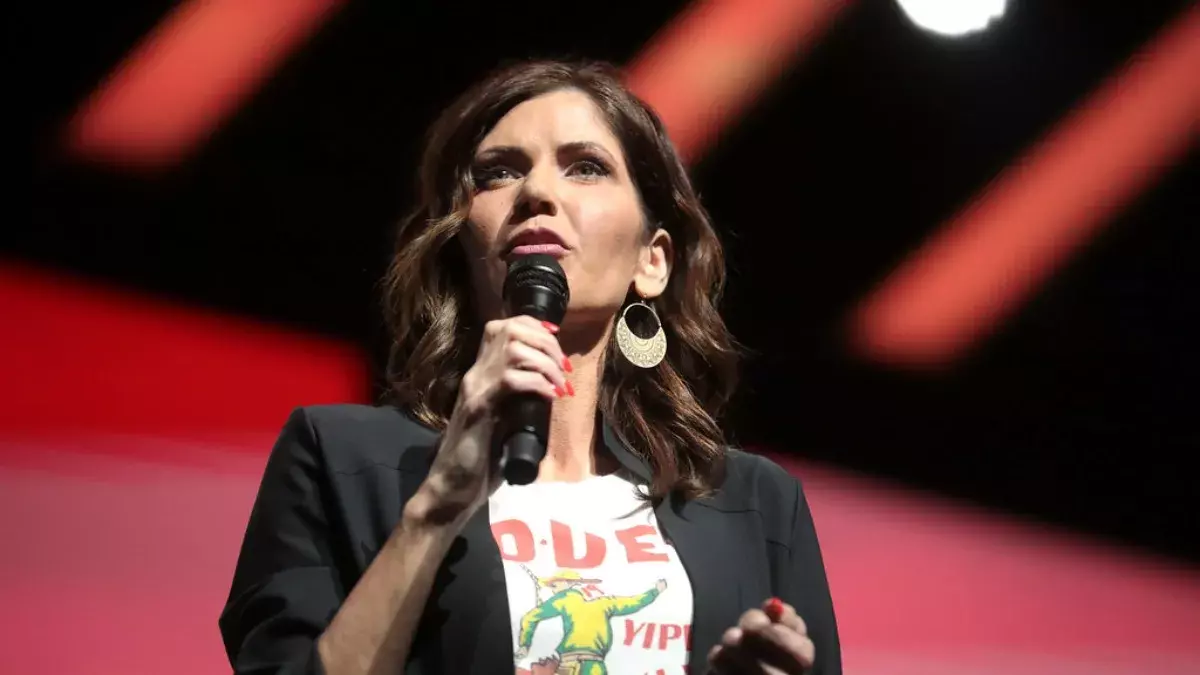
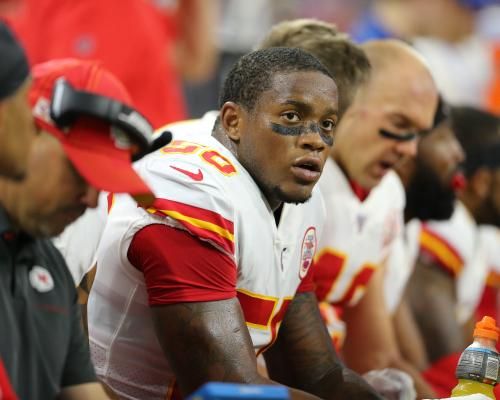

































.jpg)


.png)